- Dr Ritika Verma March 24, 2025
- A Meta Analysis on the Mental Health of War Refugees March 21, 2025
 “I object to violence because when it appears to do good, the good is only temporary; the evil it does is permanent.”, this quote by Mahatma Gandhi serves as a stark reality that war leaves individuals grappling in severe trauma. Dr Aswathy Gopi, an Assistant Professor at the Department of Psychology, explores this impact in her research paper titled “Effectiveness of Psychological Interventions for Mental Health Problems Among War Refugees: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Her paper sheds light on the profound effects of war on the mental health of refugees, emphasising the need for tailored approaches to support their psychological well-being.
“I object to violence because when it appears to do good, the good is only temporary; the evil it does is permanent.”, this quote by Mahatma Gandhi serves as a stark reality that war leaves individuals grappling in severe trauma. Dr Aswathy Gopi, an Assistant Professor at the Department of Psychology, explores this impact in her research paper titled “Effectiveness of Psychological Interventions for Mental Health Problems Among War Refugees: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” Her paper sheds light on the profound effects of war on the mental health of refugees, emphasising the need for tailored approaches to support their psychological well-being.Abstract:
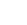
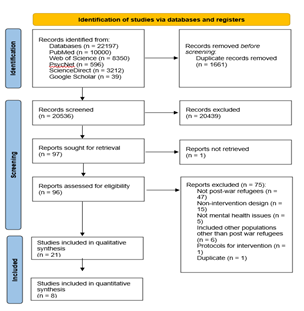
War and displacement have led to a global mental health crisis, with 117.3 million individuals displaced and one in five refugees experiencing psychological distress. Despite the availability of psychological interventions, their overall effectiveness remains unclear. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluate the impact of psychological interventions on war refugees’ mental health. A comprehensive search of PubMed, Web of Science, APA PsycNET, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar (July 2024) identified 21 studies for systematic review and eight randomized controlled trials for meta-analysis. The results indicate a significant medium effect size of psychological interventions (SMD = -0.69, 95% CI: -0.87, -0.51, p < .00001), with in-person interventions showing a large effect (SMD = -1.03) and telehealth interventions demonstrating a small effect (SMD = -0.44) in reducing the mental health issues among war refugees. Findings support the effectiveness of psychological interventions, emphasizing the need for further research on digital mental health solutions to enhance accessibility for war refugees.
Explanation in layperson’s terms
War forces millions of people to leave their homes, and many of them experience severe stress, anxiety, and depression. In fact, one in five refugees struggles with serious mental health problems. While various psychological therapies exist to support them, it is unclear how effective they truly are. The current review identified the available in-person as well as telehealth-based psychological interventions that help war refugees in addressing their mental health conditions using evidence from 21 studies. A statistical examination of eight high-quality trials found that psychological support significantly helps refugees in reducing mental health issues. Although face-to-face therapy was reported to be the most effective, online therapy also demonstrated positive results, with a smaller effect. Given the limited number of studies on digital interventions, further research is warranted due to factors like displacement and limited healthcare resources of war refugee.
Practical Implementation and Social Implications
Psychological interventions involving both in-person and telehealth showed effectiveness for mental health problems among war-refugees. Policy makers and intervention developers should provide keen attention while designing interventions for mental health issues of war refugees as their challenges are distinct from other refugees and the general population. Further, the government and healthcare authorities can aim for adopting hybrid models integrating both telehealth and in-person interventions for the effective management of mental health problems of war refugees.
Collaborations
This secondary analysis was conducted in collaboration with Indian Institute of Technology Bhilai, Chhattisgarh.
Future research plans
Dr Aswathy Gopi is currently working on positive organisational health, with several research works under review in reputed high-impact journals. The research primarily explores organisational effectiveness and mental health outcomes across various populations. She is also collaborating with IITs and central universities to conduct both primary and secondary research in this domain.
The link to the article
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2025.116432Continue reading → - Dr Rakesh Ganguly on SDG Implementation March 21, 2025
 The Office of the Quality Assurance and Rankings at SRM University-AP organised a one-day workshop on the implementation of Sustainable Development Goals on campus. The event witnessed Mr Rakesh Ganguly, Associate Director, Office of Accreditation and Regulatory Affairs, Shiv Nadar Institution of Eminence.
The Office of the Quality Assurance and Rankings at SRM University-AP organised a one-day workshop on the implementation of Sustainable Development Goals on campus. The event witnessed Mr Rakesh Ganguly, Associate Director, Office of Accreditation and Regulatory Affairs, Shiv Nadar Institution of Eminence.Mr Rakesh, a nodal officer of NIRF, IoE and QS, is also an alumnus of the UC Berkeley’s Executive Leadership. The one-day workshop aimed to provide a structured approach to SDG reporting and its role in institutional sustainability and global rankings. The session exerted emphasis to areas where institutions can
demonstrate their strengths and the importance of collaborations in enhancing sustainability efforts.Dr Ganguly examined the potential research and collaborative opportunities with industries in redressing the sustainability challenges. He also gave the participants an insight into showcasing sustainable initiatives through paperwork. Attendees got an opportunity to learn the significance of aligning sustainability development goals through research and community alignment.
The event saw the participation of faculty, PhD Scholars and Staff from various disciplines reflecting the growing interest in sustainability and SDG-driven initiatives. The workshop concluded with a valedictory session, where Dr Karthik Rajendran delivered the vote of thanks, acknowledging the contributions of the speaker, participants, and organising team.
Continue reading → - An Algorithm that Redefines Employee Attrition Prediction Technology March 21, 2025

Dr Vimal Babu, Associate Professor in the Department of Management along with his PhD scholar Ms Rukma R, have co-authored a research paper titled “Enhancement of New Random Forest Algorithm to Predict the Employee Attrition Rate.” Published in the International Journal of Enterprise Network Management (ABDC-B), the paper also includes contributions from Dr Vijaya Prabhagar M, Assistant Professor at IIM Jammu.
Their work focuses on improving machine learning techniques to better predict employee attrition, that is, the employees who are likely to leave the organisation. The study focuses on the impact of HR analytics adoption by applying algorithms to predict employee attrition. It uses the Random Forest algorithm to identify reasons for attrition. However, this algorithm can be slow due to the large number of decision trees it uses. To improve it, the study proposes a new method that selects the best decision trees using a technique called fractional factorial design, which outperforms all others in predicting employee attrition.
Abstract
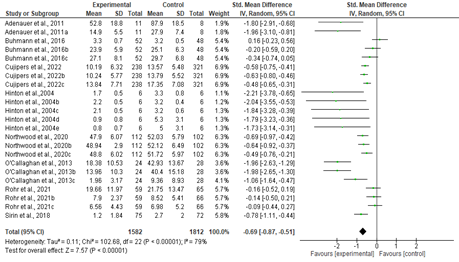
The problem of employee attrition in every organisation concerns the employee turnover ratio, thereby increasing the cost of investment in human resources. Various factors are reasonable for the rapid attritions at different phases. The purpose of the current study is to predict the employees who are likely to leave the organization. The factors that lead to attrition are identified using the Random Forest algorithm. The Random Forest algorithm is a widely used supervised machine-learning technique for classification and prediction. However, the random forest algorithm has certain issue like it is too slow and ineffective for real time predictions. i.e., the large number of trees can make the algorithm, which results in a slower model. Therefore, the study proposes, a new alternative for choosing the appropriate decision trees based on the concept of fractional factorial design of experiments. The different performance criteria were compared across the modified random forest algorithm, existing random forest algorithm, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), Navie Bayes (NB), K – Nearest Neighbour (K-NN), Decision Tree, XG Boost tree and Neural Network (NN). It was found that the modified random forest algorithm excelled in all criteria and performed better than the existing ones.
Practical Implementation/Social Implications of the Research
Practical implication: It emphasises the importance of focusing on factors like Business Travel, Job Role, Over Time, Department, Marital Status, and Education to reduce employee attrition. Organisations should design retention programs that support frequent travellers, manage overtime effectively, and address specific departmental needs. Tailoring job roles, promoting work-life balance through flexible hours, and providing educational opportunities are key strategies for enhancing employee satisfaction and retention.
Social Implication: The measures of this study can transform work culture into a more supportive and inclusive environment, promote gender equality by supporting employees with family responsibilities, and contribute to economic stability through reduced attrition. By investing in employee well-being, organizations can also strengthen their community engagement and corporate social responsibility initiatives for both employees and the broader society.
Future Research Plans
Future research could explore other factors influencing employee attrition, such as organizational culture, leadership style, and employee engagement. Longitudinal studies could track changes over time to understand the long-term effects on attrition rates. Additionally, investigating the interplay between identified factors, such as how Job Role and Over Time influence attrition, could provide deeper insights. Expanding the study across different industries and locations may reveal specific trends, allowing for tailored retention strategies. Lastly, incorporating qualitative methods like interviews and focus groups could offer a richer understanding of employees’ experiences and perceptions, complementing the quantitative findings.
Continue reading →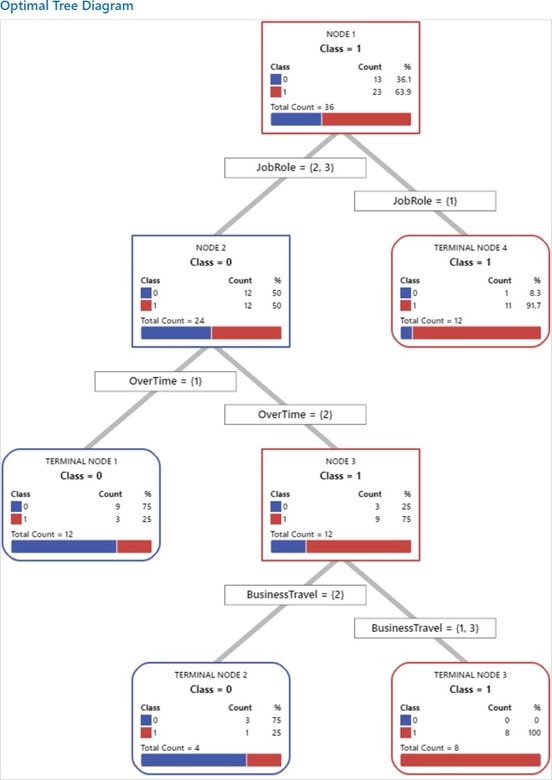
- Expert Talk by Prof. Meenakshi Munshi March 21, 2025
The Department of Biological Sciences at SRM University-AP organised an Expert Talk on “Various Funding Opportunities for Departments, Scholars, Postdocs, and Faculty of Life Sciences”. The event featured Prof. Meenakshi Munshi, Former Adviser/Scientist-G and Head of HRD & Societal Program Division at the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India.
The session had a turnout of participants and faculty members from various departments. The event, organised under the guidance of Dr Anil K Suresh, aimed to provide comprehensive information about the diverse funding landscape available to support research and academic initiatives in the life sciences domain.
During her presentation, Prof. Munshi offered a detailed overview of numerous funding sources accessible to researchers at different career stages. She expertly navigated through the complexities of eligibility criteria and application procedures, empowering attendees with practical knowledge and to identify and pursue appropriate funding opportunities. Prof. Munshi stressed on the importance of developing well-crafted research proposals and realistic budgets that align with the priorities of funding agencies, significantly increasing the chances of securing financial support.
One of the highlights of the session was Prof. Munshi’s emphasis on the value of collaborative research networks. She explained how strategic partnerships can strengthen funding applications and expand the scope and impact of research projects. This perspective encouraged participants to think beyond individual pursuits and consider the benefits of interdisciplinary collaboration, a principle that aligns perfectly with SRM University-AP’s research philosophy.
The event fostered intellectual discussions among participants, creating an environment conducive to knowledge sharing and networking. Students and faculty alike engaged with Prof. Munshi, seeking clarification on specific aspects of the funding process and sharing their experiences and challenges.
The talk built confidence in the participants’ ability to navigate the funding landscape. Armed with practical strategies for identifying suitable funding sources, understanding application requirements, crafting compelling proposals, and building collaborative networks, attendees are now better positioned to advance their research endeavours.
Continue reading →