- Neodymium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films for random access memory applications June 13, 2022
 A paper titled “Study on ferroelectric polarization induced resistive switching characteristics of neodymium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films for random access memory applications” has been published by Dr Pranab Mandal, Assistant Professor of Physics and his PhD student, Ms K N Malleswari in the journal ‘Current Applied Physics’ having an Impact Factor of 2.480.
A paper titled “Study on ferroelectric polarization induced resistive switching characteristics of neodymium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films for random access memory applications” has been published by Dr Pranab Mandal, Assistant Professor of Physics and his PhD student, Ms K N Malleswari in the journal ‘Current Applied Physics’ having an Impact Factor of 2.480.Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2022.04.013
Abstract
Resistive random-access memory (ReRAM) devices are based on the resistance switching (RS) effect. Such RS devices have recently attracted significant attention due to their potential application in realizing the next-generation non-volatile memory (NVM) devices. The present work reports on resistive switching (RS) characteristics of Neodymium (Nd)-doped bismuth ferrite (BFO) layers. The Nd (2–10 at%) doped BFO thin film layers were deposited using a spray pyrolysis method. The structural analysis reveals that a higher Nd doping concentration in BFO leads to significant distortion of the prepared Nd: BFO thin films from rhombohedral to tetragonal characteristics. The morphological analysis shows that all the deposited Nd: BFO thin films have regularly arranged grains. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis reveals that the prepared Nd: BFO thin films have a higher Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio and fewer oxygen vacancy (VO) defects which enrich the ferroelectric characteristics in Nd: BFO layers. The polarization-electric field (P-E) and RS characteristics of the fabricated Nd: BFO-based RS device were examined. It was observed that the Nd (7 at%) doped BFO RS device shows large remnant polarization (P r) of 0.21 μC/cm2 and stable RS characteristics.
Research in brief
Non-volatile resistive random access memory (RRAM) are future generation random access memory device with potential benefits such as high operational speed (nanoseconds read and write time), non-volatility, high endurance scalability and low power consumption [Namnoscale Research Lett., 15, 90, 2020]. Here in this work, we presented the resistive switching characteristics of a multiferroic material namely Nd-doped BiFeO3 material. The device shows stable resistive switching characteristics.
Practical implementation/social implications
Researchers in this field are focusing to overcome challenges of high operation current, lower resistance ratios, and reliability issues [Namnoscale Research Lett., 15, 90, 2020]. While several prototype RRAMs have been developed by other groups, future memory applications would require overcoming the challenges mentioned above.
Collaboration
The work has been conceptualized by Dr Amiruddin at Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai; and Dr Pranab Mandal and Ms Malleswari provided inputs on ferroelectric polarization – electric field (P – E) measurement and drafting.
Continue reading → - Interview mastery for global study opportunities June 13, 2022
 As you are aware, applying for international education can be daunting. Mastery of interview fundamentals is required to grab global study opportunities. Mr P Mahammad Farooq, Counselor- Student Services, Office of International Relations & Higher Studies, SRM University-AP, is conducting a session on the topic Interview Mastery For Global Study Opportunities on June 16, 2022, at 3.00 pm.
As you are aware, applying for international education can be daunting. Mastery of interview fundamentals is required to grab global study opportunities. Mr P Mahammad Farooq, Counselor- Student Services, Office of International Relations & Higher Studies, SRM University-AP, is conducting a session on the topic Interview Mastery For Global Study Opportunities on June 16, 2022, at 3.00 pm.The session aims to train students to respond to the interview questions, understand difficult interviewer personalities and showcase confidence that differentiates them from other candidates.
Avail this opportunity to sketch your study abroad pathway with the Office of International Relations and Higher Studies at SRM University-AP! Join the session on June 16, 2022, at 3.00 pm.
About the speaker
P.Md. Farooq is a well-known academician with more than five years of teaching, training research in the educational industry, and administrative experience. Before joining SRM University-AP, he was a freelance trainer for soft skills, career guidance coaching, advanced spoken English and employability skills. He expanded his academic boundaries by working at training institutions like the “Global talent track Pvt Ltd-Mumbai”, seventh sense solutions-Bangalore, Pygmalion Skills solutions Pvt Ltd-Bangalore, Rubicon Skill Development Pvt Ltd-Pune etc.
Continue reading → - Comparing organic food preferences of American and Indian consumers June 13, 2022

A paper titled “Organic food preferences: A comparison of American and Indian consumers” has been published by Prof Bharadhwaj Sivakumaran, Dean- SEAMS, SRM University-AP, Kirubaharan Boobalan (SSN College of Engineering), and Margaret Susairaj (Great Lakes Institute of Management, Chennai) in the journal Food Quality and Preference having an Impact Factor of 5.6.
This research tests a nomological model predicting organic food attitudes and purchase intentions in USA and India. Data were collected from India (n = 687) and the USA (n = 632) using Amazon M Turk and were analyzed using structural equation modelling and multi-group moderation technique. Results revealed that over and above attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioural control, response efficacy and self-expressive benefits significantly affect consumers’ attitudes and purchase intentions toward organic food among American and Indian consumers. Findings reveal that response efficacy and attitude matter more in the USA while subjective norms and self-expressive benefits exert a greater influence in India. Therefore, marketers may reinforce belief-related elements while selling organic food products in the USA and societal-related elements while selling in India. Theoretically, this work adds to the Theory of Planned Behavior by adding self-expressive benefits and develops a common model for organic food across samples in USA and India.
Continue reading → - Food safety applications of surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy June 10, 2022
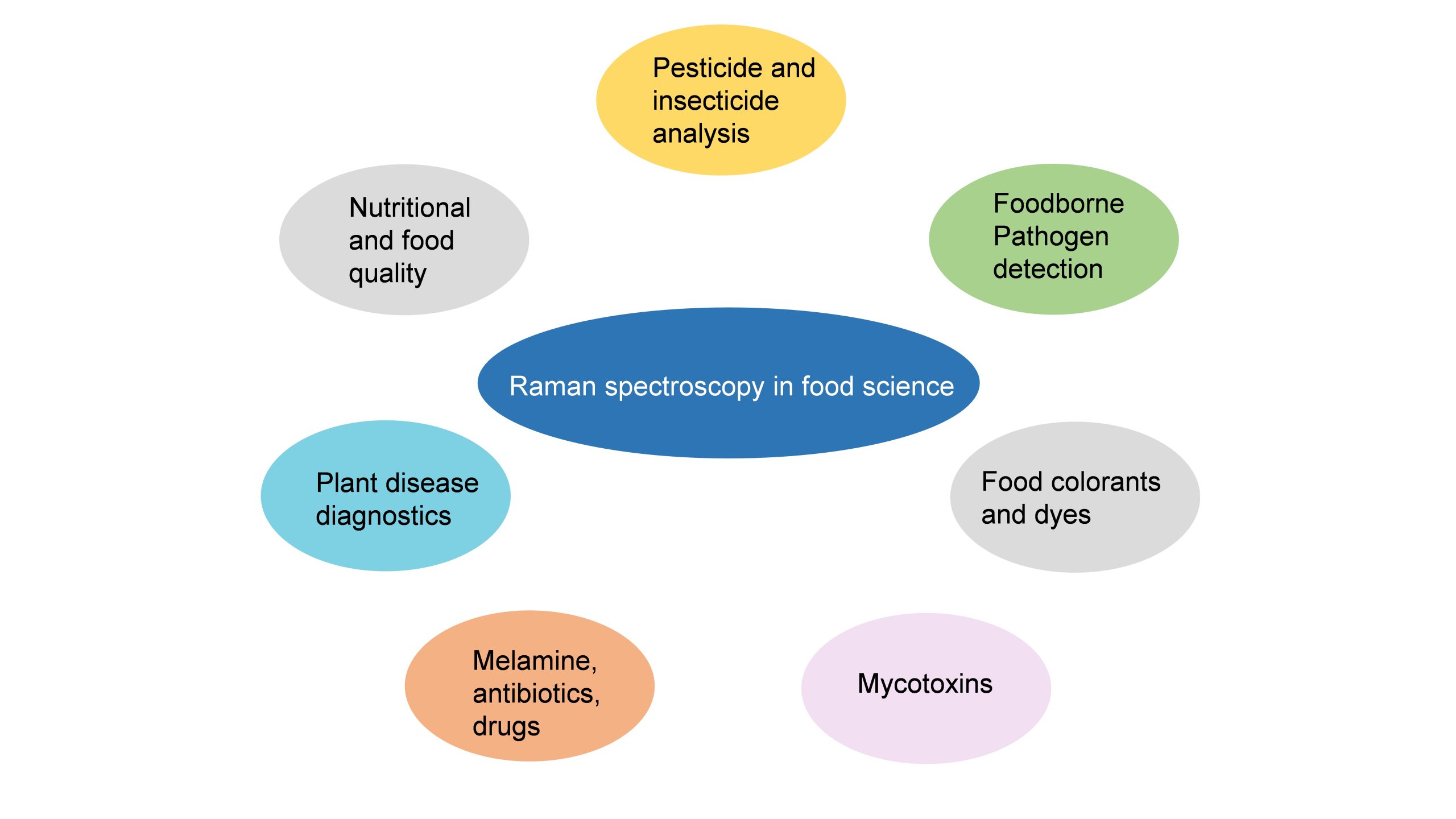
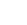
Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) is a nuanced chemical technique that amplifies the Raman scattering of molecules by utilising plasmonic nanostructured materials. SERS operates as a powerful detection tool that allows for the structural fingerprinting of a molecule. The ultra-high sensitivity and selectivity of the process offer it a vast array of applications in surface and interface chemistry, nanotechnology, biology, biomedicine, food science, environmental analysis and other areas.
Dr J P Raja Pandiyan and his PhD scholar, Ms Arunima Jinachandran from the Department of Chemistry have been keenly involved in exploring the possibilities of SERS technology in food science and other fields. The safety and quality concerns related to food were the primary reasons that impelled them to step into this domain. Their article “Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for food quality and safety monitoring” was published in the book Nanotechnology Applications for Food Safety and Quality Monitoring, published by Elsevier. The article was published in collaboration with Dr Selvaraju Kanagarajan from the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
Continue reading →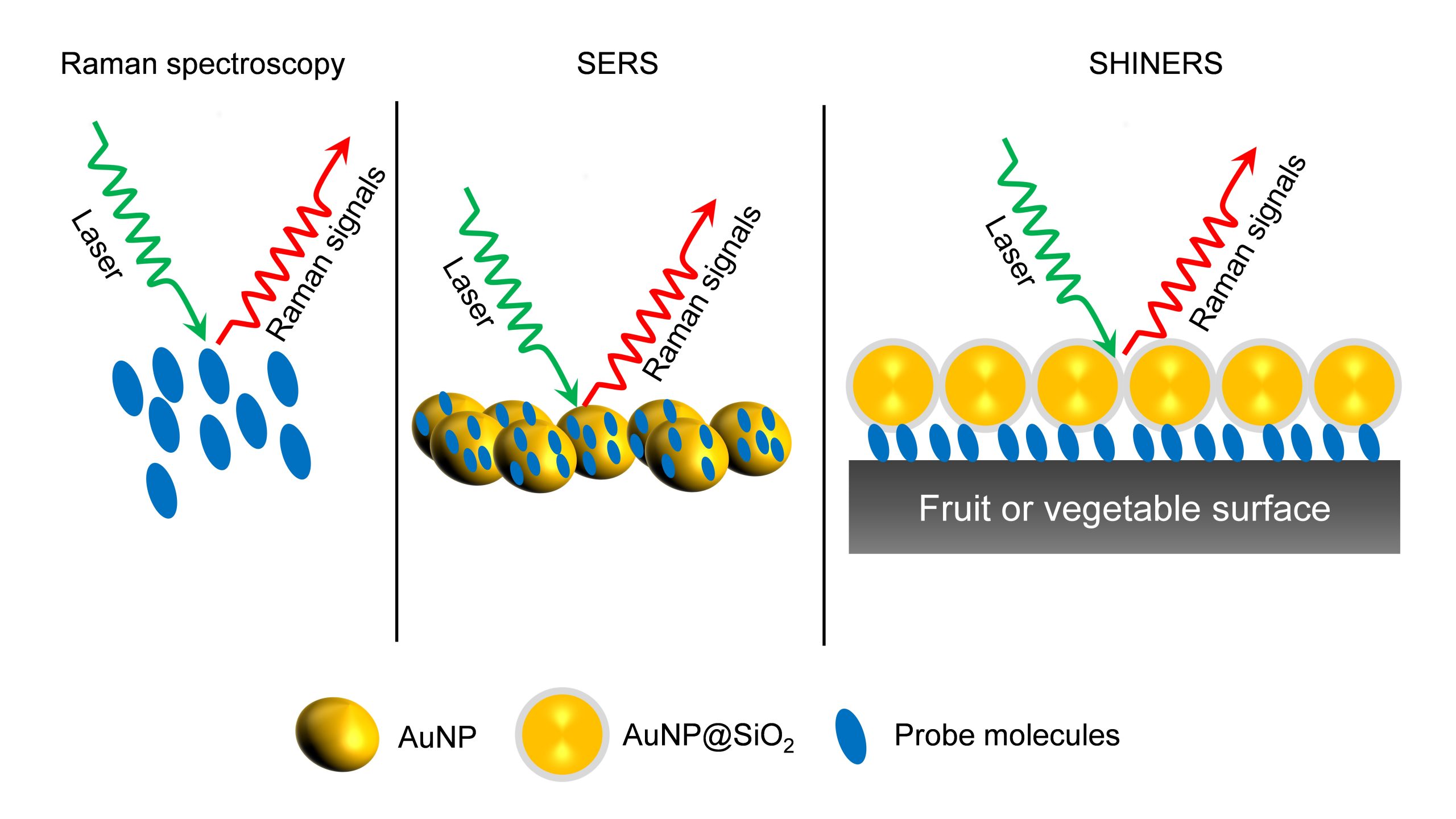 As an analytical technique, SERS possesses several advantages such as non-destructive, sensitive, and selective. In the chapter, the necessity, and applications of SERS in food science are elaborately discussed. They have also discussed all the possible food contaminants and how to identify them using SERS to ensure food quality. This book will serve as an enlightening read to research groups who are working on Raman, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and food quality analysis.
As an analytical technique, SERS possesses several advantages such as non-destructive, sensitive, and selective. In the chapter, the necessity, and applications of SERS in food science are elaborately discussed. They have also discussed all the possible food contaminants and how to identify them using SERS to ensure food quality. This book will serve as an enlightening read to research groups who are working on Raman, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and food quality analysis. - The pertinence of human activity recognition systems in the present era June 9, 2022
In recent years, human activity recognition has gained significant attention inside the scientific community. The enhanced spotlight is on the ground of its direct application in multiple domains. The latest research at the Department of Computer Science validates this assumption. Assistant Professor Dr V M Manikandan, and the 4th year B Tech Student Chaitanya Krishna Pasula have published a chapter titled An analysis of human activity recognition systems and their importance in the current era in the book Computational Intelligence Based Solutions for Vision Systems. The book is published by IOP Publishing Ltd.
Explanation of the chapter
 Human activity recognition is one of the most interesting and active research areas in computer vision. More research efforts are being put towards automatically identifying and analysing human activities due to their emerging importance in everyday applications. It serves applications in various areas like security video surveillance, smart homes, healthcare, human-computer interaction, virtual reality, robotics, and digital entertainment. Numerous papers have been published in the domain of human activity recognition. This book chapter discusses the various applications of human activity recognition, different methods available for automatic activity detection from videos, and the advantages of the human activity recognition system. It also describes the challenges in designing and implementing human activity detection schemes. Researchers further explain the publicly available datasets used for training and evaluating the systems for human activity recognition. The efficiency parameters used to evaluate the human activity recognition systems are also briefed in this chapter. The chapter is concluded by comparing the methodologies and speculating the possibilities of future research in this field.
Human activity recognition is one of the most interesting and active research areas in computer vision. More research efforts are being put towards automatically identifying and analysing human activities due to their emerging importance in everyday applications. It serves applications in various areas like security video surveillance, smart homes, healthcare, human-computer interaction, virtual reality, robotics, and digital entertainment. Numerous papers have been published in the domain of human activity recognition. This book chapter discusses the various applications of human activity recognition, different methods available for automatic activity detection from videos, and the advantages of the human activity recognition system. It also describes the challenges in designing and implementing human activity detection schemes. Researchers further explain the publicly available datasets used for training and evaluating the systems for human activity recognition. The efficiency parameters used to evaluate the human activity recognition systems are also briefed in this chapter. The chapter is concluded by comparing the methodologies and speculating the possibilities of future research in this field.In the future, the researchers are planning to design and implement an activity recognition system to identify abnormal activities in public places for safety purposes. This book chapter will be a helpful reference for UG/PG/Ph.D students who aspire to research in the domain of activity detection from video.
Continue reading →