Dr Kousik Das Receives Project Sanctioned by the Ministry of Earth Science

Dr Kousik Das, Assistant Professor from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has been sanctioned the project titled “Present Day and predicted physico-chemical and climate change influence on solute influx to Northern Bay of Bengal and its impact on biotic system”. sanctioned by the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM) of the Ministry of Earth Science, Govt. of India. Dr Kousik Das has been granted Rs. 42,42,000 as CO-PI for Rs. 1,89,19,100/- worth project, which will be undertaken in collaboration with researchers from esteemed institutes such as IIT Kharagpur and IISc Bangalore.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
The proposed research work consists of a quantitative and qualitative study of seasonal solute geochemistry of ocean water and biotic diversity in marine ecosystems, along with scenarios of predicted oceanic circulation pathways at present times and futuristic cases expected in a changing climate. The study will be done by coupling physical and chemical hydrogeological techniques, which include the installation of marine observation stations and field equipment after the generation of the conceptual framework. The project will work towards making the scientific community more acquainted with the hydrodynamics and chemodynamics of the Bay of Bengal ocean water.
Practical implementation/ Social implications of your research
Seawater characteristics in the head of the Bay of Bengal are rapidly evolving due to changing influx from terrestrial sources. In particular, the head Bay region has undergone rapid variations in water quality due to extreme climate conditions, sea level rise, tidal impact, and effects of ocean acidification. Our aim is to hypothesise the climatic and hydrological processes involved in altering the ocean water nutrient and trace element cycling and their subsequent impact on the marine biohabitat.
Future research plans
- Nutrient cycle of northern Bay of Bengal
- Trace element cycle of the Bay of Bengal
- Impact of climate change on biogeochemical cycle
- Impact of hydrological drivers on marine ecosystems
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
A Pathway to Sustainable Active Food Packaging

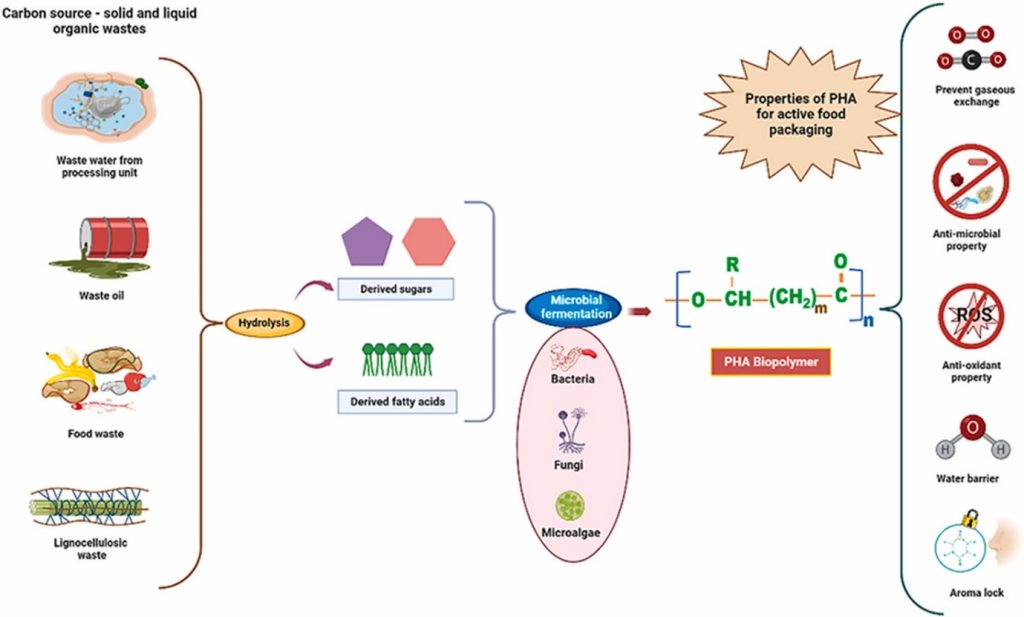
Dr Debajyoti Kundu, Assistant Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has conducted an impactful study on developing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), an eco-friendly solution that can help reduce plastic waste and make food packaging more sustainable. His recent paper “Advancements in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from wastes for sustainable active food packaging: An eclectic review”, published in the Q1 journal Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, Dr Debajyoti investigates how microorganisms can convert waste into a special type of plastic called PHA, which can be used for food packaging.
Unlike regular plastics, PHA is biodegradable and safe for both the environment and human health. The study reviews recent innovations in making PHA stronger and more effective for packaging, including its ability to prevent food spoilage and improve food safety.
Abstract
This study explores advancements in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from waste resources for sustainable active food packaging. It highlights the eco-friendly nature of PHAs as bioplastics and their potential to replace synthetic plastics in food packaging. The paper discusses recent technological improvements in PHA production and formulations, focusing on enhancing material properties to make PHA a viable alternative. It also examines trends in active packaging, including antimicrobial, antioxidant properties, and spoilage indicators, which can significantly improve food safety and quality.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The practical implementation of this research involves using PHA-based materials for food packaging to replace conventional plastics. This can lead to reduced environmental pollution due to PHA’s biodegradability and lower reliance on fossil fuels. Social implications include improved food safety through active packaging features like antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, potentially reducing foodborne illnesses and extending shelf life. Additionally, using waste to produce PHA promotes waste recycling and resource efficiency.
Collaborations
This research is a collaborative effort among various prestigious institutions including St. Joseph’s University, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Gurudas College, and SRM University-AP.
Moving forward, Dr Debajyoti will continue to work on improving the production processes and formulations of PHA to enhance its mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, he will explore new waste sources for PHA production and develop advanced active packaging technologies, such as smart packaging with sensors for real-time monitoring of food quality. Collaborations with industry partners to scale up production and test real-world applications of PHA-based packaging are another key focus.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Algae Biochar: A Promising Solution to Water Pollution

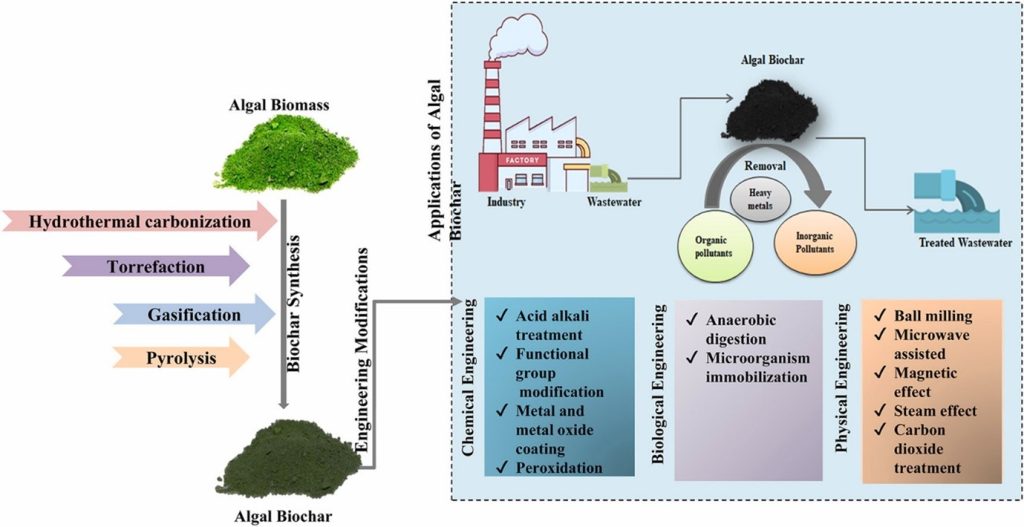
Dr Debajyoti Kundu, Assistant Professor in the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has published a research paper titled “Synthesis, delineation and technological advancements of algae biochar for sustainable remediation of the emerging pollutants from wastewater – A Review” in the esteemed Q1 journal “Environmental Research”, which has an impact factor of 8.3.
Dr Debajyoti’s research focuses on using algae biochar, which is particularly effective at cleaning polluted water. The study reviews how this biochar is made and improved and how it can effectively remove harmful substances from wastewater. This process is sustainable and environmentally friendly, offering a promising solution to water pollution.
Abstract
The study examines the synthesis, technological advancements, and applications of algae biochar for the sustainable remediation of emerging pollutants from wastewater. It highlights the unique properties of algae biochar, including its high surface area, pore volume, and adsorption capacity, which make it an effective medium for removing inorganic and organic contaminants from wastewater. The paper discusses various methods for producing algae biochar, such as pyrolysis, gasification, and torrefaction, and explores chemical and structural modifications to enhance its pollutant removal efficiency.
Practical Implementation /Social Implications of the Research
The practical implementation of this research involves using algae-derived biochar in wastewater treatment plants to remove harmful pollutants. This can lead to cleaner water, reduced environmental pollution, and improved public health. The process is also sustainable and cost-effective, contributing to environmental conservation and resource efficiency.
Collaborations
This research is a collaborative effort among various experts from institutions such as the University of Calcutta, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Graphic Era Deemed to be University, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Ranchi University, King Abdulaziz University, Incheon National University, Korea Aerospace University, and B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology.
Future Research Plans
Dr Debajyoti’s future research projects include exploring advanced modification techniques for algae biochar to further enhance its pollutant removal capabilities, investigating its application in different types of wastewater, and developing large-scale production methods. Additionally, there is an interest in studying the long-term environmental impacts and economic viability of using algae biochar in wastewater treatment.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Critical Analysis of the Influence of Hydroclimatic Variability and Anthropocene on the Groundwater of the Sundarbans

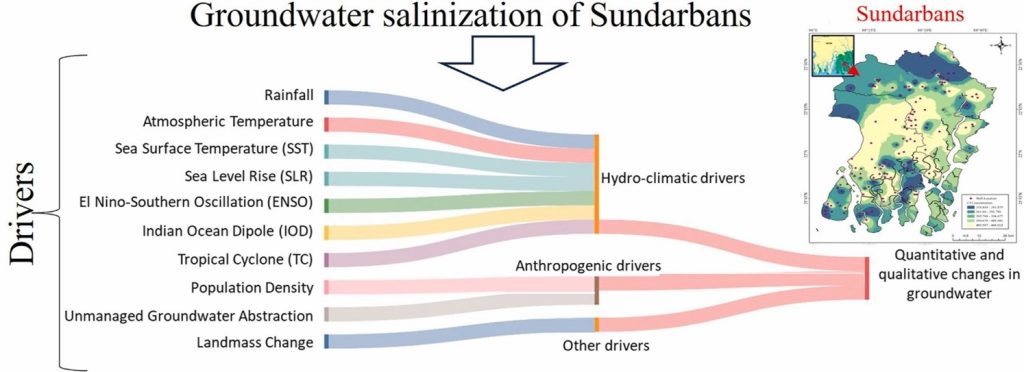
The water crisis in India, especially in the coastal regions, has worsened alarmingly, coercing environmentalists and researchers to critically study the reason behind this phenomenon. The Sundarbans region faces a scarcity of drinking water in terms of quality and quantity due to various reasons. Dr Kousik Das, Asst. Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Dr Harish Puppala, Asst Professor, Department of Civil Engineering and Mr Mijanur Mondal, Research Scholar from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has conducted a groundbreaking study on the increased salinization of water due to human activities. The research trio has published a paper titled “Understanding the susceptibility of groundwater of Sundarbans with hydroclimatic variability and anthropogenic influences” in the prestigious Q1 journal Groundwater for Sustainable Development, which has an impact factor of 5.9, critically analysing the numerous factors that affect the quality of drinking water in the Sundarbans region.
Abstract
Coastal aquifers worldwide are experiencing increased salinisation due to climate change and human activities. Sundarbans, in India, is one such area where this phenomenon is noticed at an unprecedented rate, making drinking water unpotable for consumption. Existing studies lack a comprehensive analysis of the underlying causes. This study conducts a systematic literature review to identify drivers of groundwater salinisation, examining climate change parameters such as rainfall patterns, sea level rise, El Niño-Southern Oscillation, and tropical cyclones. Significant groundwater level declines from 1996 to 2017 are primarily attributed to variations in the Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño Southern Oscillation, affecting rainfall and recharge rates. During tropical cyclones, groundwater levels rise rapidly, and quality is sensitive to El Niño Southern Oscillation. Rising sea levels, changing rainfall, and increasing population density worsen salinisation. Shallow aquifers have high salinity, whereas deep aquifers exceed permissible limits. This underscores the urgent need to address drinking water scarcity and potential migration resulting from complex interactions between climate, population, and groundwater management.
Social Implications of the Research
- Water Quality Monitoring: Implementing regular monitoring of salinity levels in groundwater to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Community Awareness Programmes: Conducting educational campaigns to inform local communities about the risks of high salinity levels in drinking water and promoting the judicious use of water sources so that unscientific abstraction can be reduced.
- Policy Development: Formulating policies at the local and national levels to regulate salinity levels in drinking water and ensure public health protection.
- Infrastructure Improvement: Investing in water treatment facilities or technologies to remove high salt levels from groundwater sources. Alternative sources and rainwater harvesting can be taken into consideration.
Collaborations – IIT Kharagpur, India
The research team plans to work on Groundwater vulnerability modelling using AI/ML in Sundarbans, India next. The team has begun collecting primary data using questionnaire surveys and interviews to throw light on socio-economic conditions and to understand the core reasons for the water crisis and health and psychological issues due to water unavailability, especially during extreme events like cyclones.
Link to the article
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
AESEE ’24: Promoting Global Dialogue on Environmental Sustainability

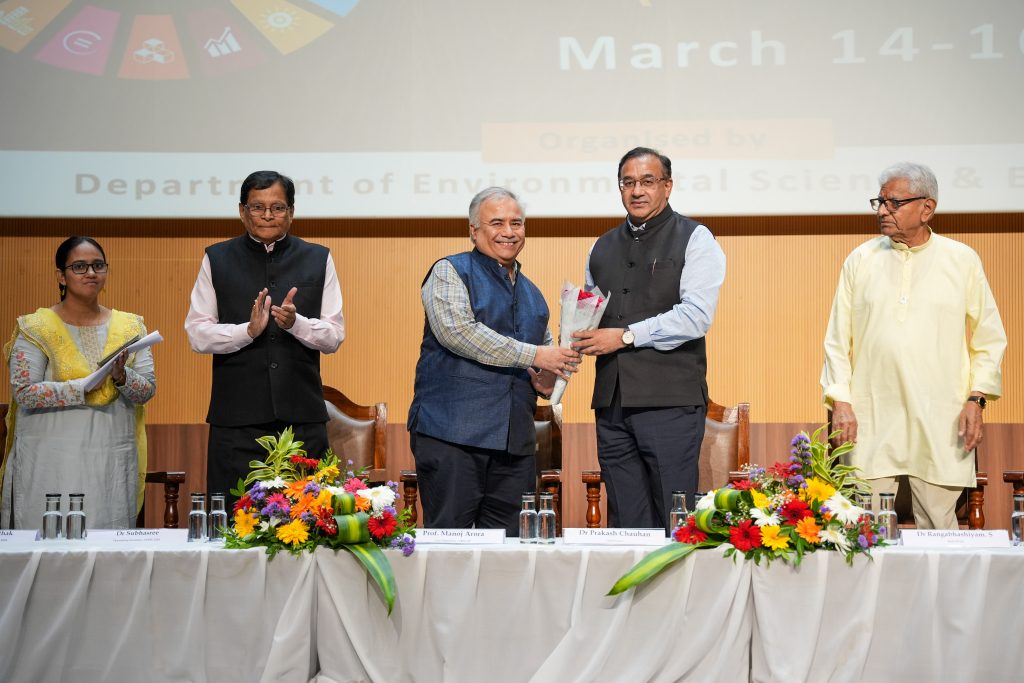
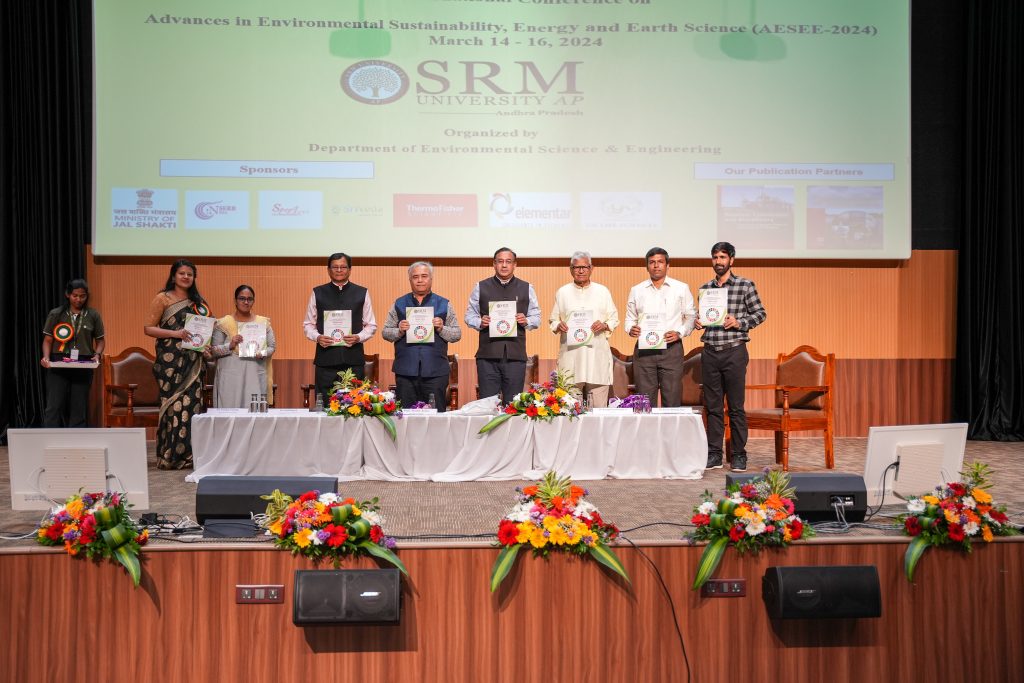
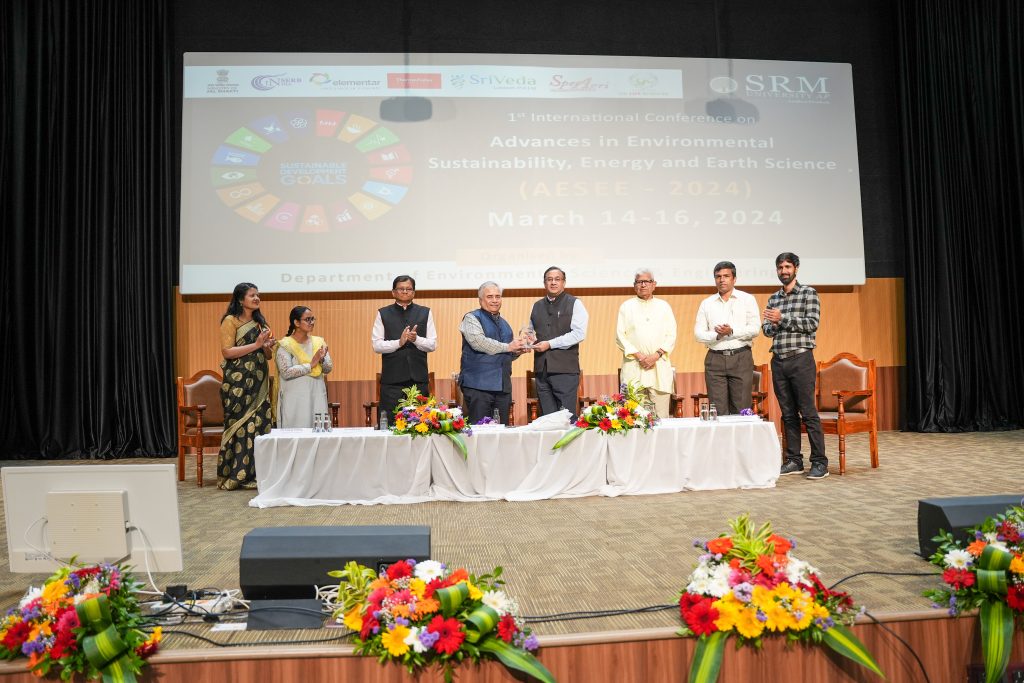
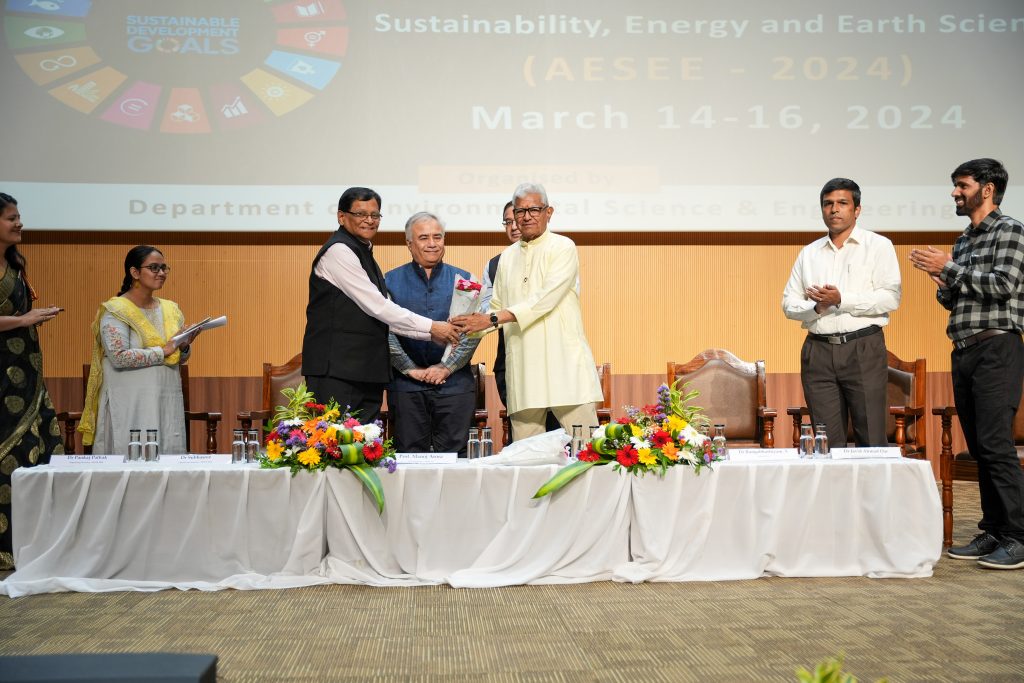
The Department of Environmental Science and Engineering at SRM University-AP organised its 3-day International Conference on Advances in Environmental Sustainability, Energy and Earth Sciences ( AESEE 2024). The inaugural session on March 14, 2024, featured industry experts, with Prof. Prakasham Tata from the Center for Transformation of Waste Technology, USA, as the Keynote Speaker and Dr Prakash Chauhan, Director-National Remote Sensing Centre, Indian Space Research Organization, as the Chief Guest for the event.
He highlighted the attributes of the department and lauded the efforts of the faculty and students who contributed to the publication of 165 articles, of which 106 were featured in Q1 Journals. This momentous occasion was witnessed by Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora; Advisor, Prof. V S Rao; Associate Professor and Head of the Department, Dr Rangabhasiyam Selvasembian; the organising secretaries, Dr Javed Ahmad Dar, Dr Pankaj Pathak and Dr Subashree Kothandaraman, along with participants from diverse parts of the globe, both online and offline.
Vice Chancellor-Prof. Manoj K Arora, in his address, emphasised that a congregation of such an intelligentsia is the need of the hour. He implored the audience to work at ground level and not confine themselves to mere talks and conferences, “go to the community and provide solutions, and solutions cannot be provided in the classrooms alone”, he stated.
Prakasham Tata, in his exuberant address, stated that the nation does not lack the intelligence or manpower to combat the alarming ecological crisis; It is the lack of trained personnel, pollution control boards, corruption and lack of effective cooperation between societal institutes that is causing a lax. Prof. Tata insisted that “universities like SRM AP are knowledge centres and have the tenacity and wisdom to combat the growing threats.” He issued a clarion call to all the youngsters and environmental enthusiasts to walk the talk.
Dr Prakash Chauhan, Director of the National Remote Sensing Centre, in his speech, cited Indians’ inherent way of living a sustainable lifestyle and went on to encourage the young participants in attendance to become true ‘karma yogis’ by innovating and finding new ways to promote and work towards environmental sustainability. He implored the youth to brainstorm innovative ideas that could gradually lead to monetisation opportunities while also benefitting the environment.
The inaugural day of the conference also marked the unveiling of the abstract book compiled by the department. Dr Javed Ahmad Dar, Assistant Professor and organising secretary of the conference, mentioned that the book consists of a total of 271 abstracts across 15 thematic areas. The event concluded with the Vice Chancellor and the Advisor honouring the guests with a token of appreciation.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News
ESE 2024: Promoting Environmental Sustainability Through Innovation
 In a remarkable display of commitment towards environmental sustainability, the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering successfully organised the ESE 2024 event. The primary objective of this event was to create awareness and encourage innovative solutions for addressing environmental challenges.
In a remarkable display of commitment towards environmental sustainability, the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering successfully organised the ESE 2024 event. The primary objective of this event was to create awareness and encourage innovative solutions for addressing environmental challenges.
More than 150 enthusiastic undergraduate students from Gujarat, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Odisha and Tamil Nadu participated in the event. Their active involvement exemplified the youth’s growing interest and concern for environmental issues.
After a highly competitive and captivating competition, the winners were finally announced. The first prize was awarded to Andhra Loyola College, the second prize went to Natubhai V. Patel College of Pure Applied Sciences, and the third prize was claimed by Government Autonomous College, Rourkela.
The winners were not only recognised for their outstanding performances but also received substantial cash prizes. The first-place winner was awarded a cash prize of INR 30,000/-, the second-place winner received INR 20,000/-, and the third-place winner was granted INR 10,000/-.
Additionally, consolation prizes of INR 5,000/- each were distributed to students securing positions from 4th to 10th. Recipients included students from Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Doon Business School, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Central University of Tamil Nadu, Sri Durga Malleswara Siddhartha Mahila Kalasala, Nehru Arts and Science College, and SRR & CVR Govt. Degree College.
The ESE 2024 event served as a platform for young minds to showcase their talents and exchange ideas, engage in meaningful discussions, and collaborate on initiatives aimed at promoting environmental sustainability. The exhibition featured a diverse range of projects spanning areas such as renewable energy, waste management, conservation efforts, and sustainable agriculture, among others.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News
Rethinking Ionic Liquids as an Environment-friendly Solvent

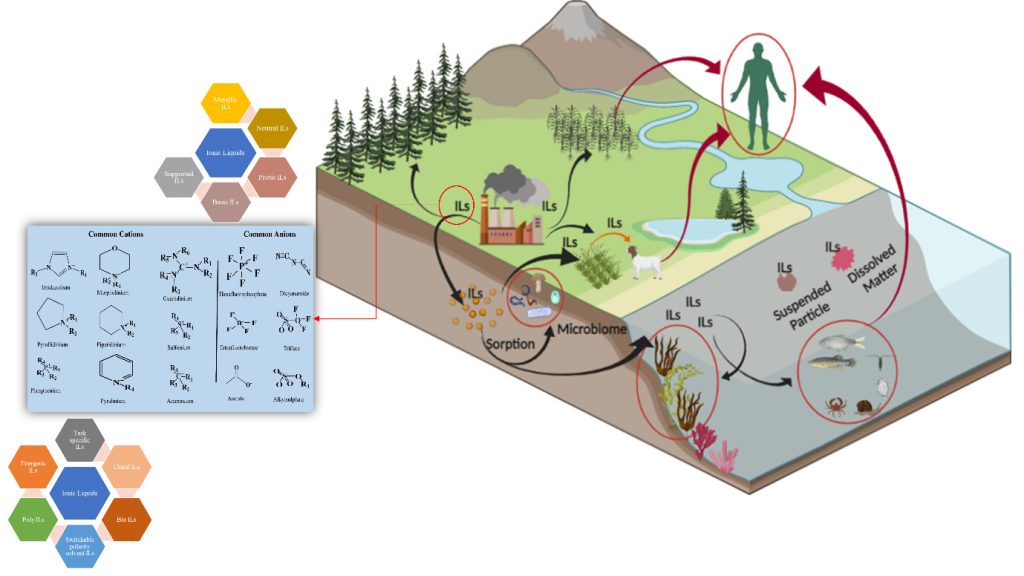
Dr Debajyoti Kundu and Dr Deblina Dutta, Assistant Professors, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, have conducted seminal research on Ionic Liquids (ILs) in their paper “Advances in ionic liquids: Synthesis, environmental remediation and reusability” published in the Q1 journal, Journal of Molecular Liquids with an impact factor of 6. In the research article, the faculty duo have delved into the unique properties of ionic liquids, focusing on their role in environmental cleanup and showcasing their ability to combat pollutants. Various methods to recycle and reuse ILs, develop eco-friendly ILs, and scale up their application for effective environmental remediation have also been extensively explored.
Abstract
Ionic liquids (ILs) are next-generation solvents synthesised by organic salts, possessing negligible vapour pressure and low flammability. They possess high thermal and electrochemical stability, can be reused for multiple cycles, and their properties can be tuned according to the components used in their synthesis. Hence, ILs are considered to be potential alternatives for conventional organic solvents for numerous applications such as environmental remediation, nanoparticle synthesis, catalysts in various chemical reactions, solvents for the extraction of biomolecules from recalcitrant lignocellulosic biomass, etc. In this review article, the holistic approach of ILs, starting from various techniques adopted for their synthesis along with its critical review, is discussed, followed by a detailed discussion of the mechanism involved in the remediation of environmental pollutants using ILs. Further, in-depth documentation of various environmental pollutants remediated using ILs has been done to date. One of the major drawbacks of solvent application is the reusability factor, and hence, in this review article, techniques adopted to recycle/reuse ILs have been discussed. Further, the adverse effects of using ILs for environmental remediation have been comprehensively discussed to present a holistic view. Future studies should focus on synthesising environment-friendly ILs and their field-scale applications for environmental remediation.
Practical implementation/social implications of the research
Their research on Ionic Liquids (ILs) presents a transformative approach to environmental challenges. By applying ILs on a larger scale for cleaning polluted air and water, promoting recycling and reusability, and developing eco-friendly ILs, the work has direct implications for industries and communities. The adoption of IL-based technologies contributes to efficient environmental cleanup and aligns with the growing societal demand for sustainable practices. Successful field-scale applications and public awareness initiatives can lead to a cleaner and healthier environment, demonstrating the tangible benefits of incorporating ILs into real-world solutions and fostering a more responsible and eco-conscious society.
Collaborations:-
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela
- ICAR-National Research Centre on Litchi
- National Institute of Technology Durgapur
- CSIR-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute
- Nguyen Tat Thanh University
Dr Kundu and Dr Dutta remarks that their future research in the realm of Ionic Liquids (ILs) will prioritise the development of environmentally sustainable synthesis methods, rigorous assessments of biodegradability and toxicity, and integrating ILs into industrial processes. Scaling up studies to evaluate their effectiveness in large-scale environmental remediation, investigating public perceptions, and fostering multidisciplinary collaborations with experts from diverse fields will be crucial for the responsible adoption of IL-based technologies. Additionally, focusing on life cycle assessments, exploration of novel applications, policy recommendations, and educational outreach can collectively contribute to advancing the understanding and practical implementation of ILs, ensuring a holistic and impactful approach to their environmental applications.
Click to read the article!
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Exploring Potential Collaboration with SUNY ESF

Prof. Bandaru Ramarao, who currently serves as the Chair of Chemical Engineering at SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry, visited SRM University-AP to explore potential collaborations between the two prestigious institutions.
During his visit, Prof. Ramarao conducted an engaging session with the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora; Director of International Relations and Higher Studies (IR&HS), Ms Aditi Jain; and senior members of the faculty where they discussed various opportunities for collaboration, including the possibility of establishing an association for Masters and Ph.D. students, faculty and student exchange programmes, and scholarship collaborations for faculty members. Dr Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Associate Dean in-charge of Sciences, proposed that the varsity could opt for a co-guide system between SUNY ESF and SRM AP.
Prof. Ramarao also delivered a seminar focused on “Techniques for Analysis of Transport Processes in Fibrous and Porous Media,” which was attended by enthusiastic masters and research scholars from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering. The session was highly informative and provided valuable insights into the techniques used for analysing transport processes in fibrous and porous media. The event concluded with an interactive Q&A session. A token of appreciation was presented to Prof. Ramarao, culminating the visit into a huge success and paving the way for fruitful collaborations between the two institutions in the future.
Predicting Biogas Production Using Time Series Algorithms
With the advent of the climate crisis, the use of the latest scientific technologies to develop methods for sustainable energy usage is pivotal. Dr Karthik Rajendran, Associate Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, his PhD scholar Mr Prabakaran G & UG Student Mr Nalluri Rishi Chaitanya Sri Prasad have filed and published a patent titled “A System and a Method for Building a Forecasting Model for Biogas Production” with Application No.: 202341074196, on their radical invention of predicting future biogas production using advanced Machine Learning techniques.
Abstract
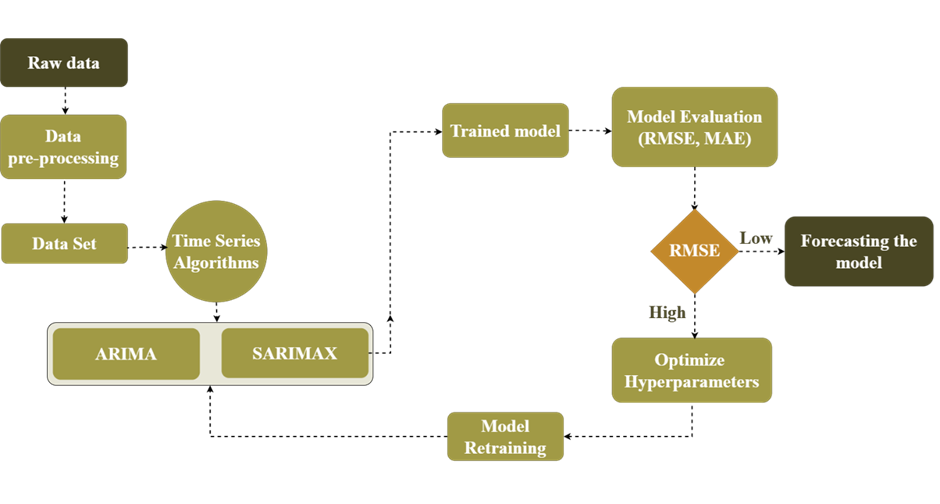
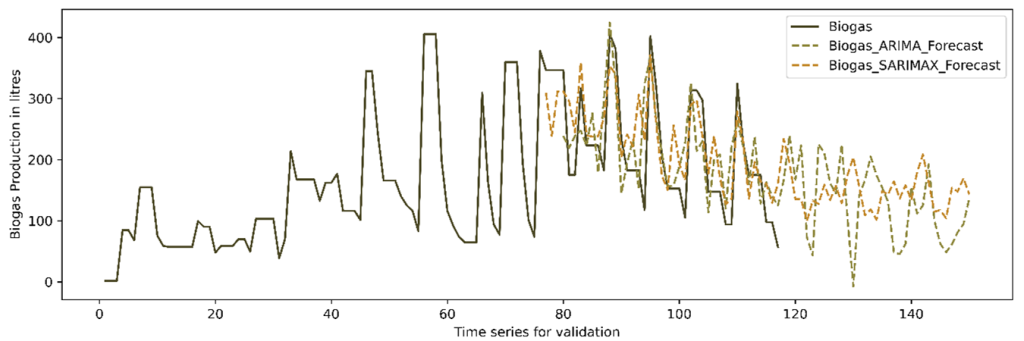
The anaerobic digestion (AD) process poses challenges in maintaining process stability and time series-based prediction and forecasting due to the intricate nature of the system. Process instability is a consequence of the unpredictability in the raw material received at the facility, as well as temperature fluctuations and pH changes resulting from microbiological processes. Consequently, it is necessary to implement constant monitoring and control measures for higher biogas production. The challenges associated with anaerobic digestion (AD) systems can be effectively addressed through the integration of advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms and industry 4.0 systems within biogas facilities. This integration holds the potential to enhance system efficiency and enable on-site control capabilities. Machine learning (ML) based solutions have the potential to enhance process performance in AD facilities, leading to improved system operation and maintenance. The present study focuses on advanced ML techniques, specifically time series algorithms (ARIMA and SARIMAX), which have been employed to forecast daily biogas production. These algorithms are trained to discern critical process parameters and forecast daily biogas production rates, measured in Liters. For forecasting, 117 days of experimental data were used and ARIMA was identified as the best algorithm to forecast the daily production. This algorithm excelled not only in predicting biogas production but also in forecasting yield, resulting in a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 3.26. Furthermore, a comparison between the forecasted values of both ARIMA and SARIMAX was conducted. The predictive ARIMA model underwent statistical validation with unknown data, resulting in a P-value is >0.05.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This paper focuses on predicting future biogas production using advanced mathematical methods. The researchers used data collected over 117 days of biogas experiments, divided into three periods. They kept track of important factors like methane production, consumed volatile solids, methane percentage in biogas, and initial and final pH levels. To make the predictions more accurate, the researchers addressed missing data and fine-tuned certain parameters using a process called hyperparameter tuning. They wanted to find the best settings for the mathematical models they used, which are called ARIMA and SARIMAX. These models consider patterns and relationships in the data to make predictions. The researchers checked their models’ using measures like AIC and BIC values and examined certain plots to ensure they were getting good results. After applying the models to the data, they were able to predict future biogas production. The accuracy of their predictions was assessed using a metric called RMSE, and they found values of 3.26 for ARIMA and 24.02 for SARIMAX. In simpler terms, these values help us understand how close their predictions were to the actual values. The researchers also did some statistical analysis, and the results showed that both methods (ARIMA and SARIMAX) were equally good at predicting biogas production. Therefore, they concluded that these mathematical models are reliable tools for forecasting biogas production in the future.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The integration of advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms and Industry 4.0 systems within anaerobic digestion (AD) facilities holds significant promise in addressing the challenges associated with process instability and unpredictability in biogas production. The utilization of ML techniques, particularly time series algorithms like ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) and SARIMAX (Seasonal AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average with eXogenous factors), to forecast daily biogas production presents a practical solution to enhance system efficiency and control.
- Real-time Decision Making
- Reduced Operational Costs
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
AESEE 2024 Receives Grants from the Ministry of Jal Shakti

The Department of Environmental Science and Engineering is thrilled to share the exciting news regarding its upcoming 1st International Conference on Advances in Environmental Sustainability, Energy, and Earth Science (AESEE 2024). The Department of Water Resources, River Development, & Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR), the Ministry of Jal Shakti, have generously sanctioned Rs. 5 lakhs to support this groundbreaking event.
The International Conference scheduled to take place from March 14 – 16, 2024 aims to explore innovative advancements in science and technology while promoting inclusive growth across various sectors. This collaborative approach between environmentalists and the academic community will ensure a sustainable future.
The financial grant sanctioned in this regard underscores the importance of AESEE 2024 and highlights the commitment of the Department to advancing knowledge in the field. AESEE 2024 promises to facilitate meaningful discussions, bringing together diverse stakeholders to contribute to a more sustainable and interconnected future.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News















