- Marketing for Entrepreneurs: Book publication from the Directorate of CR&CS September 14, 2022
 Marketing a product or service is a challenging task in an ever-evolving marketplace. The latest book publication from the Directorate of Corporate Relations and Career Services portrays how marketing and entrepreneurship are not only creative but also cohesive and interesting. Mr Sourav Biswas, Regional Placement Manager of the Directorate of Corporate Relations and Career Services, has co-authored the book Marketing for Entrepreneurs with Dr Punit Kumar Dwivedi, Dr Biswarup Neogi, and Mr Saurabh Bharti. It offers entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs a rich fare of stimulating ideas, a new vision of challenging insight, and the proper marketing and entrepreneurial solutions. It was published by Scientific International Publishing House and launched in August. The book targets an audience with a plan to start innovative ventures in the future.
Marketing a product or service is a challenging task in an ever-evolving marketplace. The latest book publication from the Directorate of Corporate Relations and Career Services portrays how marketing and entrepreneurship are not only creative but also cohesive and interesting. Mr Sourav Biswas, Regional Placement Manager of the Directorate of Corporate Relations and Career Services, has co-authored the book Marketing for Entrepreneurs with Dr Punit Kumar Dwivedi, Dr Biswarup Neogi, and Mr Saurabh Bharti. It offers entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs a rich fare of stimulating ideas, a new vision of challenging insight, and the proper marketing and entrepreneurial solutions. It was published by Scientific International Publishing House and launched in August. The book targets an audience with a plan to start innovative ventures in the future.A brief about the book
Entrepreneurs face most difficulties in two significant areas: selling their products/offerings and finance. Initial stage cash flow is required to develop the product and sustain it. If companies don’t achieve sales, their failure is impending. To bring products or services to the market, entrepreneurs must communicate their offerings to the external environment.
Entrepreneurship and Marketing have traditionally been viewed as two different subjects of study. Increasing awareness of the significance of innovations and entrepreneurship in marketing and the importance of marketing for fruitful entrepreneurial ventures has led to an effort to combine entrepreneurship and marketing as the discipline of entrepreneurial marketing. In the area of entrepreneurial marketing (EM), there seems to be an agreement among researchers and entrepreneurs to undertake marketing in different ways that seem different from the established model of the market.
Mr Sourav Biswas was a member of the IIPC (Industry Institute Partnership Cell) cell as well as a convener of the Innovation council while he started working on the book. He came across many cases where students had started their innovative ideas, which the college funded. But in 90 percent of cases, companies can’t make a profit, or it has been closed within 2-3 years due to a lack of Marketing mix (product, place, price, and promotion). Based on this observation, the authors tried to find a way to help young entrepreneurs to succeed. They envisioned a future where many more entrepreneurs come forward with innovation and proper marketing strategies.
Continue reading → - Effective combinatorial drug therapy for prostate cancer September 13, 2022
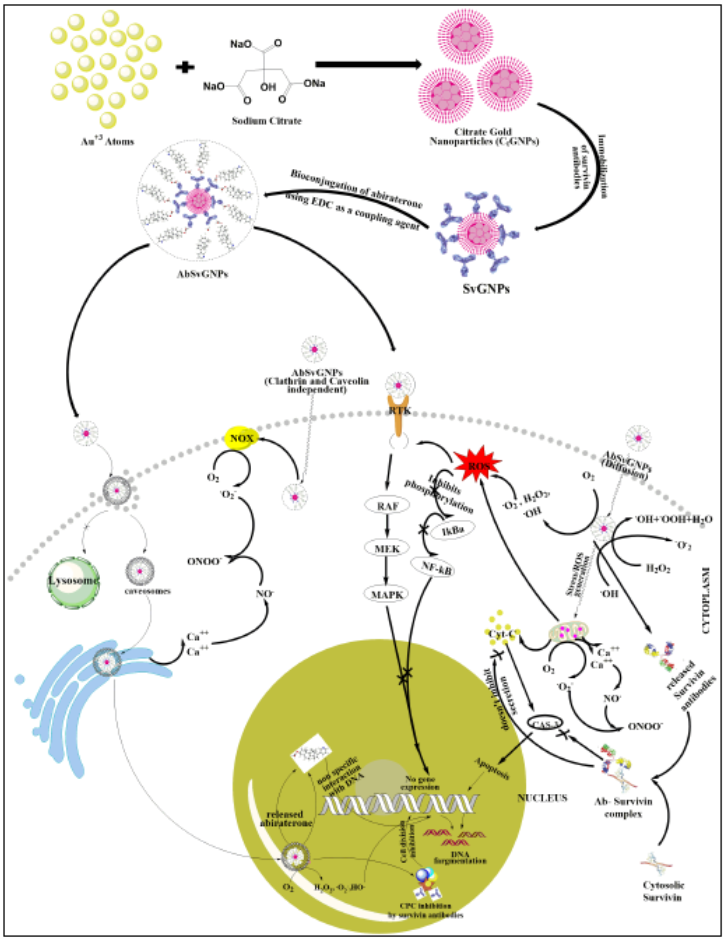
Prostate cancer is the second most frequent solid organ malignancy in males worldwide. The risk of causing prostate cancer is increased by age, race, and family history. The U.S. FDA has approved the six most successful drugs, viz., docetaxel, sipuleucel-T, abiraterone, enzalutamide, cabazitaxel, and radium-223. Despite these approved therapies, the disease state remains lethal. The recent publication of Dr Imran Uddin, Post Doctoral Fellow, Department of Physics, “Targeted non-AR mediated smart delivery of abiraterone to the prostate cancer” proposes a combinatorial system against prostate cancer using the FDA-approved drug abiraterone. The paper was published in the Q1journal PLoS ONE having an Impact Factor of 3.75. The research was done in collaboration with Dr Mohd Sajid Khan, Associate Professor, Aligarh Muslim University.
Although abiraterone is an excellent anticancer agent, it causes several side effects and becomes irresponsive after a few months of therapy. They developed a nanomedicine, along with two other components, that will deliver a substantially small dose of abiraterone for treating the same stage of cancer, and the drug will also not be resistant to the cancer cells. The delivery system delivered the drug at a specific site and modified its mode of action. The low dose of abiraterone will also not cause any substantial side effects. The combo was found to be highly biocompatible, nontoxic, and effective.
The proposed nanomedicine with established drug abiraterone, gold nanoparticles, and antibodies against cancer-promoting protein synergistically acted on prostate cancer cells. This synergism potentiated the effect of abiraterone at a very low concentration because other entities also acted via different routes and weakened the cancer cells. The low dose minimized the side effects and maintained patient compliance. This drug was delivered directly to the target, which enabled it to adopt different methods to act on cancer cells. Therefore, the results were promising but further needed to be validated in pre-clinical and clinical studies.
In future, Dr Uddin intends to focus on interdisciplinary sciences. His plans include studying the interface of biology with inorganic nanomaterials, understanding the underlying biological process, and developing new industrially relevant nanomaterials and biomedical aspects. It involves developing nano biosensors for biomolecule detection through the effective integration of the best approaches and expertise in sensor engineering with the vision to take a lead in shaping the future of biomedical monitoring systems. The timely integration of such interdisciplinary approaches will consolidate the application of Lab-on-a-Chip devices for automated biomolecular monitoring.
Abstract of the Research
Prostate cancer is the second-deadliest tumour in men all over the world. Different types of drugs with various delivery systems and pathways were developed, but no one showed prominent results against cancer. Meanwhile, nanotechnology has shown good results against cancer. Therefore, in the given study, citrate mediated synthesized gold nanoparticles (CtGNPs) with immobilized survivin antibodies (SvGNPs) were bioconjugated to the substantially potent drug abiraterone (AbSvGNPs) to develop as a combinatorial therapeutic against prostate cancer. The selected drug abiraterone possesses exceptionally good activity against prostate cancer, but cancer cells develop resistance against this drug and it also poses several severe side effects. Meanwhile, survivin antibodies were used to deliver AbSvGNPs specifically into cancer cells by considering survivin, an anti-apoptotic overexpressed protein in cancer cells, as a marker. The surviving antibodies have also been used to inhibit cancer cells as an immunotherapeutic agent. Similarly, CtGNPs were discovered to inhibit cancer cell proliferation via several transduction pathways. The given bioconjugated nanoparticles (AbSvGNPs) were found to be substantially effective against prostate cancer cells.
Continue reading → - Security concerns in digital image transmission over the internet September 13, 2022
 The research team from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering proposes a research scheme to address security concerns in the transmission of digital images of aerial Remote sensing images over the Internet. Assistant Professor Dr Priyanka, Assistant Professor Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, research scholar Ms K Jyothsna Devi, and BTech student Mr. M V Jayanth Krishna, published the paper A New Robust and Secure 3-Level Digital Image Watermarking Based on G-BAT Hybrid Optimization in the Mathematics Journal SCI, a Q1 Journal with an Impact Factor of 2.9. The research project combats various threats in the transmission of Remote sensing images, such as copyright protection, copy control, and unauthorized access.
The research team from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering proposes a research scheme to address security concerns in the transmission of digital images of aerial Remote sensing images over the Internet. Assistant Professor Dr Priyanka, Assistant Professor Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, research scholar Ms K Jyothsna Devi, and BTech student Mr. M V Jayanth Krishna, published the paper A New Robust and Secure 3-Level Digital Image Watermarking Based on G-BAT Hybrid Optimization in the Mathematics Journal SCI, a Q1 Journal with an Impact Factor of 2.9. The research project combats various threats in the transmission of Remote sensing images, such as copyright protection, copy control, and unauthorized access.Abstract
This contribution applies tools from the information theory and soft computing (SC) paradigms to the embedding and extraction of watermarks in aerial remote sensing (RS) images to protect copyright. By the time 5G came along, Internet usage had already grown exponentially. Regarding copyright protection, the most important responsibility of the digital image watermarking (DIW) approach is to provide authentication and security for digital content. The main goal of the paper is to provide authentication and security to aerial RS images transmitted over the Internet by the proposal of a hybrid approach using both the redundant discrete wavelet transform (RDWT) and the singular value decomposition (SVD) schemes for DIW. Specifically, SC is adopted in this work for the numerical optimisation of critical parameters. Moreover, 1-level RDWT and SVD are applied to digital cover images and singular matrices of LH and HL sub-bands are selected for watermark embedding. Further selected singular matrices S LH and S HL are split into 3 × 3 non-overlapping blocks, and diagonal positions are used for watermark embedding. Three-level symmetric encryption with a low computational cost is used to ensure higher watermark security. A hybrid grasshopper–BAT (G- BAT) SC-based optimization algorithm is also proposed to achieve high-quality DIW outcomes, and a broad comparison against other methods in the state-of-the-art is provided. The experimental results have demonstrated that the proposal provides high levels of imperceptibility, robustness, embedding capacity, and security when dealing with DIW of aerial RS images, even higher than the state-of-the-art methods.
The proposed scheme is easily dumped into the sender and receiver machines to work readily. MATLAB platform is the only requirement. Researchers aspire to design new image watermarking schemes using machine learning and deep learning techniques. For this project, they have collaborated with Professor José Santamaría from the Department of Computer Science, University of Jaén, and Professor Antonio Romero-Manchado from the Department of Cartographic Engineering, Geodesy, and Photogrammetry, University of Jaén.
Continue reading → - Dr Hema Kumar Yarnagula September 13, 2022
- An introduction to federated learning September 13, 2022
The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is hosting a seminar on September 16, 2022, at 4 pm as part of the Departmental Distinguished Lecture Series. Dr Anurag Singh, Dean of Research and Consultancy, NIT Delhi, will deliver a talk on the topic “Federated Learning”.
Abstract of the talk
The most crucial resource for any business, individual, or person in the world is data. Everyone, whether an individual or an institution, wants to prevent a data breach. High-quality data must be subjected to machine learning algorithms. The model is trained using traditional machine learning techniques, which save data to one server. There is a chance that this method will expose personal information. A machine learning technique called Federated Learning (FL) enables machine learning models to train on various datasets located on various sites without sharing data. Without putting training data in a centralised location, it enables the development of a common global model. Additionally, it permits personal information to stay in local places, lowering the risk.
A new area of machine learning called federated learning already offers greater advantages than conventional machine learning techniques.
Data Security: Training data is kept locally on the devices, negating the need for a data pool.
Data variety: Heterogeneous data since it incorporates information from various users.
Real-time continuous learning: Client data is used to enhance models continuously.
Federated Learning is applied in the field of IoT, Healthcare, smartphones, Advertising, Autonomous Vehicles etc.
Speaker’s Profile
Dr Anurag Singh is currently working as the Associate Professor and Dean of Research and Consultancy at NIT Delhi. He received his PhD from the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. His research areas are Network Theory, Dynamics on/of Networks, Opinion Dynamics, Epidemic Modeling, Intelligent transportation system etc. Dr Anurag Singh has teaching experience at both undergraduate and graduate levels. He has taught courses ranging from the introductory level to specialized courses in Computer Science and Engineering, and Mathematics. Currently, he is mentoring students at graduate and undergraduate levels at the National Institute of Technology Delhi, India. In addition, he has also been supervising PhD students. He has around 70 publications featured across various leading journals and three DST-funded projects to his credit.
Continue reading →