- Dr Rajiv Lochan January 7, 2022
- Innovation for sustainable smart solutions January 6, 2022

Speakers from across the globe are invited for the International Lecture Series organised by the Office of International Relations and Higher Studies, SRM University-AP. The latest session of the series aims to provide insight into how new technological developments are changing the face of society. Mr Werner Fischer, Sustainable Development Consultant, will engage the participants on the topic “Innovation for Sustainable Smart Solutions” on January 10, 2022, at 11.30 am.
The lecture aims to provide a multidisciplinary approach to environmental studies, urban planning, and development. Focus on inventive technical developments is essential for the establishment of sustainable green societies. Such conversations with experts intend to challenge academic norms, examine established knowledge-power relationships, and shine a light on issues of equality, equity, diversity, and inclusion.
Speaker’s Profile:
Mr Werner Fischer, Sustainable Development Consultant
Co-Author of “How to Create Smart Villages” book
Advisor at Brightmind.io
Advisor at UC Berkeley-led private-public sector, Rebuilding India Initiative.
Worked as a Director of research for the Smart Village Movement in India
BSc in Business Studies and Economics from the University of Konstanz
MSc in Technology Management (M.Sc.) from the Braunschweig University of Technology, Germany
Business Studies at University of California, Berkeley, Haas School of BusinessAll are invited to join the session on January 10, 2022, at 11.30 am.
Continue reading → - Dr Subhankar Ghatak January 5, 2022
- Dr Lakhveer Singh published in Advanced Functional Materials for Engineered Nanoenzymes January 3, 2022
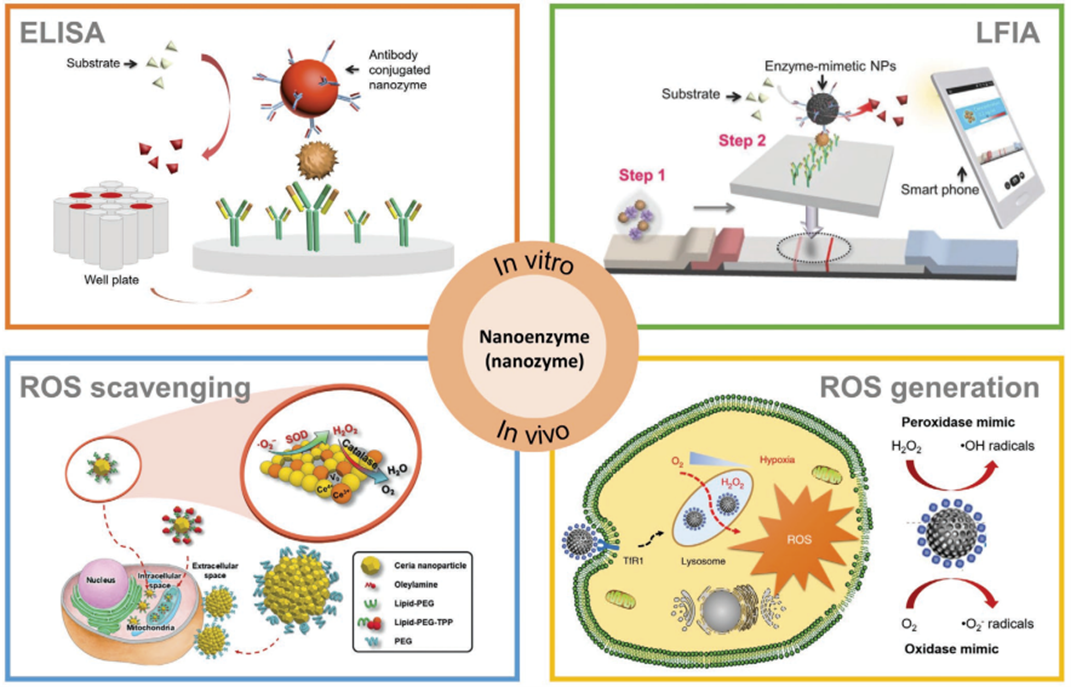 The Department of Environmental Science is proud to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Engineered Nanoenzymes with Multifunctional Properties for Next-Generation Biological and Environmental Applications” in Advanced Functional Materials with an impact factor of 18.50.
The Department of Environmental Science is proud to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Engineered Nanoenzymes with Multifunctional Properties for Next-Generation Biological and Environmental Applications” in Advanced Functional Materials with an impact factor of 18.50.About the Paper:
Enzyme mimicking studies took on a new aspect as it turns out that inorganic nanomaterials could have intrinsic enzyme-like activities. The word nanozyme (nanoenzyme) was first coined to describe the ribonuclease-like activity of ligand functionalised gold nanoparticles in 2004. Since then, various research has been continued on nanomaterials with enzyme-like activity. Thus, nanoenzyme has come to describe nanomaterials with enzyme-like activity.
Abstract:
As a powerful tool, nanoenzyme electrocatalyst broadens the ways to explore bioinspired solutions to the world’s energy and environmental concerns. Efforts to fashion novel nanoenzymes or engineering nanoenzymes for effective electrode functionalisation is generating innovative, viable catalysts with high catalytic activity, low cost, high stability and versatility, and ease of production. High chemo-selectivity and broad functional group tolerance of nanoenzyme with an intrinsic enzyme-like activity make them an excellent environmental tool. The catalytic activities and kinetics of nanoenzymes that benefit the development of nanoenzyme-based energy and environmental technologies by effectual electrode functionalisation are discussed in this article. Further, deep insight on recent developments in the state-of-art of nanoenzymes either in terms of electrocatalytic redox reactions (viz. oxygen evolution reaction, oxygen reduction reaction, nitrogen reduction reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction) or environmental remediation/treatment of wastewater/or monitoring of a variety of pollutants. The complex interdependence of the physicochemical properties and catalytic characteristics of nanoenzymes are discussed, along with the exciting opportunities presented by nanomaterial-based core structures adorned with nanoparticle active-sites shell for enhanced catalytic processes. Thus, such modular architecture with multi-enzymatic potential introduces an immense scope of making its economical scale-up for multielectron-fuel or product recovery and multi-pollutant or pesticide remediation as reality.
Collaboration:
The assignment on “Engineered Nanoenzyme” was completed with the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 291 Daehak-Ro, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon 34141, the Republic of Korea, along with other universities.
Social and Industrial Implications:
Trends of nanoenzyme are replacing conventional enzymes, particularly in a microbial bioelectrofuel biosystem, as cheap and efficient electrocatalysts. In this account, various strategies from altering scaffold to point alteration and iterative targeted tailoring have been applied to improve the enzyme-like activity and selectivity of the artificial enzymes.
Future Plans:
Strategies need to be devised to increase the mass loading of both homogenous and heterogeneous nanoenzyme for higher current density. Though, area of nanoenzyme is in its growing stage, engineering nanoenzyme with improved catalytic performance comparable to or even higher than that of the natural enzyme is one of the most concerning issues at this moment. Besides, the future breakthrough in nanoenzyme technology will lead to the development of novel catalysts with wider applications in multiple disciplines.
- National Indoor Archery Championship-2021 January 3, 2022
Global GreenNews – Dec 31

Andhra Prabha – Dec 31

Vartha – Dec 31

Prajasakthi – Dec 31

Surya – Dec 31

Sakshi – Dec 31

Visaalandhra – Dec 31
Continue reading →