IIT Indore Selected Akash Yadav for M-Tech Programme with Scholarship
 SRM University AP is happy to inform everyone that IIT Indore selected Akash Yadav of our Mechanical Engineering Department class of 2021 into a coveted Master’s Program. Akash is excited to start his M-Tech journey in Production and Industrial Engineering Program at IIT Indore in Madhya Pradesh.
SRM University AP is happy to inform everyone that IIT Indore selected Akash Yadav of our Mechanical Engineering Department class of 2021 into a coveted Master’s Program. Akash is excited to start his M-Tech journey in Production and Industrial Engineering Program at IIT Indore in Madhya Pradesh.
Indian Institute of Technology, Indore or IIT Indore was established by the Government of India for Engineering Studies to provide research-based education. It has become one of the pioneer research institutes in the country and is known for its innovation driven research and entrepreneurship.
Getting selected into IIT Indore is not the first of Akash’s many successes. Akash hails from Nepal and is a recipient of a prestigious scholarship under “Dr. Homi Jahangir Bhabha Scholarship Scheme” from Embassy of India, Kathmandu for his higher education. This scheme provides full scholarship to all students and even provides stipend to selected students.
Akash showed tremendous potential and was a feather in the cap of SRM University AP even before getting selected for M-Tech at IIT Indore. Along with pursuing his Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering, he completed four projects in four years in our labs. His project titled “Experimental Investigation of laminar length for Non-impinging Submerged Jets” was also awarded with a gold medal.
“I cannot forget the conscientious support of my mentors Dr. Prakash Jadhav and Dr. Surfaraz S Halkarni from Department of Mechanical Engineering during my projects.” Akash said, “Research based learning at SRM University AP, is the key to my success.”
We, the SRM Family, wish Akash all the success in his chosen path and are proud to share the table with IIT Indore as his alma matres. We are pleased that our research facilities could accommodate his innovative mind in the classroom and his ideas and designs in our laboratories.
- Published in Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Students distribute winter clothing among slum dwellers
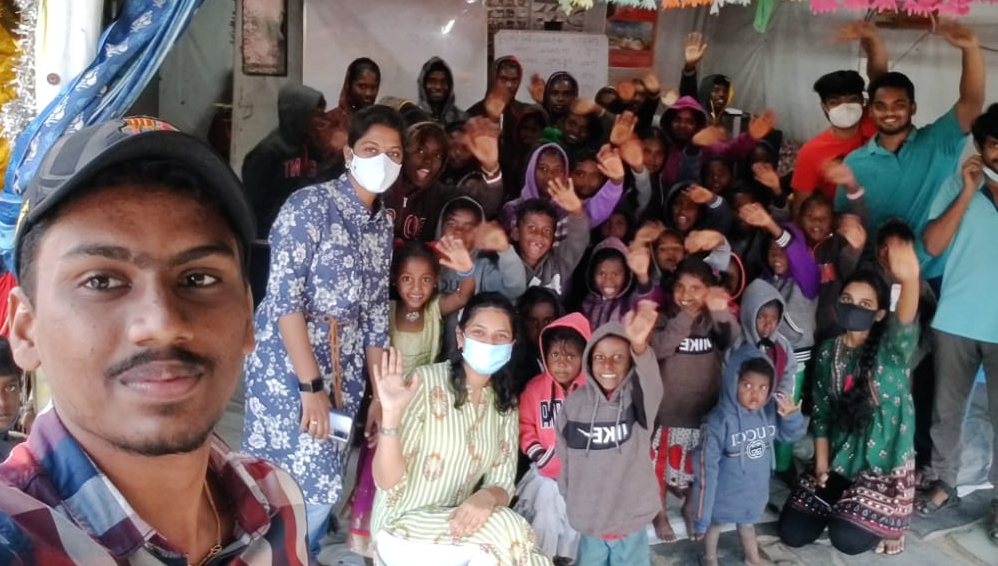 In a major initiative by the students of SRM University-AP, sweaters were distributed among the poor kids living on the streets of Guntur. Under the initiative, students from the 2018 batch of Computer Science Engineering, Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics and Communication Engineering, and Management Studies visited slum areas on the roadside near Shri Hospital, Guntur and distributed clothing among 44 kids ranging from 3 to 16 years old.
In a major initiative by the students of SRM University-AP, sweaters were distributed among the poor kids living on the streets of Guntur. Under the initiative, students from the 2018 batch of Computer Science Engineering, Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics and Communication Engineering, and Management Studies visited slum areas on the roadside near Shri Hospital, Guntur and distributed clothing among 44 kids ranging from 3 to 16 years old.
“We know how the families whose sustenance depends on the street have suffered during the pandemic. I am sure these small acts will bring cheers to these families,” said Prof V S Rao– Vice-Chancellor of the university. Prof B V Babu– Dean, School of Engineering and Sciences- highlighted the wonderful gesture saying “I am really glad to see the sensitivities and sensibilities our students have in sharing and giving”. Ms Revathi Balakrishnan– Assistant Director, Student Affairs appreciated the efforts, selfless service and compassion of SRM AP students to the lesser privileged.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, CSE NEWS, ECE NEWS, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News
An incredible feat of Mechanical Engineering student

It is a moment of pride and celebration for the Department of Mechanical Engineering at SRM University-AP as Hariharan D, Final year, BTech Mechanical Engineering bags admission offers from multiple top-ranked overseas universities including the University of Manchester that ranks 27 in the QS World University Rankings.
Moulding up the students through the right training and plotting out the right pathway for them to scale further heights have always been the primary objective of the faculty of SRM University-AP. “Happy to hear that you got placed in a core dream company. I hope this will not dampen your aspirations to go for higher studies. Indeed, students like you should study as far as you can. You should bring more laurels to this institution and make us proud”, this was the message Hariharan received from his faculty mentor, Dr Pramod Jammy, which kindled his spirit to set off for higher studies abroad.
“I am ever grateful to my beloved faculty mentors, Dr Pramod Jammy, Dr Lakshmi Sirisha and Dr Surfaraz Halkarni, for their constant support, inspiration and Letter of Recommendations provided amidst their busy schedules. I also thank my Department Head, Dr Prakash Jadhav, for his continuous motivation”, remarked Hariharan.
According to him, creating an imposing CV and impactful SoP is the deciding factor of the application process. He expressed his gratitude to the entire department for their effective involvement in every bit of the application process. “To build an attractive SoP and resounding CV, we need credentials like decent CGPA, involvement in departmental activities such as webinars, internships, workshops, minor projects, software skills, etc. Also, the close association with the department faculties right from the first year is essential to get their affinity and the commendable Letter of Recommendations” he added.
Forging a conducive platform to actualize one’s potential and chase after the life of one’s dreams is what makes SRM University-AP the topmost priority of students. Hariharan has set out an ideal example for many to follow and believe in their dreams coming true with SRM University- AP.
SRMAP signed MoU with Speed Engineering Solutions
SRM University-AP has inked a Memorandum of Understanding(MOU) with Speed Engineering Solutions Pune. The MoU will significantly benefit the students of the Department of Mechanical Engineering in their studies and overall industry exposure. As part of the understanding, the following activities will be carried out-
- Speed Engineering will deliver interactive and insightful webinars on Product Design-Development and similar topics to all students of the university.
- Speed engineering will conduct online workshops on product design at subsidised charges for BTech and MTech students.
- Speed engineering will offer full-time summer internships on Industry oriented product design and development to our BTech and MTech students.
- Speed engineering will offer a series of skill-building projects based on industry work to the BTech and MTech students. They will work under the joint guidance of SRMAP faculty and experienced Speed Engineering professionals. These projects will be based on real-life industry problems.
- Speed engineering will offer in-campus internships to some of the students of SRM AP based on their project performance.
- Speed engineering will offer jobs to some of the brightest students based on their project performance.
Prof Prakash Jadav welcomed the initiative and said, “This MOU is an excellent initiative for the mechanical engineering department. Our students will get huge benefits such as the latest training on Product design and Simulations, CAD, CAE and many other things. The benefits do not end here. Our students will further be able to convert opportunities to work on live industry projects and internships into attractive job offers. I am certain that our students will reap all the benefits from this collaboration.”
Know more about Speed Engineering Solutions: About Us – Speed Engineering Solutions
- Published in Collaborations, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News
Chanakya Karra admitted to PhD at Purdue University, USA
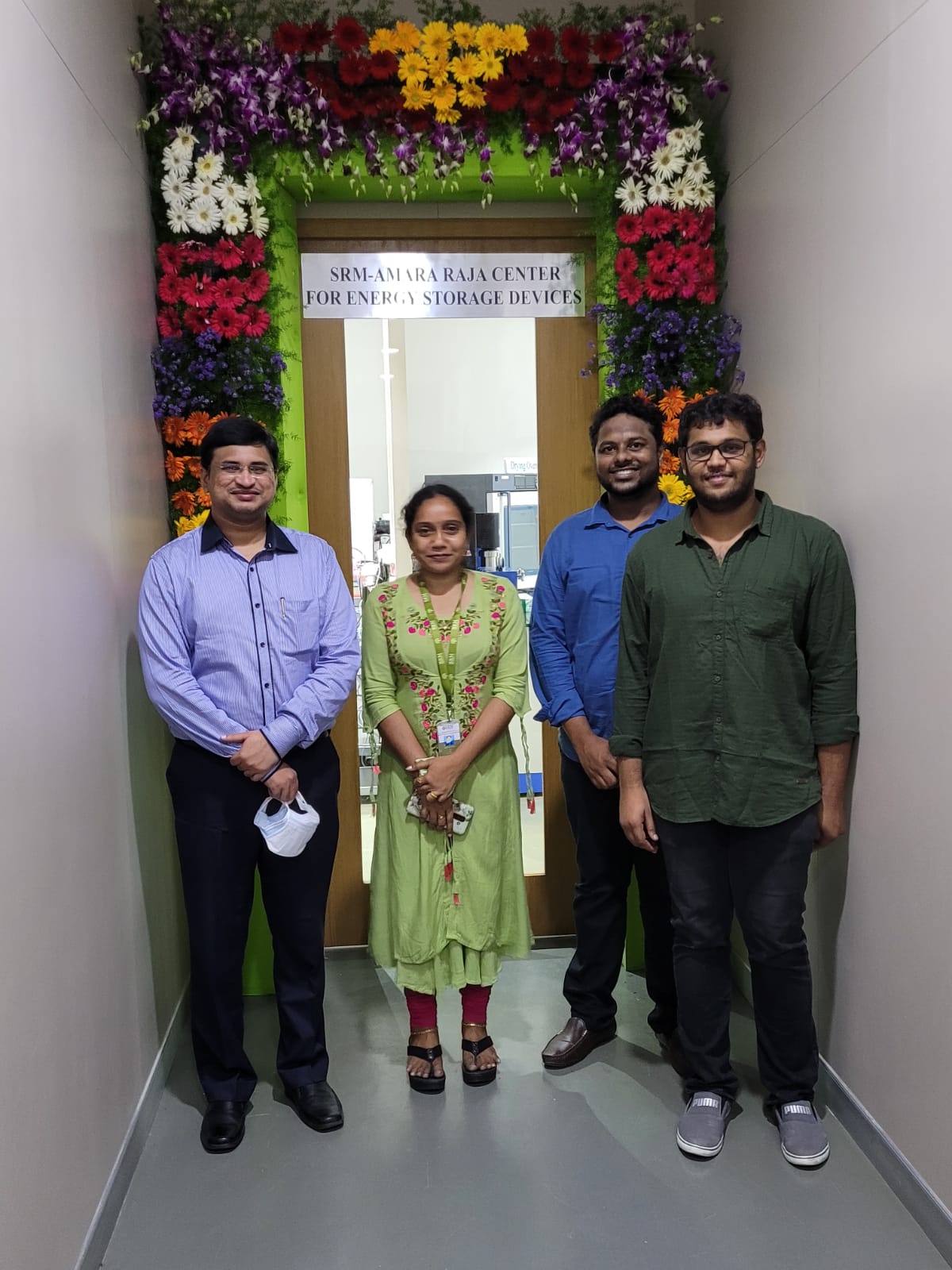 Once you are a part of SRM University-AP, we ensure that your future is secured! With the guidance of Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Mr Chanakya wends his way to Purdue University, USA, a world-renowned research university, for doing his PhD. He secured admission with a full tuition fee waiver and teaching assistantship. Chanakya Karra spent his two years DST-SERB JRF position at SRM AP and has made remarkable contributions to SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices.
Once you are a part of SRM University-AP, we ensure that your future is secured! With the guidance of Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Mr Chanakya wends his way to Purdue University, USA, a world-renowned research university, for doing his PhD. He secured admission with a full tuition fee waiver and teaching assistantship. Chanakya Karra spent his two years DST-SERB JRF position at SRM AP and has made remarkable contributions to SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices.
DST-SERB JRF position helped Chanakya resume his research career, which had a pause for over a year. “It fills me with immense joy to see the SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices shape up with every possible equipment to conduct research on batteries. Kudos to the management and the efforts of the faculty associated with the centre,” says Mr Chanakya. He further mentioned that the research work conducted at SRM-Amara Raja Centre enabled him to write over three papers that catapulted his chances of admission.
“I would urge the students to make the best use of the opportunities available at SRM-AP and discuss their plans with the faculty. I am sure new avenues will open with the mentoring of world-class faculty at SRM”, says Mr Chanakya to the junior batches of students aspiring for a research career.
Mr Chanakya expressed his gratitude to the faculty members associated with Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices- Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, Associate Professor, Chemistry, Dr Surfarazhussain S Halkarni, Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Dr Laxmi Narayana Patro, Assistant Professor, Physics, and others.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Physics News
Dr Sheela Singh secures patent for novel method of engine piston rings
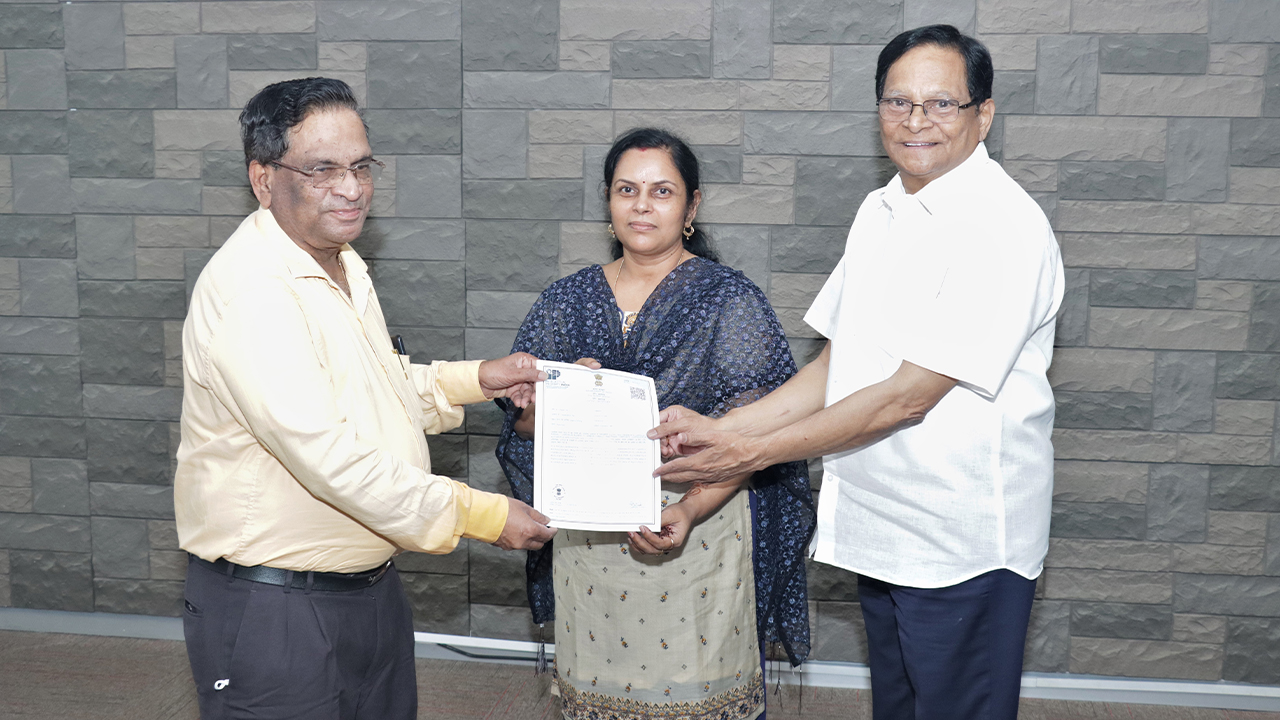

Research at SRM University-AP shows that applying a composite coating of chromium aluminum carbide (CR2 ALC) to the engine piston rings not only improves piston performance but also increases engine life, efficiency and lubrication. The university obtained a patent for the same under the title “NICKEL MOLYBDENUM ALUMINIUM (NIMOAL) – CHROMIUM ALUMINIUM CARBIDE (CR2ALC) MAX PHASE COMPOSITE COATINGS FOR AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AND A METHOD FOR MAKING THE SAME”.
For any vehicle to run efficiently for a long time, its engine must be good. The rings on piston further improve the engine performance. It is in this context that many efforts are being made by scientists to develop piston rings with the new scientific technologies. Dr Sheela Singh, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at SRM AP, has been conducting comprehensive research on the subject for three years with research student Deepak Davis.
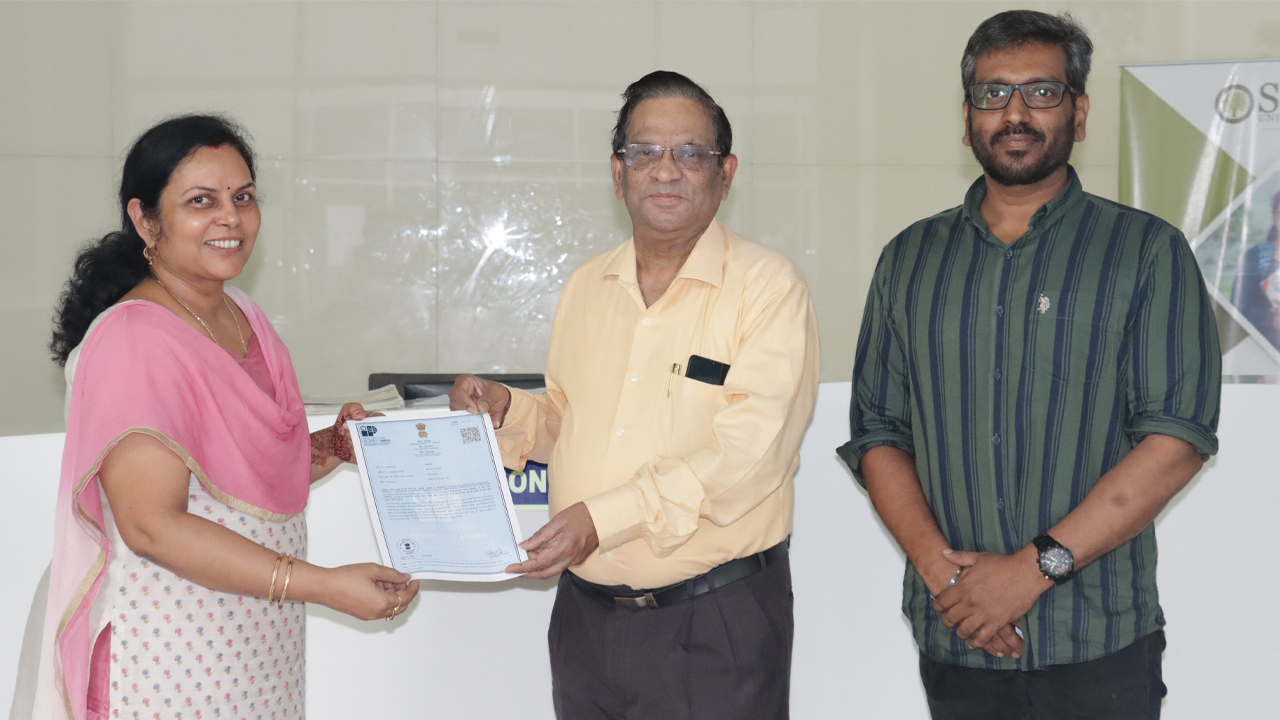

The piston rings of motor vehicles currently on the market have a coating with nickel molybdenum aluminum. SRM University-AP researchers say it would be better to use a composite coating made with chromium aluminum carbide instead. If the piston rings have high velocity and lubrication properties, their rigidity is good and it is better to use chromium aluminum carbide (CR2LC).
The Patent Certificate is issued by the Patent Office, Government of India, after thorough examination. University President Dr Satyanarayanan, Vice-Chancellor Prof V S Rao, Pro Vice-Chancellor Prof D Narayana Rao and others lauded Dr Sheela Singh and Deepak Davis for their fervent research and innovation. This is the second patent granted to SRM University-AP.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Remodelling fan blades to downsize the bird strike impact
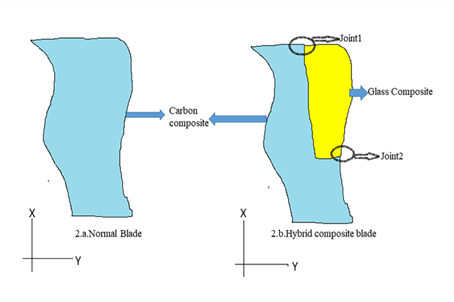 Bird strikes are a crucial phenomenon that should be taken into consideration while designing aircraft. Bird strikes have been reported since the early days of flight causing fatal disasters. It is estimated that around 300 people were killed, and several aircraft were destroyed because of bird strikes. A great deal of research has been conducted to tweak the design of aircraft to bring down the impact of bird strikes. Prof Prakash Jadhav and his PhD scholar Gruhalakshmi Yella from the Department of Mechanical Engineering have published a paper offering an appropriate solution in this regard.
Bird strikes are a crucial phenomenon that should be taken into consideration while designing aircraft. Bird strikes have been reported since the early days of flight causing fatal disasters. It is estimated that around 300 people were killed, and several aircraft were destroyed because of bird strikes. A great deal of research has been conducted to tweak the design of aircraft to bring down the impact of bird strikes. Prof Prakash Jadhav and his PhD scholar Gruhalakshmi Yella from the Department of Mechanical Engineering have published a paper offering an appropriate solution in this regard.
Their paper titled “Hybrid joint interface in composite fan blade subjected to bird strike loading” has been published in the international journal, ‘Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science’ having an impact factor of 1.76. The research puts forward an ideal solution to alter the design of the aircraft fan blades which are frequently being subjected to such collisions. The duo proposes a hybrid joint interface using two fibres instead of a single fibre.
Some delamination failures observed in the trailing edge of the blades could probably increase the effect of such bird strikes. For rectifying the delamination problem, the proposed solution is to use a material with higher strain capability such as glass fibres in the areas on the fan blade which are prone to delamination, while maintaining carbon material on the remaining blade. The concept is proved by first performing a static analysis on 3D FEA coupons with an in-built hybrid interface joint and next by performing a dynamic bird strike analysis on 3D FEA coupons and sub-element models with an in-built hybrid interface.
Abstract of the Research
Fan blades are one of the most important components of an aircraft engine. Bird strikes on fan blades have always been a cause of worry and it can cause slices of birds to hit other parts of the engine which may lead to greater damage. Bird strikes cannot be completely avoided. Although current composite blades can withstand the bird strike impact, some delamination failures are still observed on the trailing edge side of the blade, possibly due to vibration bending modes. This paper talks about using two fibres in a composite blade instead of the current single fibre one. For this to be feasible, two fibre joints at various locations on the blade must be properly designed. The design criteria used here is the lowest inter-laminar shear strain level at critical joint locations.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
A solar-powered innovation of Venkata Sree Harsha

Student innovations that render hope and reassurance to an ever-changing society with booming demands indeed call for sweeping appreciation and recognition. We are elated to present the story of one of our budding masterminds who has brought us laurels through his trailblazing invention. Our first-year Mechanical Engineering student, Venkata Sree Harsha has developed the prototype of a solar electric bicycle with iconic features. This is a well-timed invention presented in the face of exacerbating pollution and energy insufficiency.
There have been endless studies and research going on to discover alternate solutions to bring down the imprudent use of conventional sources of energy. We are running out of our resources on one hand, and they are causing irreversible damage to the environment on the other hand. Tapping the invaluable potential of solar energy is the ideal way to welcome a new era of renewable energy resources. Solar inventions are therefore encouraged and put to implementation. This is believed to expedite the use of such renewable resources.
Venkata Sree Harsha’s solar-powered bicycle can run for unlimited distance in sunlight and for 2 hours at night when fully charged. It is fitted with a 24 Volt, 350-Watt DC motor, two 12 Volt batteries, two 6-Watt solar panels, and other components. The rechargeable batteries are attached to a 36 Volt motor, and it is connected in a series fashion. The solar power panels are fastened to the rear end of the vehicle which actively charges the bicycle while it is running on the sun. The total investment for this environment-friendly solar bicycle came approximately to rupees 15,000. This is a fruitful innovation when the escalating fuel prices are causing hardships in an average Indian household.
The young innovator expressed his delight and contentment over making his tiny share of contribution to the lives of those who are struggling to make ends meet in a world where expenses are soaring high without limits. His passion for science and determination to bring technology to right and productive use are what made this innovation possible. Mr Venkata also thanked his teachers and fellow friends who helped and guided him throughout this rewarding journey.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Design methodologies for composite structures in aircraft engines
 Dr Prakash Jadhav, Professor and Head, Department of Mechanical Engineering at SRM University-AP has published a chapter titled “Design Methodologies for Composite Structures in Aircraft Engines” in the book Advanced composites in aerospace engineering applications, Feb 2022, ISBN 978-3-030-88191-7, Springer.
Dr Prakash Jadhav, Professor and Head, Department of Mechanical Engineering at SRM University-AP has published a chapter titled “Design Methodologies for Composite Structures in Aircraft Engines” in the book Advanced composites in aerospace engineering applications, Feb 2022, ISBN 978-3-030-88191-7, Springer.
Abstract of the book chapter
Recently there have been many successful attempts to implement the use of fibre-reinforced composite structures in commercial aircraft engines. The author has been part of these efforts while working in the aviation industry. This article describes these efforts to design, analyze, manufacture, and implement the composite structures inside the low-pressure and low-temperature zones of the engine. Very innovative out-of-the-box design methodologies were used to design these components. These efforts elaborate on the design, optimization, and improvement of the composite fan blade, the composite fan platform, and the composite booster blade inside the engine. It focuses on structural design, aerodynamic efficiency, and specific fuel consumption improvement efforts along with the usual reduction of weight targets. This work successfully demonstrates the systematic steps in the design and implementation like preliminary coupon-level simulations, coupon-level manufacturing, coupon/prototype testing, and final part-level simulations followed by part tests.
The target readers for the book are all engineers, professionals and researchers from the aerospace field. Dr Prakash Jadhav’s future research plan is to continue to develop new methodologies to implement more composites into the aerospace industry. The book chapter will be extremely useful for engineers working on the design of composite structures for aerospace applications.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Recasting high-entropy alloys for enhanced performance

High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are gaining research significance in recent times as they propose novel alloy designs and concepts demonstrating better performance. HEAs constitute multiple principal elements in varying concentrations and combinations to produce new materials with excellent physical properties and superior performance at extreme temperature conditions. Recent studies have brought out a few high-entropy alloys possessing exceptional properties, even capable of challenging the existing theories and models for conventional alloys. However only very little has been explored within this multidimensional space leaving limitless possibilities to be explored and materialized.
Dr Sheela Singh, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, has been conducting rigorous research in this domain and she has published research articles proposing novel ideas to tweak the properties of HEAs. In one of the articles co-authored by Dr Sheela, “Effect of minute element addition on the oxidation resistance of FeCoCrNiAl and FeCoCrNi2Al high entropy alloy”, published in the journal Advanced Powder Technology, she investigates the effect of Ti0.1 and Ti0.1Si0.1 addition on the high-temperature isothermal oxidation behaviour of dense FeCoCrNiAl and FeCoCrNi2Al high entropy alloys.
Mechanical properties such as hardness & young’s modulus, thermal properties such as melting temperature, specific heat capacity and coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) were investigated by Nano hardness tester (NHT), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dilatometer, respectively. The phases present in the HEAs produced by hot vacuum pressing and after isothermal oxidation were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscopy and Raman Spectroscopy.
The weight gain recorded after isothermal oxidation for 5,25,50 and 100 hours at 1050°C was found to be parabolic in nature. X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), as well as Raman spectroscopy analysis of HEA’s oxidized at 1050°C for 100 hours, shows the formation of the Al2O3 phase. A homogeneous thin oxide scale without any discontinuity was observed throughout the cross-section. It has been confirmed that Ti & Si addition in minute amount (0.1 at. % each) improves the mechanical properties and oxidation resistance as well as reduces the waviness of the oxide scale.
Another article co-published by her, “Enhanced Magnetization with Increased Chromium Concentration in FeCoCrxNi2Al High-Entropy Alloy”, in Materials and Science Technology, reports the effect of increasing the concentration of antiferromagnetic element Cr in FeCoCrxNi2Al (x = 0.5, 1.5) High Entropy Alloy (HEA) on their magnetic properties. It was found that the structure and composition of different phases, and the likely degree of spinodal decomposition in the Cr-Fe rich BCC phase significantly affects the magnetic properties.
Interestingly, the sample with Cr concentration x=1.5 showed two times larger saturation magnetization as compared to x=0.5. Furthermore, the magnetization versus temperature response shows a multi-phase character and exhibits distinct behaviour in low temperature and high-temperature regimes in both samples. The obtained soft ferromagnetic behaviour of these HEAs is crucial for the development of a new class of HEA for various applications.
The considerable structural and functional potential, as well as the richness of design, make HEAs promising candidates for new applications prompting further studies in the field. There remains a vast compositional space that is yet to be discovered. New studies have to be initiated finding out effective ways to recognise regions within this space where high-entropy alloys with potentially interesting properties may be lurking. Dr Sheela’s research is a right step in this direction to pave the way for fruitful developments in the future.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News


