- Saraswat inaugurates Centres of Excellence in SRM November 9, 2021

New Indian Express – Nov 09

The Hawk – Nov 09

Andhra Prabha – Nov 09

Eenadu – Nov 09

Praja Sakthi – Nov 09

Sakshi – Nov 09

Surya – Nov 09

Vaartha – Nov 09

Visalaandhra – Nov 09
Continue reading →

- STIP 2020: “Impartial inclusion will make India global scientific superpower” November 9, 2021
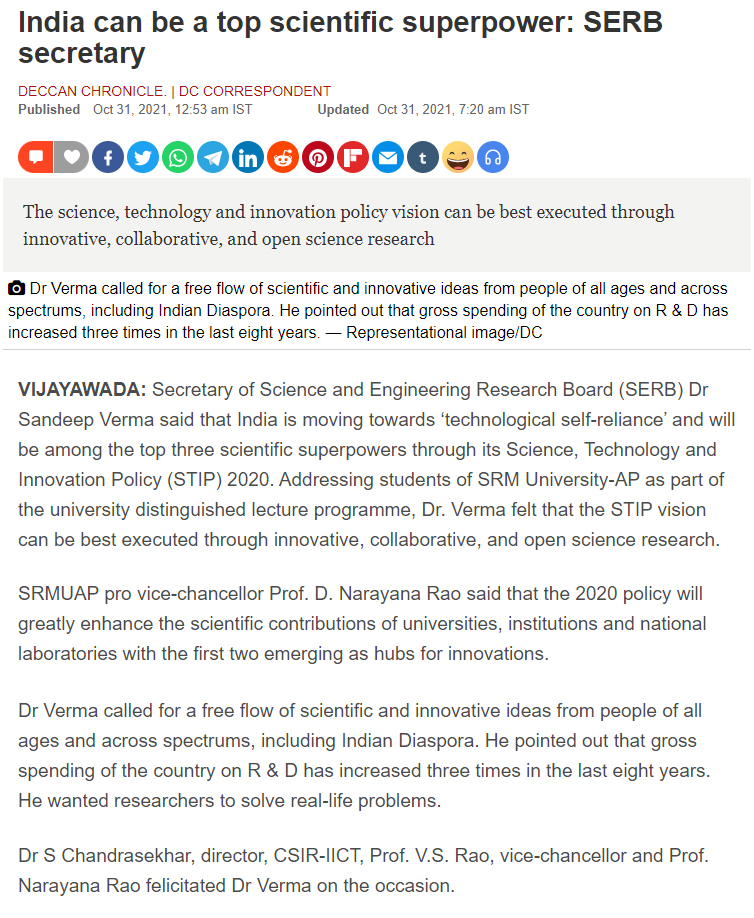
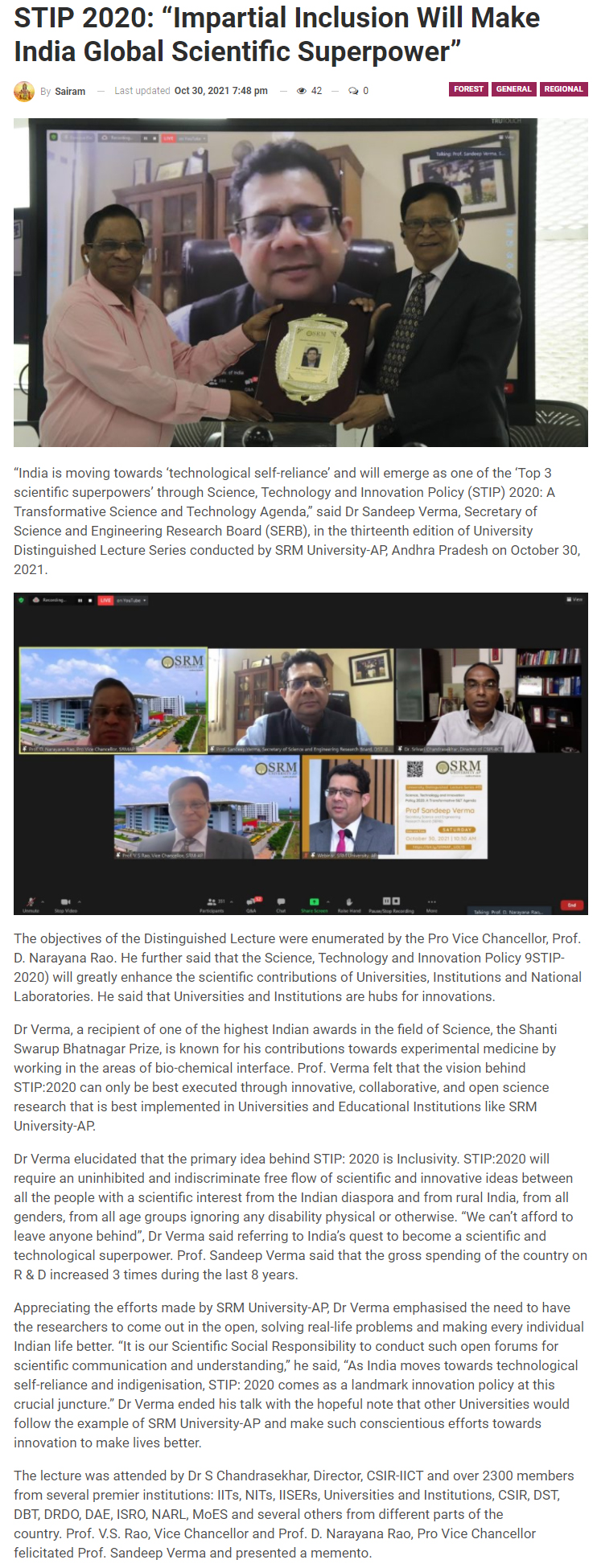
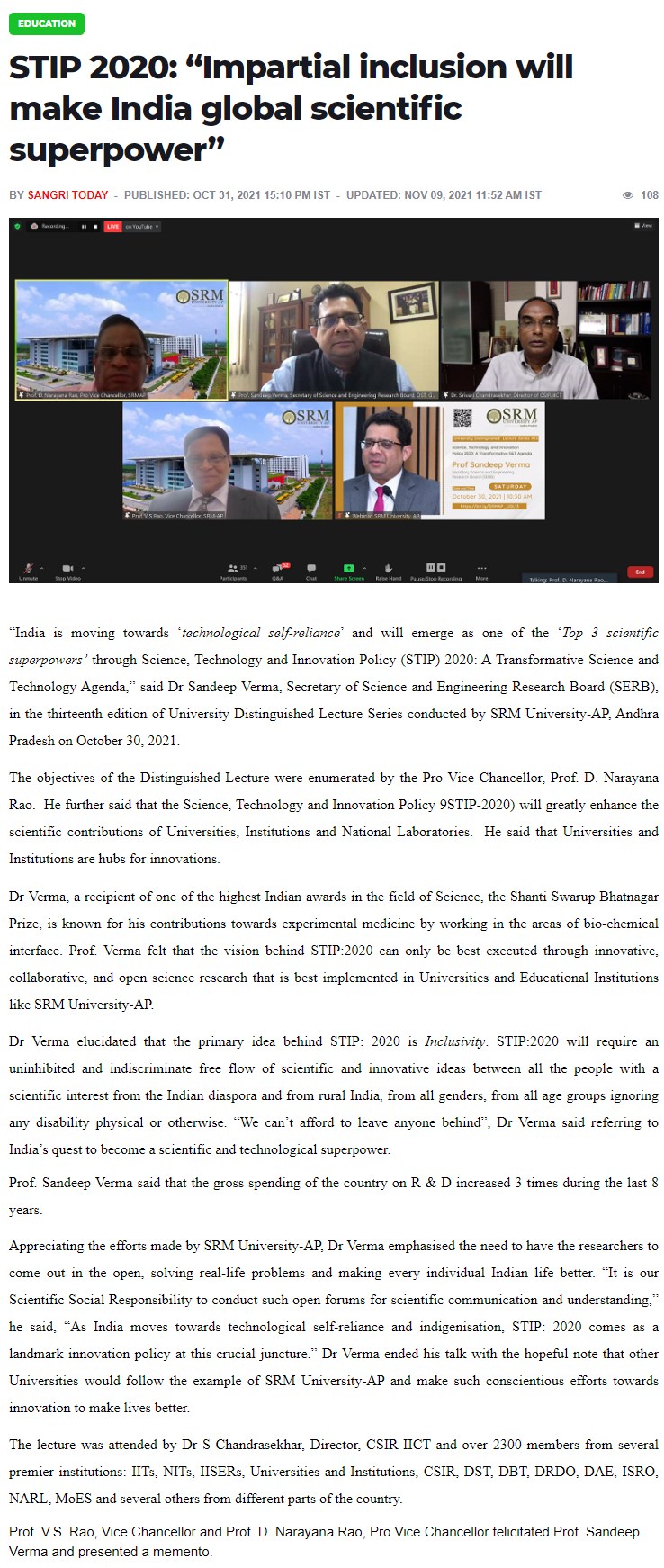
Deccan Chronicle – Oct 31
Daily Pioneer – Oct 31

The Hawk – Oct 31

Andhra Prabha – Oct 31

Eenadu – Oct 31

Praja Sakthi – Oct 31

Surya – Oct 31

Vartha – Oct 31

Vartha Prapancham – Oct 31
Continue reading →

- Why India needs innovation and leadership? November 9, 2021
 To nurture and cultivate innovation, there are no best-practice solutions. The structures and processes that many leaders employ instinctively to foster it are vital but insufficient. The Department of Entrepreneurship and Innovation at SRM University-AP is organising an influential session by Jyothsna Yerramsetti, CEO & Co-Founder- IUThink, on November 10, 2021, at 6.00 pm to promote and integrate innovative leadership among students. All participants will be given various gifts and certificates and participation.
To nurture and cultivate innovation, there are no best-practice solutions. The structures and processes that many leaders employ instinctively to foster it are vital but insufficient. The Department of Entrepreneurship and Innovation at SRM University-AP is organising an influential session by Jyothsna Yerramsetti, CEO & Co-Founder- IUThink, on November 10, 2021, at 6.00 pm to promote and integrate innovative leadership among students. All participants will be given various gifts and certificates and participation.IUThink is an organisation with a vision to provide a platform for grassroots, student and rural Innovators. It focuses on connecting students, innovators, startups and entrepreneurs to mentors, investors and creates opportunities to network with successful entrepreneurs. IUThink organises Startup/Innovation Summits where innovators and startups get a chance to exhibit their ideas and also provides entrepreneurial functionality support for college incubations. The main objective of IUThink is to create a proper Start-up Ecosystem to connect all the startups/entrepreneurs. In 2019-2021 it organised 3 innovation summits and connected 5000+ students/innovators/startups/ entrepreneurs and created a huge impact by organising awareness programmes.
About the Speaker:
Jyothsna Yerramsetti, CEO & Co-Founder- IUThink completed Graduation in Information Technology 2013. She worked as a software engineer for 5 years in one of the big MNCs at Hyderabad and established her startup company “IUThink” in 2018 August along with Cofounder Divya Kalikota. IUThink encourages startups, entrepreneurs and innovators. She is a recipient of the “Outstanding Educator” by South India Women Achievers Award (SIWAA) in Chennai and was recognised as “Young Leader” by Niti Manthan, New Delhi.
Unlock the innovator inside you with SRM E-Cell, grabbing gifts and certificates! Stay tuned to this inspiring session on November 10, 2021, at 6.00 pm.
Continue reading → - Navier stokes equations: A million dollar open problem November 8, 2021
 The second lecture in the Distinguished Lecture Series organised by the Department of Mathematics at SRM University-AP will be held on November 10, 2021, at 4.30 pm. Prof Amiya Kumar Pani from the Department of Mathematics, IIT Bombay, will elucidate the lecture on the topic “Navier Stokes Equations: A Million Dollar Open Problem”.
The second lecture in the Distinguished Lecture Series organised by the Department of Mathematics at SRM University-AP will be held on November 10, 2021, at 4.30 pm. Prof Amiya Kumar Pani from the Department of Mathematics, IIT Bombay, will elucidate the lecture on the topic “Navier Stokes Equations: A Million Dollar Open Problem”.On August 8, 1900, David Hilbert delivered his famous lecture about 23 open mathematical problems at the second International Congress of Mathematicians in Paris. This influenced the decision of a recently formed Clay Mathematical Institute (CMI) to announce the seven Millennium Prize Problems in the CMI Millennium Meeting held on May 24, 2000. One such problem is the theme of the present talk. Now it is widely accepted that the motion of an incompressible viscous fluid with moderate velocity is described by the Navier-Stokes Equations. Although these equations were written down in the 19th century, the existing mathematical results are not adequate to unfold the secrets hidden in the Navier-Stokes equations.
In this talk, Prof Amiya shall concentrate on a brief description of this problem, mathematical model, a quick look at history, what is known at this point, some important approaches and what is possibly needed. Finally, he will conclude the talk with a note on the present state of Indian applied mathematics and whether we are ready to contribute towards this millennium problem.
About the Speaker:
Prof Amiya K Pani is Professor at IIT, Bombay. He is well known for his research work in the area of numerical approximations of partial differential equations. His expertise includes construction, stability, and convergence analysis of finite element methods, finite difference schemes, orthogonal spline collocation methods for free boundary problems, partial integrodifferential equations, coupled equations in Oil Reservoir Studies, evolutionary variational inequalities, and scientific computations for industrial applications. Professor Pani is a fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences and National Academy of Sciences, India. He was awarded the Best Young Mathematician for his outstanding contributions to Numerical Analysis, Partial Differential Equations, and Industrial Mathematics by the Indian Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (ISIAM).
Tune in to this intriguing lecture on Navier stokes equations on November 10, 2021, at 4.30 pm.
Continue reading → - Fully automated quality control of rigid and affine registrations of T1w and T2w MRI in Big Data using Machine Learning November 6, 2021
 “Research is seeing what everybody else has seen and thinking what nobody else has thought.”
“Research is seeing what everybody else has seen and thinking what nobody else has thought.”
– Albert Szent-Györgyi“Fully Automated Quality Control of Rigid and Affine Registrations of T1w and T2w MRI in Big Data using Machine Learning” is the latest research paper published by Dr Sudhakar Tummala, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, SRM University-AP in ‘Computers in Biology and Medicine Journal’ having an Impact Factor of 4.6.
Abstract of the paper:
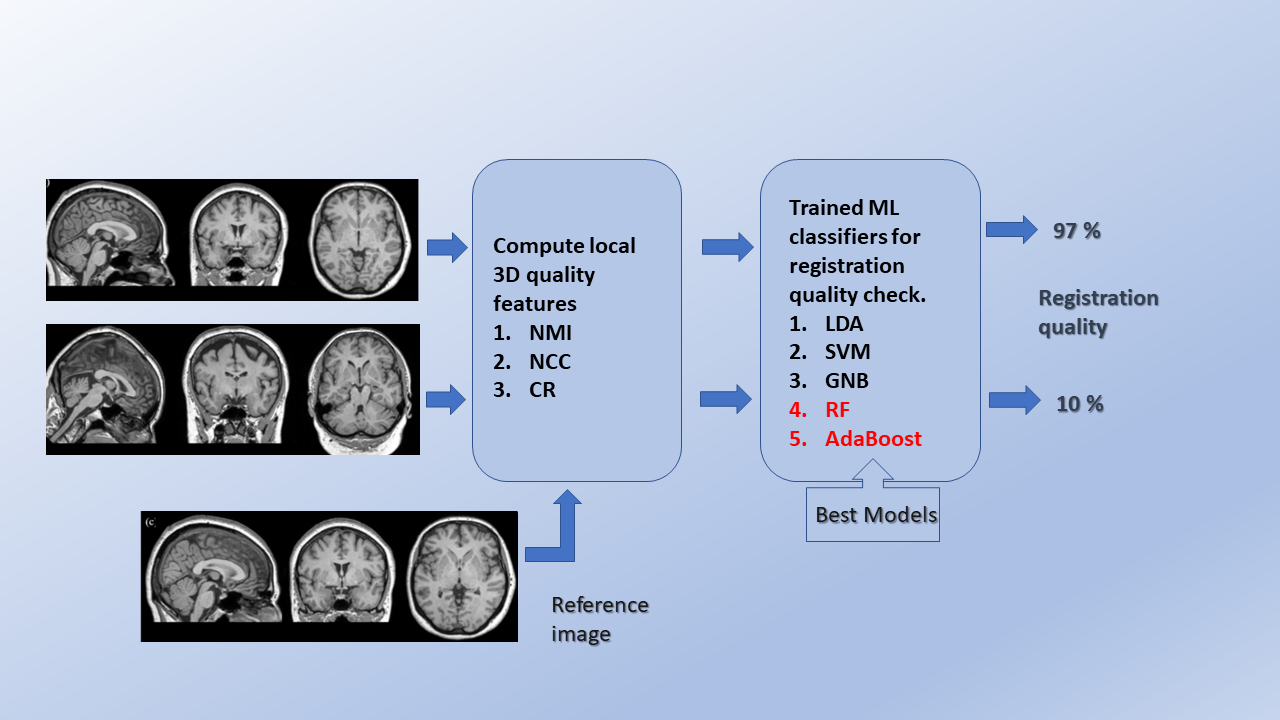
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based morphometry and relaxometry are proven methods for the structural assessment of the human brain in several neurological disorders. These procedures are generally based on T1-weighted (T1w) and/or T2-weighted (T2w) MRI scans, and rigid and affine registrations to a standard template(s) are essential steps in such studies. Therefore, a fully automatic quality control (QC) of these registrations is necessary for big data scenarios to ensure that they are suitable for subsequent processing.
Method: A supervised machine learning (ML) framework is proposed by computing similarity metrics such as normalized cross-correlation, normalized mutual information, and correlation ratio locally. We have used these as candidate features for cross-validation and testing of different ML classifiers. For 5-fold repeated stratified grid search cross-validation, 400 correctly aligned, 2000 randomly generated misaligned images were used from the human connectome project young adult (HCP-YA) dataset. To test the cross-validated models, the datasets from autism brain imaging data exchange (ABIDE I) and information eXtraction from images (IXI) were used.
Results: The ensemble classifiers, random forest, and AdaBoost yielded the best performance with F1 scores, balanced accuracies, and Matthews correlation coefficients in the range of 0.95-1.00 during cross-validation. The predictive accuracies reached 0.99 on Test set #1 (ABIDE I), 0.99 without and 0.96 with noise on Test set #2 (IXI, stratified w.r.t scanner vendor and field strength).
Conclusions: The cross-validated and tested ML models could be used for QC of both T1w and T2w rigid and affine registrations in large-scale MRI studies.Medical imaging is basically a method to see inside the body non-invasively. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the medical imaging modalities to see inside the body. MRI works on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance. T1-weighted (T1w) and T2-weighted (T2w) MRI can enable us to see the brain without opening the skull and to monitor brain structural changes that occur in several medical and neurological conditions. It is important to monitor these structural changes over time to understand the disease progression. For example, in Alzheimer’s disease, it is important to monitor the hippocampus (memory storage centre) Recently, due to the advances in computational power such as high-performance GPUs and the availability of publicly accessible big data MRI, scientists around the world now conducting big data research studies. In group-based big data studies, for fair comparison of the brain between healthy and diseased individuals, it is necessary that the brain MRI images are registered to a common coordinate system. Therefore, quality control (QC) of these registrations is necessary to ensure that they are suitable for further processing. Further, in big data studies that involve several thousands of images, manual QC is not feasible and hence there is a need for a fully automated QC mechanism at the pre-processing stage. Checking the quality of rigid and affine registrations is one such task.
The research group implemented a fully automated QC mechanism based on computing several quality metrics local to the image and trained several machine learning classifiers based on these locally computed quality measures. The trained classifiers include linear discriminant analysis, support vector machine, Gaussian naïve Bayes, random forest and adaptive boosting. The developed ML models generalize well to detect misaligned registrations across different MRI scanner vendors and field strengths and even under noisy image situations. Therefore, the classifiers could be employed in big data studies for fully automated QC of registrations, especially T1w and T2w MRI.
Big data MRI studies are generally conducted using a large number of subjects. The conclusions drawn based on big data analysis are more reliable and help to understand the disease mechanics better. The developed method can help to reduce the manual labour for various QC mechanisms required during the pre-processing stage.This work is done in collaboration with
a. Prof Erik B Dam, Machine Learning Group, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark.
b. Prof Niels K Focke, Clinic for neurology, University Medical Centre, Göttingen, Germany.In future, the idea is to implement the QC framework using sparse autoencoders in an unsupervised manner and also using Siamese neural networks via deep representation learning.
Continue reading →