- Rajiv Senapati February 22, 2020
- C Upendra Reddy February 22, 2020
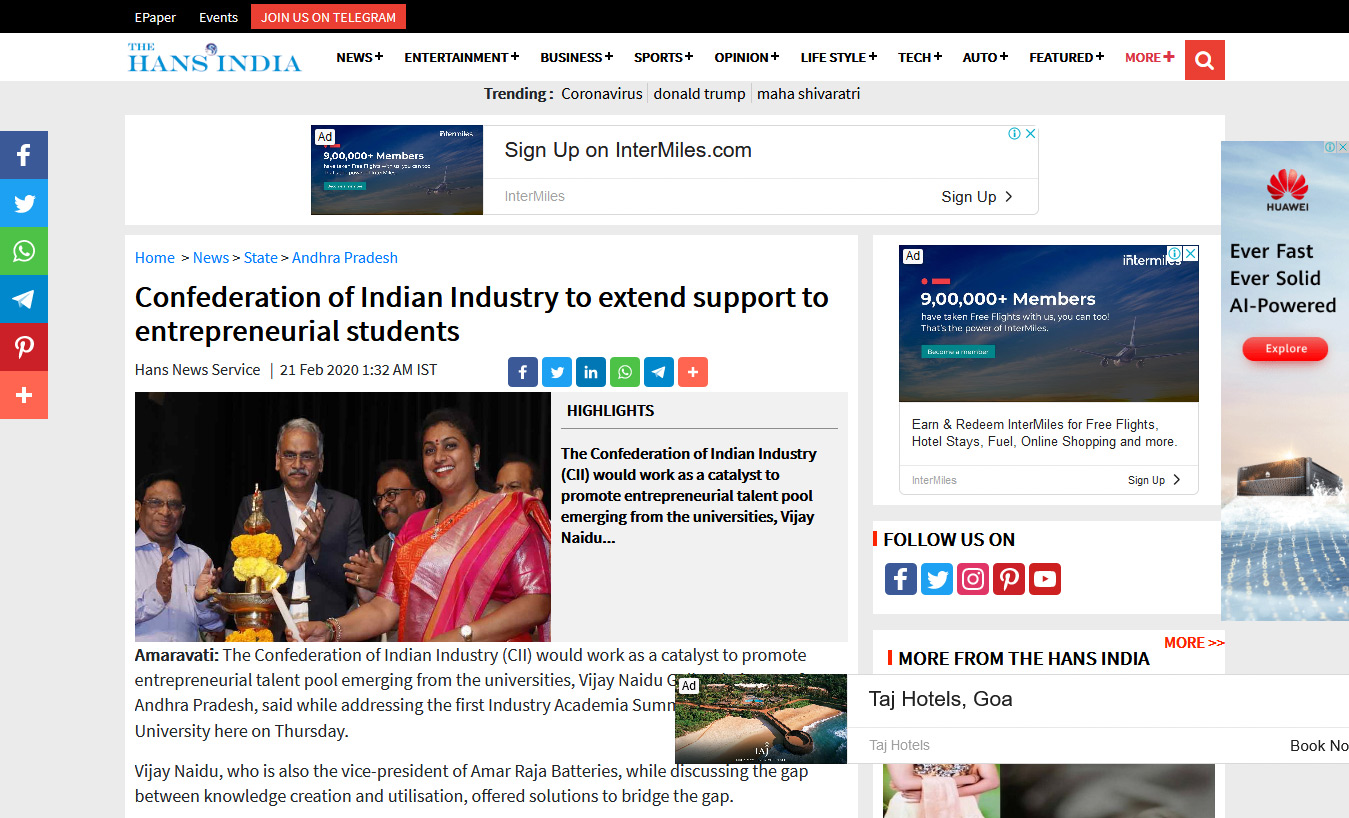
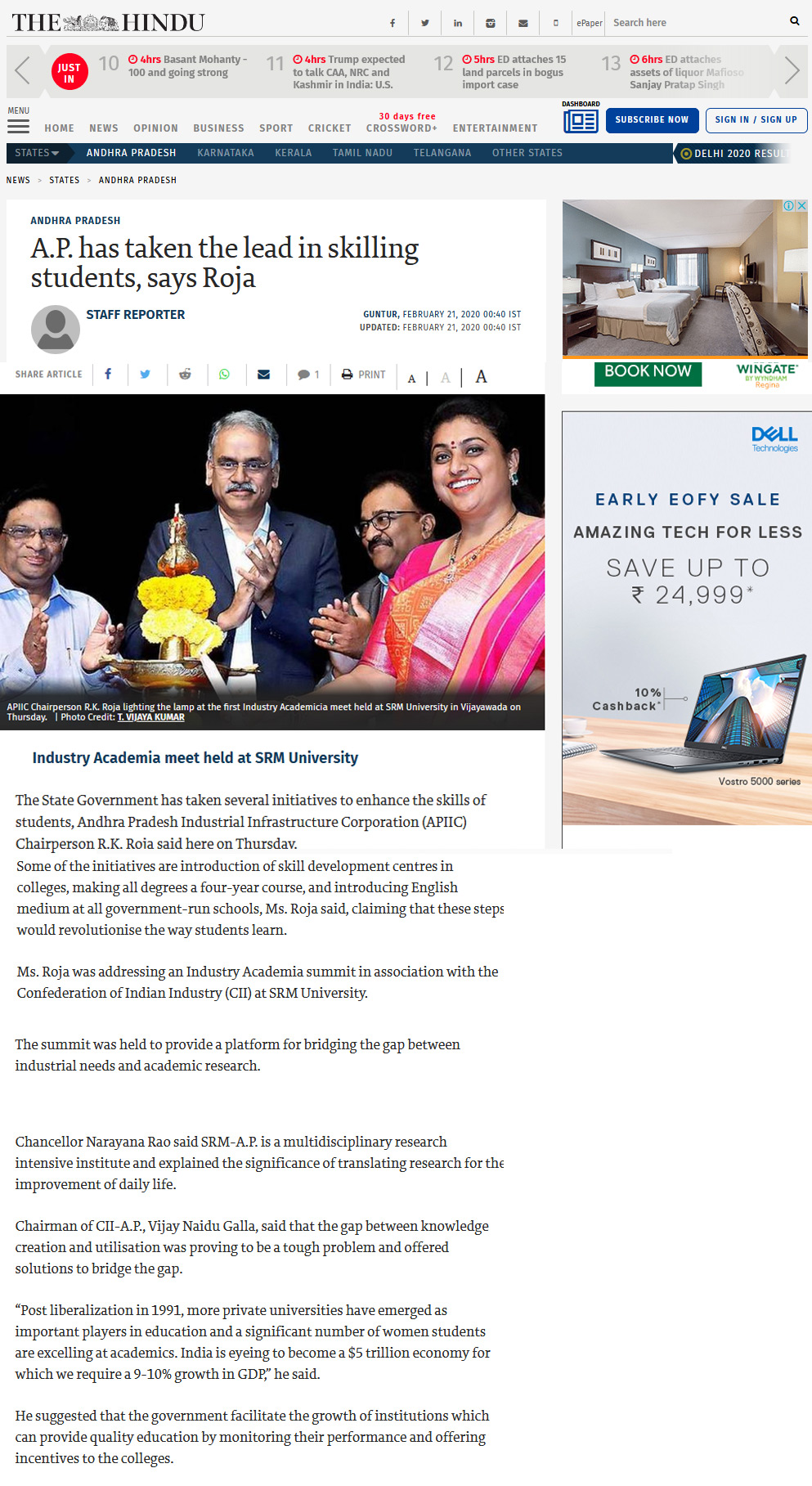
- Industry Academia Summit 2020 February 22, 2020
- What A Business Studies Courses Needs To Be Future Ready February 22, 2020
Learning business management is a complicated enough exercise with experts divided on whether management is science or art, or both. In the current era, the complications are compounded by the pace of change. Theories and frameworks are getting outdated rapidly, and textbooks can be obsolete by the time they reach the student’s desk from the printer. In this scenario, how does a student ensure that the business studies course is keeping him or her future-ready? The answer is not easy given the situation, but there are 5 universal aspects that few would dispute.
1. Practical experience
Many business studies courses are geared towards freshers with limited to no work experience. If the class itself offers no avenues for practical experience, then the student graduates with a skill handicap. Look for courses that provide hands-on business experience during studies. This can be in the form of industrial projects from real companies, internships, assistance on faculty research projects for companies, or even simple opportunities for interaction with the real business world. Being in actual situations, facing real problems of real people shapes your world view and the sooner you can gain this experience the better. For this, look for institutions that have tie-ups for such opportunities with their recruiters and other corporates.
2. Soft skills
Multiple surveys of companies show that one of the most significant handicaps campuses hire suffer from is poorly developed soft skills. This includes presentation skills, workplace etiquette, grooming, and general communication. All of these are essential requirements for workplace success and for moving into leadership roles. Some institutes have begun to focus on soft skills and developing the behavioural aspects of students. Conducting exercises and workshops on etiquette, grooming, communication, art, and team exercises are some of the means. Innovatively, some of this is being achieved through training in theatre or focus on the liberal arts.
3. People matter
In a networked and ever-changing business world, no one can function in a silo. Effective teamwork is essential in an era where multiple perspectives are needed to solve complex problems. And this means people need to be effective at working together. Empathy, accommodation, appreciating diversity, understanding and working with differences, and sensitivity are the critical skills that need to be developed for success and these are timeless. Institutes that build in teamwork and people dependencies into course work will help groom managers who can work effectively and efficiently with any group of co-workers. This is why many courses involve a large volume of team assignments, presentations, and projects.
4. Global perspective
Globalisation is a reality that no business, big or small, can ignore and this will only compound in the future as trade and people mobility go up in future. Even an entry-level business manager needs to be mindful, aware and prepared to work in a complex and interlinked world. How do you achieve this when many entry-level managers have not even stepped out of their city of birth? Developing the ability to work with different nationalities, being comfortable in foreign environments, and being able to blend into the unfamiliar is going to be must-have skills for the future and preparation needs to begin early. Courses that offer foreign language courses, cross-cultural collaboration opportunities, international exchange programs, diverse pool of international students, and opportunities to learn from visiting foreign faculty are one way to prepare for this business reality.
5. An entrepreneurial approach
Some theoretical concepts are timeless, while others whither away. However, new approaches to solving old problems and developing abilities to deal with new issues are always evolving. After all, many of the challenges and opportunities are seen today did not exist even 5 years ago. How would a graduate from then cope today and how will he/she deal tomorrow? The dynamism needed to face unique situations and problems come from developing an entrepreneurial mindset in students from an early stage. This mindset can be developed through a pedagogy that focuses on doing, experimenting, failing, learning, unlearning, and taking responsibility for one’s efforts. Courses that spoon-feed will soon disappear into the sands of time, as will the students who learned with such approaches.
Bear in mind that there is no course which will teach you all the skills you will need in the future. A course can provide you with timeless skills, some of which are listed above, and it can provide you with a mindset of flexibility, entrepreneurship, ownership, responsibility, and risk-taking. If you have these, then your skillset is indeed timeless.
At SRM University, AP the curriculum structure and pedagogy is designed to incorporate all of the above aspects. In addition to this, regular feedback from industry and recruiters is obtained to keep education relevant. Moreover, campus life, extracurricular activities, and the work involved in running the students clubs and societies provide students with exposure in all of these must-haves.
Continue reading → - Engineering Physics: Great Career Choices February 22, 2020
What is it?
Engineering Physics refers to the combined disciplines of physics, mathematics, and engineering. The field seeks ways to apply, design, and develop new solutions in engineering and holds promising career prospects for interested graduates of science or engineering.
Engineering Physics is unlike both traditional engineering or science disciplines – it does not restrict itself to one area. The focus is on applied physics covering highly specialised fields such as quantum physics, materials science, applied mechanics, electronics, nanotechnology, microfabrication, microelectronics, computing, photonics, nuclear engineering, biophysics, control theory, aerodynamics, energy, solid-state physics, and others.
The focus on coming up with integrated solutions sourced from multiple specialities ensures that the solutions are more optimal, effective, and efficient. The cross-functional focus also closes the gap between theoretical and practical sides of science and engineering.
Is it for me?
As stated, graduates of science or engineering can look to specialise in Engineering Physics. Scientists looking to move beyond theory, or engineers looking to create real solutions to tangible problems using theoretical rigour find this field exciting.
What kind of jobs can I get?
Qualified engineering physicists fit in into opportunities within high technology industries, some of which are in emergent domains. The roles span research and development, design, and analysis. The sector will depend on the engineering specialisation that is selected, i.e. mechanical, computer, nuclear, aerospace, etc.
Engineering Physics is well poised to grow as a segment specifically because of the many new sectors in which it has application as well as the technological progress in the last decade that has created entirely new industries. Some of the critical areas that will see job growth are discussed below.
Agro Physics
The pressures of a growing global population and the need for sustainable agriculture are going to [belatedly] lead to science and engineering, playing a more significant role in how we grow crops. Agro Physics is an evolving field, and it involves the study of materials and processes in the sowing, harvesting, and processing of agricultural produce.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence or AI refers to machines that mimic human cognitive functions such as learning and problem-solving. This exciting field is growing by leaps and bounds and holds great promise in the automation of many processes besides an exponential growth in processing capacities.
Biomechanics
Biomechanics involves the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of living systems. The field touches applications such as aerodynamics, orthopaedics, locomotion, pathology, oncology, among others.
Bionanotechnology
Bionanotechnology refers to the combination of nanotechnology and biology. Here, biosystems within nature are used as inspiration for creating new nanodevices or nanoparticles. Nanomedicine is the open field that is looking to benefit from the progress made in Bionanotechnology, while agriculture is another sector that will see the application of new solutions.
Composite materials
A composite material is made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties that, when combined, produce a material with characteristics different from the individual components. The objective could be to make the composite lighter, stronger, harder, softer, resistant, flexible, rigid, etc. While composite materials have existed since ages (concrete and steel are composite materials!), limits in the development of new materials are constantly being pushed through progress in Engineering Physics.
Machine learning (ML)
ML is a subset of AI and refers to algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to perform a task without any instructions input by human operators, relying on patterns and inference instead. ML is beginning to find application across many sectors including primarily Economics, Finance, Forensics, Medicine, Search Engines, etc.
Microfabrication
The miniaturisation of various devices (think about the first cell phones and compare them with devices today) has led to the need for Microfabrication, which is the process of fabricating miniature structures of micrometre scales and smaller. Progress in material science, nanotechnology, and other fields have led to growth in possibilities in this field.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale. Apart from medicine, Nanotechnology holds immense potential for multiple industrial sectors such as defence, textiles, food packaging, sports, construction, and energy. The fruits of the research conducted in this exciting field over the years are only just beginning to be realised.
Neural engineering
The human neural system is an extremely complex arrangement linking the brain with the rest of the body. Neuroscience is still making tentative progress in understanding how this system works and this pace has quickened lately, thanks to the improvement in imaging systems. Neural engineering is a discipline within bioengineering that uses engineering to understand, repair, replace, or enhance these complex neural systems. Aspects such as Neuroimaging, Neuromechanics, Neuromodulation, Neurorobotics, and Neuroregeneration hold great promise for patients who have been resigned to living with neurological disorders.
Robotics
Robotics is the right combination of Computer, Electronics and Mechanical Engineering with Physics. While Robots have existed since many decades now, the application across more sectors, the sophistication of the robotic systems, and their efficiency are being enhanced through the many technological developments. This will lead to productivity and efficiency gains across multiple sectors.
Continue reading →