Assessing the benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture
 Heat stress negatively affects crop yield and its impact has increased over time. Researchers in India study this situation with utmost priority. Consequently, Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Assistant Professor in the Department of Economics at SRM University-AP has co-authored a paper with Pratap S Birthal and et. al titled “Benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture: Evidence from wheat crop in India” in the journal Agricultural Water Management, Vol 255, having an Impact factor 4.02.
Heat stress negatively affects crop yield and its impact has increased over time. Researchers in India study this situation with utmost priority. Consequently, Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Assistant Professor in the Department of Economics at SRM University-AP has co-authored a paper with Pratap S Birthal and et. al titled “Benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture: Evidence from wheat crop in India” in the journal Agricultural Water Management, Vol 255, having an Impact factor 4.02.
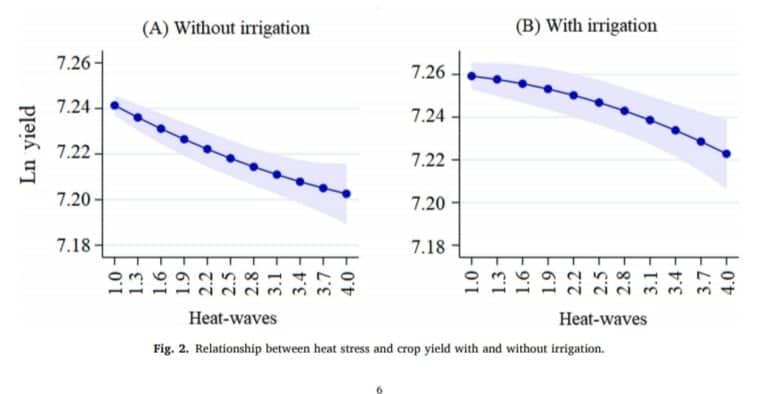
Applying the fixed effects regression technique to the highly spatially disaggregated district-level data from 1966–67 to 2011–12. This paper has assessed the impact of heat stress on wheat production in India and concurrently evaluated the role of irrigation in offsetting its harmful impact. The study has brought out three key highlights:
(i) Heat stress negatively impacts crop yield, and the impact has increased over time.
(ii) Irrigation, besides its contribution towards improving crop yield, also moderates the harmful impact of heat stress, but over time its effectiveness has declined.
(iii) The measure of heat stress built on multiple aspects of excess temperature (i.e., intensity, persistence, and frequency) explains variation in crop yield better than working on a single aspect of it.
Given the increasing scarcity of irrigation water and rising temperature, these findings suggest the need for exploring technological and policy options for improving irrigation water use, efficiency, and breeding of crops for heat tolerance and low water footprints.
This research paper is written in collaboration with ICAR-National Institute of Agricultural Economics and Policy Research, PUSA, New Delhi. Dr Ghanshyam’s future projects are focused on climate change and agriculture, and the effect of climate change on the livestock sector in India.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106950
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News, Research News
Dr Nimai Mishra’s research group studies new surface capping ligands
 Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group pursuing PhD under him-Ms V.G.Vasavi Dutt and Mr Syed Akhil- have published a research article titled “Enhancement of Photoluminescence and Stability of CsPbX3 (X= Cl, Br, and I) Perovskite Nanocrystals with Phthalimide Passivation” in the Journal “Nanoscale” (The Royal Society of Chemistry, Impact Factor-7.8).
Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group pursuing PhD under him-Ms V.G.Vasavi Dutt and Mr Syed Akhil- have published a research article titled “Enhancement of Photoluminescence and Stability of CsPbX3 (X= Cl, Br, and I) Perovskite Nanocrystals with Phthalimide Passivation” in the Journal “Nanoscale” (The Royal Society of Chemistry, Impact Factor-7.8).
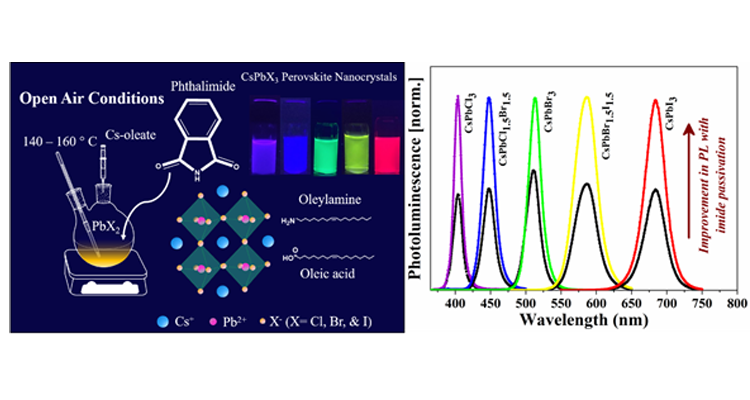
Caesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbX3 NCs) have been the flourishing area of research in the field of photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications because of their excellent optical and electronic properties. However, they suffer from low stability and deterioration of photoluminescence (PL) properties post-synthesis. One of the ways to minimize the surface defects in the surface treatment with suitable ligands is to achieve the NCs with superior PL properties for light-emitting applications.
In this article, Dr Mishra’s research group demonstrates that incorporating an additional ligand can further enhance the optical properties and stability of NCs. Here, we introduced phthalimide as a new surface passivation ligand into the oleic acid/oleylamine system in situ to get near-unity photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of CsPbBr3 and CsPbI3 perovskite NCs. We observed, phthalimide passivation dramatically improves the stability of CsPbCl3, CsPbBr3, and CsPbI3 NCs under ambient light and UV light. The PL intensity is recorded for one year which showed a dramatic improvement for CsPbBr3 NCs. Nearly 11% of PL can be retained even after one year for phthalimide passivated samples, on the other hand, the PL of as-synthesized NCs completely diminishes in four months. CsPbCl3 NCs exhibit 3 times higher PL with phthalimide and retain 12% PL intensity even after two months while PL of as-synthesized NCs completely diminishes by then. Under continuous UV light illumination, the PL intensity of phthalimide passivated NCs is well preserved while the as-synthesized NCs exhibit negligible PL emission in 2 days. About 40% and 25% of initial PL is preserved for CsPbBr3 and CsPbCl3 NCs in the presence of phthalimide. CsPbI3 NCs with phthalimide exhibit PL even after 2 days while the PL is rapidly declined for as-synthesized NCs in the first 10 hours. The presence of phthalimide in CsPbI3 NCs could maintain stability even after a week while the as-synthesized NCs under transition to non-luminescent phase within 4 days.
Furthermore, blue, green, yellow, and red-emitting diodes by using CsPbCl1.5Br1.5, CsPbBr3, CsPbBr1.5I1.5, CsPbI3 NCs respectively are fabricated by drop-casting NCs onto blue LED lights which show the great potential of the use of these phthalimide passivated NCs in the field of display and light technologies.
Read the full paper here: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/nr/d1nr03916d
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Vivek Vardhan from ECE files design copyright
 Bitragunta Vivek Vardhan, a final year student from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, has filed a design copyright for developing a “UV Ray Wooden Sanitizer Disinfection Box”. This is a safe chemical-free product designed to disinfect the surfaces of items. In this period of the Covid-19 pandemic, it has been difficult to sanitize mobile phones, tabs, laptops, car/bike keys, wallets, currency/coins, credit/debit cards, newspapers, pens, goggles, spectacles, accessories, milk packets, bakery items, water-absorbing products, delivery packages, toys, clothes etc with liquid sanitisers or else with water.
Bitragunta Vivek Vardhan, a final year student from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, has filed a design copyright for developing a “UV Ray Wooden Sanitizer Disinfection Box”. This is a safe chemical-free product designed to disinfect the surfaces of items. In this period of the Covid-19 pandemic, it has been difficult to sanitize mobile phones, tabs, laptops, car/bike keys, wallets, currency/coins, credit/debit cards, newspapers, pens, goggles, spectacles, accessories, milk packets, bakery items, water-absorbing products, delivery packages, toys, clothes etc with liquid sanitisers or else with water.
Researchers say that the coronavirus stays on surfaces of plastic (3-7 days), stainless steel (3-7 days), copper (up to 4 hours), paper (up to 4 days), glass (4 days), cardboard (24 hours), and wood (up to 2 days). UVC has a wavelength of 10 nm to 400 nm and is used for the disinfection method that has short-wavelength light to kill or inactivate microorganisms by destroying nucleic acids and disrupting their DNA, leaving them unable to perform vital cellular functions. The UVC light used in the product will not penetrate into solid surfaces and it is safe to use on touchscreen mobiles, laptops, tabs, etc. It is also proven that the disinfection box can destroy the bacteria and viruses on the surface of food items without causing any harm to the edibility.
“In future, I have plans to take this project to the next level by designing large dimensions of the box and making it work automatically with remote control through our mobile phone. I am extremely happy about filing the copyright and I express my heartfelt gratitude to Prof Siva Sankar Sir and Pro VC Prof D Narayana Rao Sir for giving me the opportunity and supporting me to expand my idea up to the level of implementation. And I thank Prof Vinod Kumar Sir for taking care of the filing process. Finally, I thank SRM University-AP for encouraging and nurturing young talents in all ways possible, “ Vivek stated.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News, Students Achievements
Advances of surface-enhanced Raman and IR spectroscopies
 Dr Rajapandiyan Paneerselvam from the Department of Chemistry has published a paper titled “Advances of surface-enhanced Raman and IR spectroscopies: from nano/microstructures to macro-optical design” in the journal Light: Science & Applications, Volume 10, Article number: 161 (2021) having an Impact factor of 17.7.
Dr Rajapandiyan Paneerselvam from the Department of Chemistry has published a paper titled “Advances of surface-enhanced Raman and IR spectroscopies: from nano/microstructures to macro-optical design” in the journal Light: Science & Applications, Volume 10, Article number: 161 (2021) having an Impact factor of 17.7.
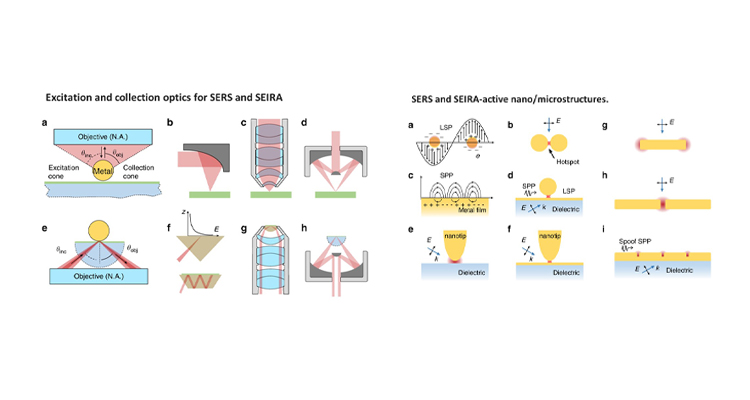
Raman and infrared (IR) spectroscopy are powerful analytical techniques, which are widely used for a variety of applications including food analysis, environmental analysis, chemical, and biomolecule analysis. This review article presents some latest advancements in vibrational spectroscopic techniques, and further developments in this field are given with emphasis on emerging techniques and methodologies.
This article has been published with Prof Zhong-Qun Tian’s group, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005, China.
Furthermore, Dr Rajapandiyan’s research group will focus on the development of plasmonic nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and its applications in food science, spectroelectrochemistry, and microfluidics in the future.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-021-00599-2
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
PhD scholars engage in conversation with Pro-Vice-Chancellor
 A conversation session between Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor and the research scholars of SRM University-AP was held on August 10, 2021. On this occasion, Prof Ranjit Thapa’s research scholar from the Department of Physics and Dr Nimai Mishra’s research group from the Department of Chemistry were felicitated for their sustained progress in carrying out research.
A conversation session between Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor and the research scholars of SRM University-AP was held on August 10, 2021. On this occasion, Prof Ranjit Thapa’s research scholar from the Department of Physics and Dr Nimai Mishra’s research group from the Department of Chemistry were felicitated for their sustained progress in carrying out research.
Prof D Narayana Rao elaborated on the state of the art research facilities that SRM University-AP provide to carry out research 24×7. The university has completely centralized laboratories and the scholars can use any lab and equipment depending on the nature of their research. Well furnished lab spaces and working models with fire/safety and security provisions, modernized synthesis equipment and High-end characterization equipment, and fabrication facilities are available for custom made research.
X-ray diffractometer lab; Advanced Materials Laboratory with Radiant Ferroelectric analyser (DST project), custom made furnace for impedance measurements; Applied Nano Materials Lab with Electrochemical reactor, Photochemical reactor, Potentiostat-single channel; Genetics of Aging Laboratory; Colloidal Chemistry Laboratory; Organic Synthesis Lab; are few among the numerous laboratories that SRM University-AP extend to vigorous research projects that are being carried out on our campus.

Faculty members and PhD students have published papers in top-ranking journals like Nature, Nature Microbiology, Advanced Energy Materials, Journal of American Society (JACS), Advanced Functional Materials, Advanced Sciences, ACS Nano, IEEE Journals etc The university conducts joint research programmes with NARL, ISRO/DoS and has two industrial projects.
Dr Nimai Mishra expressed that the university has been supportive in moulding young and vibrant researchers. “The scholars of SRM University-AP match up to the level of students from IITs, presenting papers in international conferences and publishing articles in Scopus indexed journals”, he added. Lately, Vasavi Dutt Vankadaru, one of the brilliant minds working on perovskite nanocrystals for light-emitting application, along with Akhil Syed, delivered flash presentation ( e-Poster) at an international conference organised by the Indian Society for Radiation and Photochemical Sciences (ISRAPS).
- Published in News, Research News
Heterojunction photocatalyst for the degradation and mineralization of pharmaceutical effluent: Clozapine
 A research paper titled “Robust visible light active PANI/LaFeO3/CoFe2O4 ternary heterojunction for the photo-degradation and mineralization of pharmaceutical effluent: Clozapine” has been published by Dr Lakhveer Singh from the Department of Environmental Science at SRM University – AP, as a co-author, in Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, having an Impact Factor of 5.90.
A research paper titled “Robust visible light active PANI/LaFeO3/CoFe2O4 ternary heterojunction for the photo-degradation and mineralization of pharmaceutical effluent: Clozapine” has been published by Dr Lakhveer Singh from the Department of Environmental Science at SRM University – AP, as a co-author, in Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, having an Impact Factor of 5.90.
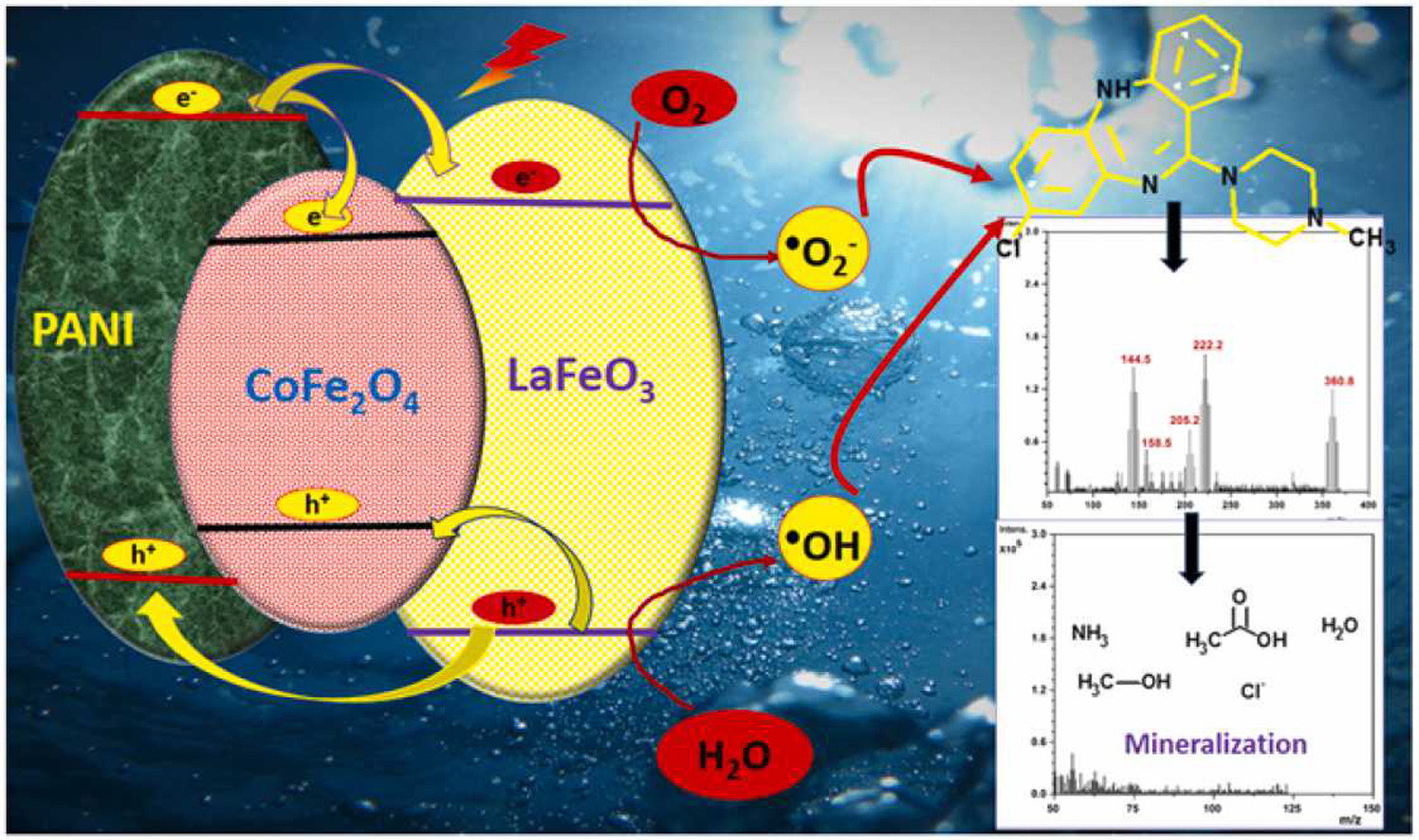
Clozapine (CZP) is a second-generation antipsychotic medicine prescribed for the treatment of resistant schizophrenia. The reported side effects of CZP includes cardiometabolic, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, seizures, myocarditis, weight gain and obesity. In this research, a novel magnetic ternary PANI/LaFeO3/CoFe2O4 (PLC) heterojunction photocatalyst was developed for the degradation and mineralization of pharmaceutical effluent: Clozapine. The photocatalysts were found to be re-usable for 5 consecutive cycles.
This work has been in collaboration with Central University Jammu. The present study has a new insight into the development and fabrication of efficient ternary heterojunction towards promising application prospects in wastewater remediation.
Dr Lakhveer Singh is an Editorial Board member of the Journal of Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery – Springer (I.F. 2.60) and a Guest Editor for Bioresource Technology Reports- Elsevier.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106159
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Dr Balaga Mohana Rao receives Best PhD Thesis award from IIT Bombay
 Dr Balaga Mohana Rao, Assistant Professor from the Department of Economics has been awarded the best PhD thesis award in the 59th IIT Bombay convocation held on August 07, 2021. The thesis titled The Early Warnings of the Impending Currency Crises and the Ensuing Macroeconomic Costs aims to develop an Early Warning System to identify the Currency Crises that would help in preventing an impending crisis and also in mitigating the devastating aftermath effects if that occurred.
Dr Balaga Mohana Rao, Assistant Professor from the Department of Economics has been awarded the best PhD thesis award in the 59th IIT Bombay convocation held on August 07, 2021. The thesis titled The Early Warnings of the Impending Currency Crises and the Ensuing Macroeconomic Costs aims to develop an Early Warning System to identify the Currency Crises that would help in preventing an impending crisis and also in mitigating the devastating aftermath effects if that occurred.
The financial crises have enthused a huge theoretical and empirical debate in current times due to their recurrent nature in the history of economics. To highlight the importance of an economic crisis among various sections, Kaminsky et al. (1998) quote Kindleberger (1978) saying that academics are interested in a crisis as they have had a history of fascination for the crises, policymakers are interested because they want to prevent the crisis, and financial market participants are interested as they can make money out of it. The financial crises can be divided into two broad categories—currency and sudden stop crises, and debt and banking crises. The currency crises have not only swept away Argentina (2001), Brazil (1998–1999), Latin America (the 1980s), Russia (1998), Southeast Asia (1997) and UK (1992) (to name a few) but they also have caused serious economic adversities to India and BRICS in the recent past. A currency crisis encompasses one of the following four features or a combination of them owing to a speculative attack—both successful and unsuccessful attacks—on a currency: A sharp depreciation of a currency (possibly followed by devaluation) and/or huge depletion of foreign exchange reserves or an increase in interest rates by the central bank or imposing restrictions on capital flows. In this context, Dr Balaga Mohana Rao’s thesis focuses on developing an early warning system to identify the impending crises, finding the common determinants of currency crises and the aftermath effects on macroeconomic indicators.
“One may wonder why the crisis should be prevented or mitigated. The reason is that a full-blown crisis will not be just confined to the foreign exchange market or some other segment, but it will affect the whole economy” Dr Balaga said. He plans to extend his PhD work on Currency Crises and see it in the context of the International Price System.
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News, Research News
SRM University-AP observes Research Day to promote research among students
 The third edition of Research Day was held at SRM University-AP on August 21, 2021, to provide an excellent opportunity for all the faculty members, research scholars and students to exchange and exhibit their ideas on research. Prof U B Desai, Chancellor, Anurag University-Hyderabad, was the Chief Guest of the event.
The third edition of Research Day was held at SRM University-AP on August 21, 2021, to provide an excellent opportunity for all the faculty members, research scholars and students to exchange and exhibit their ideas on research. Prof U B Desai, Chancellor, Anurag University-Hyderabad, was the Chief Guest of the event.
In his speech, Prof UB Desai admitted that creating a research ecosystem in education has truly become important. During the last decade, the realisation happened, and it has been reflected in the National Education Policy, yet there is a long way to go. He further congratulated SRM University-AP for dedicating a day for research to motivate students towards the research pursuits. In his keynote address, “India’s Ascent to 5G”, he discussed some pertinent queries and showed the way forward. In every 10 years, there is an evolution in Communications. He made the audience aware of the 10 key technological trends- Artificial Intelligence, Autonomous Networks, Cyber Security, Distributed Ledgers, Dynamic Data, Extended Reality, Internet of Things, Quantum Computing, Autonomous Systems along with 3 software trends- Softwarization, Cloudification, Virtualisation which will shape the digital future. He further explained how Network evolution beyond the currently planned 5G is taking place. Research on 6G has already started, and in the future, it is poised to dominate 5G.
 Prof Desai pointed out that India can make much improvement in Edge Computing and Metadata as these domains do not require huge resources. He further delved into the Evolved Network architecture and Indian Scenario and thrusts. He expressed that Research on 5G, Internet of Things and Cyber Security is critical to the National Interests. The nation thus is enhancing current Research and Developmental capabilities- domestic manufacturing and export-oriented. With interesting facts and charts, he laid down the mobile communication roadmap in India. In our country, mobile broadband is the premium source of the internet, with 80% of the internet traffic generated by it. An Indian consumes 11 Gb data per month per smartphone on an average which is the highest in the world. It need not be overemphasized that there is huge scope and opportunities in 5G research and beyond. Similarly, the Internet of Things is going to be another big wave. The next-generation devices and appliances will be hugely IoT based with less hassle in operation. Smart Cities-Sensors, Precision Agriculture, Digital Health, Industry 4.0, Automative are some of the sectors where it has substantial scope for application. Indian operators are also to launch nationwide NB-IoT services in the coming days.
Prof Desai pointed out that India can make much improvement in Edge Computing and Metadata as these domains do not require huge resources. He further delved into the Evolved Network architecture and Indian Scenario and thrusts. He expressed that Research on 5G, Internet of Things and Cyber Security is critical to the National Interests. The nation thus is enhancing current Research and Developmental capabilities- domestic manufacturing and export-oriented. With interesting facts and charts, he laid down the mobile communication roadmap in India. In our country, mobile broadband is the premium source of the internet, with 80% of the internet traffic generated by it. An Indian consumes 11 Gb data per month per smartphone on an average which is the highest in the world. It need not be overemphasized that there is huge scope and opportunities in 5G research and beyond. Similarly, the Internet of Things is going to be another big wave. The next-generation devices and appliances will be hugely IoT based with less hassle in operation. Smart Cities-Sensors, Precision Agriculture, Digital Health, Industry 4.0, Automative are some of the sectors where it has substantial scope for application. Indian operators are also to launch nationwide NB-IoT services in the coming days.
In his welcome speech, Prof D. Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor, SRM University-AP, said that the universities and educational institutes need to trigger the thought process and inquisitiveness among the students beyond the classroom. Universities should give top priorities for research that creates a positive impact or change in society. The country’s universities and educational institutions need to be encouraged to perform transactional research that leads to the development of products needed for societal development. Universities and educational institutes should also look for collaborative research with the industry. Universities are the creators of knowledge and innovative ideas, providers of skilled manpower, agents of societal changes and symbols of international attention and prestige. Therefore rather than counting the number of publications, more focus is to be given to translational research.
Universities and educational institutes need to synergise so that both of them can be benefitted from the collaborative research outcomes. Falling behind innovation would mean falling behind in becoming a world leader. Therefore, for a country like India, aspiring to attain global economic leadership needs to be strongly encouraged and supported in research. Sri Narendra Modi, our Hon’ble Prime Minister, firmly believes that our future will be secure and global leadership will sustain only when we produce the next generation of world-class scientists, technologists, researchers and innovators. As India emerges as a global power, we need to move forward from being a knowledge consumer to a knowledge producer. It is the responsibility of universities and educational institutes to create knowledge.
 SRM University-AP provides abundant opportunities to faculty and students to carry out frontline research. National Education Policy-2020’s sharp focus is on research and multidisciplinary approach. National Research Foundation has been set up as per the recommendation of National Education Policy-2020 to significantly enhance the research contributions. Research is the way forward to be a world superpower. We must inculcate the desire to perform quality research in students even from the undergraduate days.
SRM University-AP provides abundant opportunities to faculty and students to carry out frontline research. National Education Policy-2020’s sharp focus is on research and multidisciplinary approach. National Research Foundation has been set up as per the recommendation of National Education Policy-2020 to significantly enhance the research contributions. Research is the way forward to be a world superpower. We must inculcate the desire to perform quality research in students even from the undergraduate days.
In his speech, Prof V S Rao asserted how the nascent university has created its reputation in the education world of India. In fact, SRM University-AP has achieved several marvels in the last 30 months, including many research publications, projects, and several patents. Since its inception in 2017, the university has published over 500+ papers, 22 patents and 36 funded projects with an outlay of about Rs. 20 crores. He further emphasised that, unlike several other universities, SRM University-AP has research embedded in the curriculum. SRM University-AP does not believe in keeping research outside the curriculum. The capstone projects, research based learning, undergraduate research project, research internships with international universities or industry-SRM University-AP offer a plethora of opportunities to the students to bring out the inner researcher among them.
SRM University-AP firmly believes that a research eco-system should be inculcated among the students. The students must learn how to think and question and how to find the answers. Agreeing with Prof D. Narayana Rao, Prof VS Rao also mentioned that the National Education Policy-2020 puts a great emphasis on research since the importance of research need not be debated today. SRM University-AP thus introduced Research Day to impart curiosity towards transcendental knowledge among the students.
“Book of Abstracts” was launched by Prof V S Rao in the gracious presence of Prof UB Desai, Prof T Ragunathan, Associate Dean-Engineering, Prof Bandi Kamaiah, Dr B Siva Kumar, Deputy Dean and other dignitaries. 217 research abstracts were selected for presentation after review and scrutiny. 22 students out of them have received Gold medals for the research, and 9 students secured silver medals. All medal winners were felicitated in the event.
- Published in News, Research News
Resource and network-aware data placement algorithm for periodic workloads in cloud
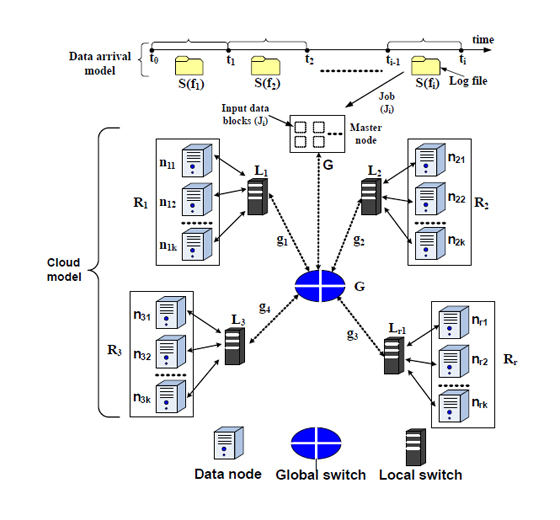 Dr Hirenkumar Thakkar from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has published a research paper titled “RENDA: Resource and Network-aware Data Placement Algorithm for Periodic Workloads in Cloud” in the journal IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems Vol. 32, No. 12, pp. 2906-2920.
Dr Hirenkumar Thakkar from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has published a research paper titled “RENDA: Resource and Network-aware Data Placement Algorithm for Periodic Workloads in Cloud” in the journal IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems Vol. 32, No. 12, pp. 2906-2920.
Each year, tech giants are spending millions of dollars to purchase the resources to store the data. However, efficient data placement is a critical issue for companies that experience several terabytes of data generation on daily basis. With such speed of data generation, it is the need of the hour to come up with a strategy for an efficient storage mechanism. This research investigates the data placement problems in cloud data centres and assists several tech giants such as Google, Facebook etc., to manage the cloud resource properly.
This research benefits society with a lower cost of cloud subscriptions, as tech giants are able to save several thousands of dollars by means of an efficient storage mechanism. This ultimately enables the tech giants to offer cloud service subscriptions at a reasonable cost.
The study was carried out in collaborations with Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Computing Lab (ABC Lab), Chang Gung University, Taiwan with Prof. Prasan Kumar Sahoo and in collaboration with Prof. Bharadwaj Veeravalli from the National University of Singapore. In addition to the current collaboration, there are several collaborations with the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT-BHU) as well as the University of Tartu, Estonia.
In future, Dr Thakkar is planning to come up with a book on cloud resource management using Nature-inspired learning. In addition to that, there are few projects such as filing two separate patents on Healthcare data analysis and opinion feature mining in collaboration with Chang Gung University, Taiwan, the National University of Singapore, and the University of Tartu, Estonia.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2021.3080582
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
First patent granted to SRM University-AP
Title of the Patent: A Process for Preparing Magnesium Foams
Patent applicant: SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh
Patent Application number: 202041001715
Date of Filing: 14/01/2020
Date of Publication: 24/01/2020
Date of Grant: 16/08/2021
 Prof G S Vinod Kumar and his PhD Scholar Mr Dipak Nandkumar Bhosale from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has brought the first granted patent to SRM University-AP. The patent titled “A Process for Preparing Magnesium Foams” is on the novel processing of Magnesium alloy foams via molten metal route. Metal foams are the class of novel ultra-lightweight and high strength materials used for engineering structures. Under the light-alloy category, Magnesium alloys possess greater challenges to foam and the inventors Mr Dipak Bhosale, PhD scholar and Prof Vinod Kumar (PhD supervisor) of Dept. of Mechanical Engineering have come up with a novel process to foam Magnesium alloy effectively. The patent was filed on January 14, 2020, and granted on August 16, 2021. It is indeed commendable that the patent grant is obtained in just 16 months from the date of application.
Prof G S Vinod Kumar and his PhD Scholar Mr Dipak Nandkumar Bhosale from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has brought the first granted patent to SRM University-AP. The patent titled “A Process for Preparing Magnesium Foams” is on the novel processing of Magnesium alloy foams via molten metal route. Metal foams are the class of novel ultra-lightweight and high strength materials used for engineering structures. Under the light-alloy category, Magnesium alloys possess greater challenges to foam and the inventors Mr Dipak Bhosale, PhD scholar and Prof Vinod Kumar (PhD supervisor) of Dept. of Mechanical Engineering have come up with a novel process to foam Magnesium alloy effectively. The patent was filed on January 14, 2020, and granted on August 16, 2021. It is indeed commendable that the patent grant is obtained in just 16 months from the date of application.
Metal foam is a cellular structure consists of solid metal with gas-filled pores. The pores can be sealed (closed-cell foam) or interconnected (open-cell foam). The present patent relates to a process for the preparation of closed-cell Magnesium foams using dolomite [CaMg (CO3)2] as a blowing agent (gas source), through a liquid metal route. The inventors have demonstrated economical and naturally occurring mineral dolomite to be an effective blowing agent for preparing magnesium foams and in-situ formed MgAl2O4 (spinel) particles as the stabilizing agent during stabilization of foams. The Magnesium foams produced by the process of the present disclosure have a good expansion, lower density, uniform pore size distribution and polyhedral pore structure. Through the present process Magnesium foams with 88% porosity 0.20 g/cm3 foam density was obtained. Magnesium foam is an attractive material that exhibits a unique combination of mechanical, physical, thermal, electrical and acoustic properties. It has high strength to weight ratio, good compressive strength and high energy/shock/vibration/sound absorption efficiency. Owing to these properties the magnesium foam finds potential in lightweight structural applications, sound-absorbing, energy and vibration and shock damping application.

