Recent News
- Research Paper on Efficient Resource Orchestration Algorithm April 30, 2025
 Dr Asif Thanedar, Assitant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering in research titled “An Efficient Resource Orchestration Algorithm for Enhancing Throughput in Fog Computing-enabled Vehicular Networks,” discusses issues faced by fog nodes (FNs) when serving connected vehicles during busy times. The research introduces an Efficient Resource Orchestration (ERO) algorithm designed to improve network performance by optimising resource use within the limits of FNs. The study aims to make a valuable contribution to the fields of vehicular fog computing and resource management.
Dr Asif Thanedar, Assitant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering in research titled “An Efficient Resource Orchestration Algorithm for Enhancing Throughput in Fog Computing-enabled Vehicular Networks,” discusses issues faced by fog nodes (FNs) when serving connected vehicles during busy times. The research introduces an Efficient Resource Orchestration (ERO) algorithm designed to improve network performance by optimising resource use within the limits of FNs. The study aims to make a valuable contribution to the fields of vehicular fog computing and resource management.Abstract :
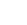
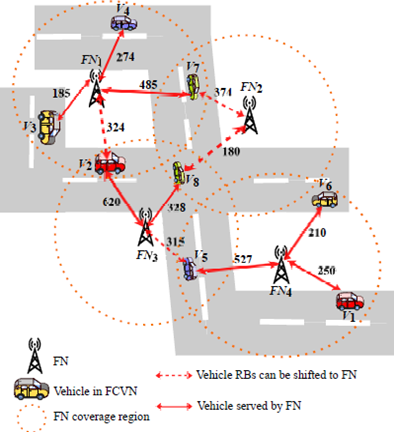
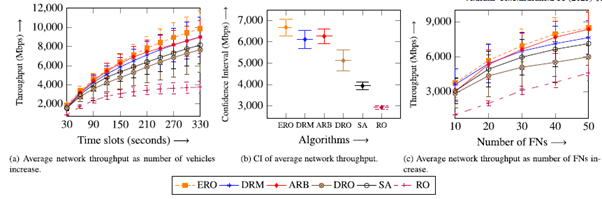
The intelligent vehicles are connected to the roadside infrastructure, such as high power nodes (HPNs) and roadside units (RSUs), also called fog nodes (FNs), for obtaining on-demand services. These FNs possess finite resources and can provide services to limited vehicles. However, when vehicles reach the network spike in demand, the FNs become impuissant in furnishing services in the existing solutions. As a result, there is a significant reduction in the network throughput. Therefore, we propose an efficient resource orchestration (ERO) algorithm to maximize the throughput by reducing the allocated resource blocks (RBs) of FNs.
Explanation in layperson’s terms:
The throughput is maximized by migrating allotted RBs of vehicles in non-restricted coverage regions such that the allotted RBs of these vehicles are minimized among pairs of FNs.
We formulated the RBs migration problem in FCVNs to an integer linear programming (ILP) by scrutinizing the variables influencing the network throughput and FNs resource constraints.
We propose an ERO algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm, which constructs the minimum priority queue for optimal RBs migration between pairs of FNs to augment the network’s throughput. The ERO algorithm synchronizes the RBs allocation for offloading upstream services such that throughput is maximized by partitioning the coverage of FNs into restricted and non-restricted coverage regions.Practical implementation:
For practical implementation we consider the FNs are equipped with large batteries and deployed across the highway segments of remote areas (i.e., forests or hill terrain) with no consistent power supply. In this context, we present an efficient resource orchestration (ERO) algorithm for harmonizing RB allocation and offloading upstream services among FNs to maximize the network throughput during battery depletion.
Collaborations:
Dr Sanjaya Kumar Panda, Assistant Professor, Dept. of CSE, National Institute of Technology Warangal.
Future Research Plans:
Resource Provisioning in Fog environment.
Energy Efficiency in vehicular fog computing (VFC).
Multi-objective optimization in fog computing.
Continue reading → - Dr Priyanka Singh and Students Collaborate on Innovative Approach of Image Retrieval April 30, 2025
 The patent titled “A System and Method for Image Retrieval Using Color Model and Histograms“, with application number 202241053488, presents a novel approach to image retrieval. Authored by Syed Yaser, Sai Aashrit Surapaneni, and B Venkatesh Reddy, with guidance from Dr Priyanka Singh, Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, this work explores the efficient and effective retrieval of images from large databases. The findings contribute significantly to advancements in various fields, including medical imaging and digital libraries.
The patent titled “A System and Method for Image Retrieval Using Color Model and Histograms“, with application number 202241053488, presents a novel approach to image retrieval. Authored by Syed Yaser, Sai Aashrit Surapaneni, and B Venkatesh Reddy, with guidance from Dr Priyanka Singh, Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, this work explores the efficient and effective retrieval of images from large databases. The findings contribute significantly to advancements in various fields, including medical imaging and digital libraries.Abstract:
Content Based Image Retrieval; a widely researched area in the past few decades when it comes to image retrieval and searching images in a large database. The proposed scheme is based on Hue, Saturation, Value (HSV) components of an image and compares images by calculating the distance between histograms is used to implement CBIR using global and local comparison. Histogram of hue and saturation is generated for global comparison. The image in the database which has the minimum distance to our query image is the most similar image of all images. Which means when the distance is 0 the query image is the same as the target image which concludes the image retrieval process. The above algorithm has been completely implemented using python. Python was chosen because of its inbuilt libraries like cv2 for image processing, numpy for mathematical calculations and matplotlib for visualisation
Practical Implementation:
The system can be applied in various fields like medical imaging, digital libraries, surveillance, and e-commerce platforms where quick and accurate image search is necessary. It can also enhance accessibility tools for the visually impaired by recognising images based on content.
Collaborations:
This project was done with the support and guidance of professors and fellow students from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at SRM University AP, Amaravati. The main team from SRM included:
Syed Yaser
Sai Aashrit Surapaneni
B Venkatesh Reddy
Dr Priyanka
Dr Naushad Varish from Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Guntur, also made significant contributions to the work.
Continue reading →