SLP-E: Enhancing Privacy and Lifespan in WSNs for IoT
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is thrilled to share that the paper titled, “A Total Randomized SLP Preserving Technique with Improved Privacy and Lifetime in WSNs for IoT and the Impact of Radio Range on SLP” has been published by Dr Manjula R, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, and BTech-CSE Student Mr Tejodbhav Koduru in “Sensors“, a Q2 journal, having an Impact Factor of 3.9. Their research addresses the critical need for improved source location privacy and extended network longevity, presenting a pioneering solution known as Source Location Privacy with Enhanced Privacy and Network Lifetime (SLP-E).
Abstract
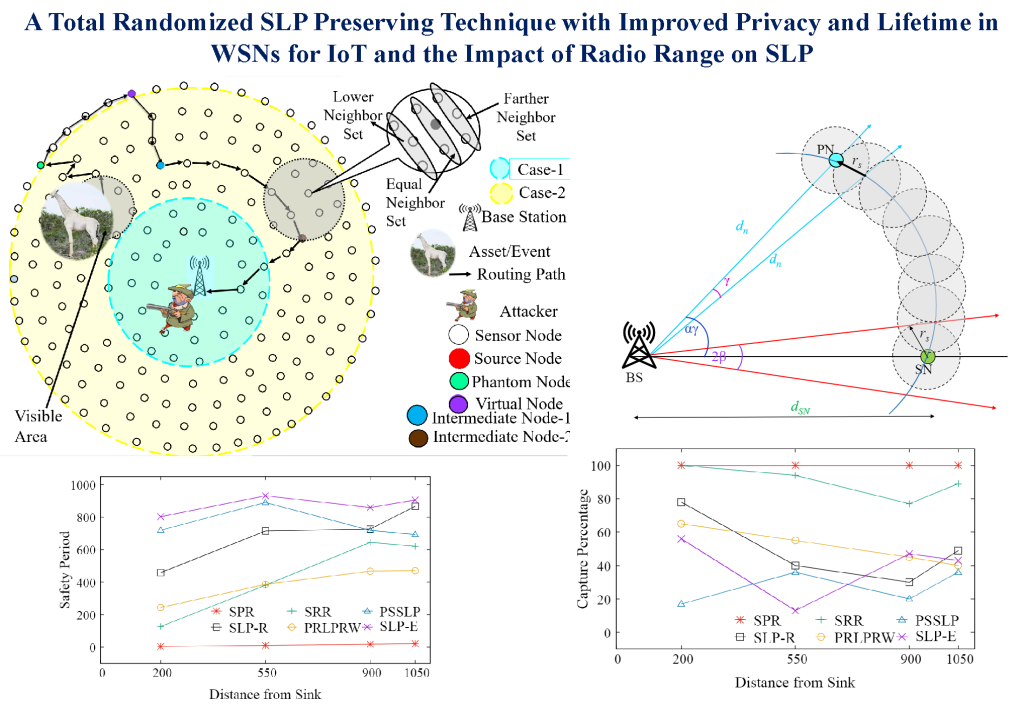
SLP-E utilises a unique combination of techniques, including a reverse random walk, a walk on annular rings, and min-hop routing, to diversify routing pathways within the network. Unlike existing SLP techniques that either prioritize privacy over network lifetime or vice versa, this approach aims to simultaneously enhance safety period, network lifetime, and privacy uniformly. Notably, this research also explores the impact of sensor radio range on Network Lifetime metrics and privacy strength within the context of SLP in WSN.
Practical Implementation/Social Implications of the research
This research holds real-world significance, especially in scenarios like protecting a lone white giraffe in Kenya fitted with a GPS tracker. Poachers pose a serious threat to such animals, hacking GPS devices to locate and harm them. This solution offers a viable approach to mitigate these threats, providing practical implications for the conservation of endangered species.
Collaborations
- Mr Tejodbhav Koduru from SRM University-AP
- Prof. Raja Datta from IIT Kharagpur
- Ms Florence Mukamanzi, Dr Damien Hanyurwimfura and Prof. Mukanyiligira Didacienne from the African Center of Excellence in the Internet of Things, University of Rwanda
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Teacher-Student Duo Author a Chapter on Graph Neural Networks

Dr Ravi Kant Kumar, Assistant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at SRM University-AP and his research scholar, Ms Gayathri Dhara have recently made a significant contribution to the field of Graph Neural Networks. The teacher-student duo have offered relevant analysis of visual saliency applications using Graph Neural Networks (GNN) in their book chapter titled “Study and Analysis of Visual Saliency Applications Using Graph Neural Networks” in the book, Concepts and Techniques of Graph Neural Networks. The topic of their study will prove to be a key source of reference for industry professionals, researchers, scholars, academicians, practitioners, instructors, and students.
Description and Significance of the Chapter
The chapter covers the practical applications of GNN in the field of visual saliency. Various applications of computer vision problems implemented using graph neural networks (GNNs) have been studied and analysed in this chapter. It also includes the design approach of GNN, the various computational models used in GNN, its challenges and recommendations. The social significance of GNN in visual saliency extends to various domains like Human attention modelling, Advertising and marketing, Visual content understanding, and so on.
Significance of GNNs
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have gained significance in the field of visual saliency due to their ability to model complex relationships and dependencies within visual data. Visual saliency refers to the process of predicting the most visually prominent regions or areas in an image or video that attract human attention. It plays a crucial role in various computer vision applications, such as image understanding, object recognition, and scene understanding. GNNs can learn spatial dependencies and feature representations from visual data. There are many methodologies that address the detection of the salient object using GNN. GNNs can handle multi-modal data, combining visual information with other modalities such as textual or semantic features. This integration allows GNNs to leverage additional cues and contextual information to improve visual saliency prediction. So, studying these different salient object detection methods using GNN and knowing the challenges of GNN will help in meeting our research objectives.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Young minds excelled at national level Hackathon
Amidst the quarantine, students of SRM AP and members of NEXT TECH LAB, have exhibited their expertise in HACKNITR, a national level hackathon organized by NIT Rourkela on 21-22 March 2020. The outstanding merit of their project has enabled them to bag the Runner-Up and 2nd Runner-Up position at the hackathon.
 Team ASTUTE BOTS consulting
Team ASTUTE BOTS consulting
Team ASTUTE BOTS, comprising of 1st-year students, Tankala Yuvaraj, Karthikay Gundepudi and Joseph K. Paul, was recognized as the Runner-Up. They used the AI-IoT platform to develop DRONEYES; a prototyped solution that can be used to reduce poaching. It is an aerial reconnoiter which flies in stealth mode and takes the video or photo of a suspected poacher. This is done by the highly trained object detection model called YOLOv3. These eyes not only detect objects on the terra firma but also sends the exact location via GPS. “With the help of cloud technology, we can share the data in real-time so that the user/organization can take the required initiative by locating the exact place of poaching”, explains Karthikay. We were inspired to attend hackathons by Anshuman Pandey, and Next Tech Lab supported this achievement.
Another team PUSH, where Karthik Epperla, 2nd year, and Ishita Agarwal, 1st year, participated, has received the 2nd Runner’s up award. The students worked on an AI-VR-Blockchain based application to help people with autism improve communication, social and other basic abilities required to live in a society. It gives a set of YES/NO questions that are to be answered by either the parent of the child or the adult suffering from Autism and then it matches those answers with the dataset which then returns the level of autism that the child/adult is suffering from. Depending on the level, the user can choose the extremity of VR therapy. When the child goes through the VR session, the parent can view what their child/ adult is doing in the virtual environment using the parent app from anywhere and advise their ward offering extra support to the patient. ” Our application has 3D simulations of real-life situations wherein autistic children/ adults (mostly children) can practice and understand how to behave/react in those situations and overcome their fear while facing a similar situation in real life. “, adds Karthik.
Karthik acknowledges Adithya Ramakrishnan the founder of Next Tech Lab and his lab mate, Lakshmi Vallala for implanting the noble idea that AI can help in the rare medical condition, Autism. They have constantly been in touch with a few special schools and treatment centers to know about the behaviour and nature of autistic people so that they can keep on building different versions of applications.
In the natal stage of their academic career, the students are guided and nurtured in an environment by the Next Tech Lab and the faculty members which inspires them to positively impact the society. The ample exposure offered to the students will not merely encourage them, but also enable them to improve their concepts.
Next-Tech Lab Scaling New Heights: Won Three Hackathons in a Row
The unstoppable team of Next-Tech Lab of SRM University- AP, has again brought laurels to the University by winning three hackathons in a row. During this lockdown while some devoted their time to newfound hobbies, our young researchers successfully developed a fresh multiplayer virtual reality game – ‘Whack A Mole’ and a cloud-based multiplayer FPS in Virtual Reality- ‘Desert Shooter’. The three-member team has successfully bagged the second prize in the International / Professional Award at SKYHacks2020; Best echoAR Hack at Silicon Valley Hacks; and Best AR/VR hack at HackNow, organized by Cal Hacks, a non-profit organization at the University of Berkeley, California.

Karthik, Koushik & Khushboo (Clockwise)
When asked how the idea of making such a game crossed their minds, Epperla Karthik, a 2nd Year student of Computer science and Engineering and a member of the team, said, “My family loves attending Tradeshows, every time we attend one my dad and I challenge each other to win a game of Whack A Mole. But, due to strict quarantine that my family is following, it’s been a while now for such challenges. My teammates and I, being gaming and virtual reality enthusiasts, decided to develop a VR version of ‘Whack A Mole.’”
‘Whack A Mole’ is a multiplayer virtual reality game that allows users to play against the computer or their families or both! One can use it on iOS or Android. It is built on Unity3D, on top of Photon PUN and GoogleVR SDK. It is also integrated with Google Firebase. “This was the very first time we were working on the development of virtual reality games and networking. As we had to run the game on our phone to record the gameplay, the output video on YouTube is a bit blurry,” explained Khushboo Sharma, another member of the team and a 2nd-year student of Computer Science and Engineering. “We completed the development of the game in only 20hrs, starting from scratch. We developed a few of our own UI elements and game assets. I feel the User-Interface of the app and the effects are pretty cool. VR development is real FUN! Moreover, there are a lot of API and SDK that unity supports,” exclaimed Koushik Bhargav, a 3rd-Year student of Computer Science and Engineering and the third member of the team.
‘Desert Shooter’ is another multiplayer virtual reality game developed by the team that allows users to play against the computer or their families or both. You can connect with your friends and play together. The game consists of a swarm of robot ships moving towards you and you have to protect yourself from them. “The interesting part is that all of this happens in Mixed Reality which makes the game immersive. We built it on Unity3D, on top of Photon PUN and GoogleVR SDK, Echoar. It is also integrated with Google Firebase and the assets are stored in echoar cloud. This project won the best AR/VR hack at “Hack: Now” which is organized by the University of California Berkeley,” said Epperla Karthik.
The team has plans to make this game to be a cross-platform game. Therefore, their next plan of action is to make the web version of it. The team is also planning to release it to production so that users can have an immersive experience of modern gaming techniques.
It is again proved that pure talent can never be put in quarantine. It will always find a way to express itself to the world. Our young developers have brilliantly used the ample time and opportunity to put their brains in best use and to bring recognitions from nationally and globally acclaimed competitions.
- Published in CSE NEWS, News, Students Achievements
CSE student presented paper on Data Hiding
K. Sree Rama Murthy, Second Year B. Tech-CSE student presented a paper at a conference in IIT-Kharagpur
 K. Sree Rama MurthySRM University-AP always inspires the students in their pursuits, be it a job of their choice or a career in research and higher studies. K. Sree Rama Murthy, a 2nd-year student of B.Tech in Computer Science and Engineering, has recently presented a research paper on “A Block-wise Histogram Shifting based Reversible Data Hiding Scheme with Overflow Handling” in the Eleventh International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (11th ICCCNT), held at IIT Kharagpur, India in association with IEEE Kharagpur Section, during July 1 – 3, 2020.
K. Sree Rama MurthySRM University-AP always inspires the students in their pursuits, be it a job of their choice or a career in research and higher studies. K. Sree Rama Murthy, a 2nd-year student of B.Tech in Computer Science and Engineering, has recently presented a research paper on “A Block-wise Histogram Shifting based Reversible Data Hiding Scheme with Overflow Handling” in the Eleventh International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (11th ICCCNT), held at IIT Kharagpur, India in association with IEEE Kharagpur Section, during July 1 – 3, 2020.
Data hiding is a process of embedding a secret message into a cover medium for secure message transmission. The reversible data hiding techniques are recently explored in the domain of data hiding in which the cover image can be recovered while extracting the hidden secret message. The overview of a reversible data hiding scheme is shown in Figure. 1.
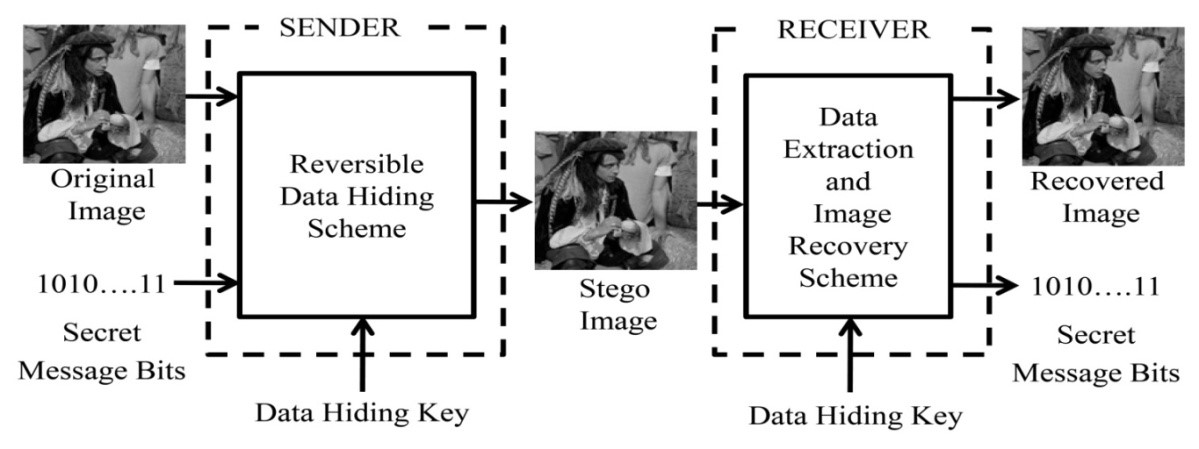 Figure 1. Overview of reversible data hiding
Figure 1. Overview of reversible data hiding
In this research paper, Sree Rama Murthy introduced a new reversible data hiding algorithm based on the histogram of the blocks of the cover images with an efficient overflow management technique to achieve a better embedding rate without compromising the visual quality of the stego image.
Design and development of reversible data hiding schemes are widely studied topic due to its wide scope in cloud computing and medical image transmission. This paper introduces a new reversible data hiding algorithm based on the histogram of the blocks of the cover images with an efficient overflow management technique. In the new scheme, the peak intensity value from each block is used for data hiding, and to make sure the correct recovery of the original image, the grayscale value used for data hiding from each block is embedded in the same block itself by replacing the least significant bits of eight selected pixels. The lossless recovery is ensured by embedding those least significant bits in the same block itself along with the secret message. Detailed theoretical analysis and experimental study of the scheme are carried out and discussed in this paper. The images from the standard image dataset of the University of Southern California (USC-SIPI) are used in their study.
“To be able to publish a research paper at such an early stage in a reputed conference like ICCCNT-2020 is an achievement that has acted as a cornerstone for my research aspirations. I feel highly encouraged, motivated and inspired to contribute more in the fields of research. I express my sincere gratitude to my professors, especially to Dr Manikandan V. M for providing me with the opportunity to collaborate. He put his trust on me, encouraged to do research with him and guided me with his knowledge and experience throughout the journey. I feel this is only the beginning for me, and I will try my best to accomplish more and retain more knowledge,” said Sree Rama Murthy.
Sree Rama Murthy plans to acquire a master’s degree in computer science and aspires to be a researcher who can make significant contributions in the domain of Computer Science and Engineering.
- Published in CSE NEWS, News, Research News
Energy-Aware Task Allocation for Multi-Cloud Networks
Smart algorithm to optimize performance of the heterogeneous multi-cloud network
 Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra
Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra
As the world goes more digital in the future, the dependability on cloud computing is going to be more. The availability of high-capacity networks, low-cost computers and storage devices as well as the widespread adoption of hardware virtualization, service-oriented architecture and autonomic and utility computing has led to growth in cloud computing. But is it enough? How to improve its performance? How to make it more reliable with high-end technology and impeccable performance quality? Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra’s research has an answer to that.
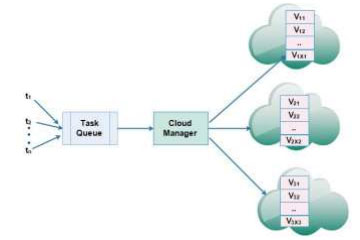 System Model for Multi-cloud Networks Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra, Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering has published a paper “Energy-Aware Task Allocation for Multi-Cloud Networks” in renowned journal IEEE ACCESS with an Impact Factor: 3.745. The research was done in collaboration with Dr Sonali Mishra, SOA (Deemed to be) University Bhubaneswar, India; Dr Ahmed Alsayat, College of Computer and Information Sciences Jouf University, Al-Jouf, Saudi Arabia; Dr N Z Jhanjhi and Dr Mamoona Humayun, School of Computer Science and Engineering (SCE), Taylor’s University, Malaysia; Dr Ashish Kr. Luhach, The PNG University of Technology, Papua New Guinea Lae, Morobe; Dr Kshira Sagar Sahoo, VNRVJIET, Hyderabad, India.
System Model for Multi-cloud Networks Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra, Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering has published a paper “Energy-Aware Task Allocation for Multi-Cloud Networks” in renowned journal IEEE ACCESS with an Impact Factor: 3.745. The research was done in collaboration with Dr Sonali Mishra, SOA (Deemed to be) University Bhubaneswar, India; Dr Ahmed Alsayat, College of Computer and Information Sciences Jouf University, Al-Jouf, Saudi Arabia; Dr N Z Jhanjhi and Dr Mamoona Humayun, School of Computer Science and Engineering (SCE), Taylor’s University, Malaysia; Dr Ashish Kr. Luhach, The PNG University of Technology, Papua New Guinea Lae, Morobe; Dr Kshira Sagar Sahoo, VNRVJIET, Hyderabad, India.
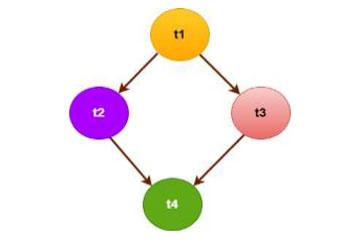 Example of Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG)with four TasksIn recent years, the growth rate of Cloud computing technology is exponentially, mainly for its extraordinary services with expanding computation power, the possibility of massive storage and all other services with the maintained quality of services (QoS). The task allocation is one of the best solutions to improve different performance parameters in the cloud, but when multiple heterogeneous clouds come into the picture, the allocation problem becomes more challenging. This research work proposed a resource-based task allocation algorithm. The same is implemented and analysed to understand the improved performance of the heterogeneous multi-cloud network. The proposed task allocation algorithm (Energy-aware Task Allocation in Multi-Cloud Networks (ETAMCN)) minimizes the overall energy consumption and also reduces the makespan. The results show that the makespan is approximately overlapped for different tasks and does not show a significant difference. However, the average energy consumption improved through ETAMCN is approximately 14%, 6.3%, and 2.8% in opposed to the random allocation algorithm, Cloud Z-Score Normalization (CZSN) algorithm, and multi-objective scheduling algorithm with Fuzzy resource utilization (FR-MOS), respectively. An observation of the average SLA-violation of ETAMCN for different scenarios is performed.
Example of Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG)with four TasksIn recent years, the growth rate of Cloud computing technology is exponentially, mainly for its extraordinary services with expanding computation power, the possibility of massive storage and all other services with the maintained quality of services (QoS). The task allocation is one of the best solutions to improve different performance parameters in the cloud, but when multiple heterogeneous clouds come into the picture, the allocation problem becomes more challenging. This research work proposed a resource-based task allocation algorithm. The same is implemented and analysed to understand the improved performance of the heterogeneous multi-cloud network. The proposed task allocation algorithm (Energy-aware Task Allocation in Multi-Cloud Networks (ETAMCN)) minimizes the overall energy consumption and also reduces the makespan. The results show that the makespan is approximately overlapped for different tasks and does not show a significant difference. However, the average energy consumption improved through ETAMCN is approximately 14%, 6.3%, and 2.8% in opposed to the random allocation algorithm, Cloud Z-Score Normalization (CZSN) algorithm, and multi-objective scheduling algorithm with Fuzzy resource utilization (FR-MOS), respectively. An observation of the average SLA-violation of ETAMCN for different scenarios is performed.
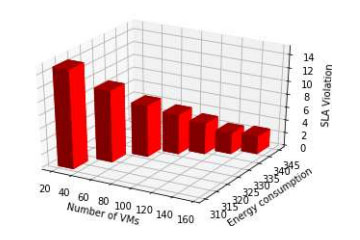 Energy Consumption Vs SLA Violation when
Energy Consumption Vs SLA Violation when
the number of VMs varies and the number of Task is 100.The multi-cloud strategy offers flexibility to service providers. It allows businesses to be productive while using the proper set of services to optimize their opportunities. Adopting a multi-cloud network enables an enterprise to implement a “best of breed” model for the services. Organizations’ ability to choose the vendor that offers the best price for their workload is added significant advantage of multi-cloud. Thus, the optimization of energy consumption in a multi-cloud environment is necessary for the current generation.
However, this proposed work has not considered any priority-oriented users, such as task execution through reserve resource in the network, which will be considered as his future work. The future work also aims to propose a task cum resource-aware scheduling approach that will exploit the nature of the presented workload and efficiently map on the available Cloud resources so that energy consumption will optimize.
Link to the research paper: Please Click Here
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Undergrad student receives envious internship offer from Adobe India with 1 LPM
 Khushboo Sharma is one of the brightest gems in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. She is currently pursuing her third year in undergraduate studies. She has recently bagged an envious summer internship offer at one of the most reputed companies- Adobe India, a multinational software company. Through their women-only hiring challenge “SheCodes”, Khushboo not only bagged an internship offer but she may also have an opportunity of a Pre Placement Offer, upon successful review after this internship with attractive pay package. She will be joining Adobe India in May 2021 for the internship of 10-12 weeks with a stipend of 1 lakh rupees per month.
Khushboo Sharma is one of the brightest gems in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. She is currently pursuing her third year in undergraduate studies. She has recently bagged an envious summer internship offer at one of the most reputed companies- Adobe India, a multinational software company. Through their women-only hiring challenge “SheCodes”, Khushboo not only bagged an internship offer but she may also have an opportunity of a Pre Placement Offer, upon successful review after this internship with attractive pay package. She will be joining Adobe India in May 2021 for the internship of 10-12 weeks with a stipend of 1 lakh rupees per month.
Mr Vivekanandan, Assistant General Manager, Department of Corporate Relations and Career Services (CR&CS), says “It is a proud moment for the university. SRM University-AP is full of bright students with huge potential. It is our sincere responsibility to bring out the best in them and help them find the right place in the industry.” Khusboo asserted that the training process in the Department of CR&CS was rigorous. Be it attitude development or interview preparations, the CR&CS department has extended continuous guidance and support along with mock sessions. Mr Vivekanandan further informed that the training programmes of SRM University-AP are designed by the experts to make students prepare for every challenge that they might face in a competitive world. They even organise some training sessions that are company-specific. Needless to say, that the placement department is not ready to leave any stone unturned when it comes to the future of its students. The placement team thoroughly guided Khushboo in the four-month-long hiring process in Adobe.
Khushboo expressed her gratitude, saying that it would not have been possible for her to crack this challenge without the continuous guidance and support provided by her teachers and the placement team. The modernised industry-oriented curriculum helped her gain the necessary in-depth knowledge to excel in her studies. Khushboo is also a part of tech-based clubs of SRM university-AP and always strives to think something out of the box. Her zeal towards scaling new heights and perseverance her made her achieve this offer.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements
Young researcher presents research paper amidst scholars at global conference – ICCCS 2020
Nikhila Korivi offers revolutionary approach to ensure Data Security
 Nikhila Korivi, third year, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University- AP, Andhra Pradesh was steered by Dr Manikandan V M, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, to present the pioneering research paper “Reversible Data hiding in encrypted images using checkerboard based pixel inversion” in the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS-2020), IIT Patna, held on October 14-16, 2020.
Nikhila Korivi, third year, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University- AP, Andhra Pradesh was steered by Dr Manikandan V M, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, to present the pioneering research paper “Reversible Data hiding in encrypted images using checkerboard based pixel inversion” in the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS-2020), IIT Patna, held on October 14-16, 2020.
Nikhila and her mentor, Dr Manikandan V M, worked on the paper conjointly for which, she is profoundly grateful to the professor. She says, “I thank Dr Manikandan and my other professors at SRM University-AP for their continuedguidance that inspired me to do research. Their encouragement propelled me to successfully present the research paper at ICCCS-2020, a conference revered by the entire scientific community.”
Nikhila has been keen on exploring and broadening her horizon of knowledge. Right from her early undergraduate days, Nikhila was intrigued by Information Security, an emerging discipline in the modern era. Soon she recognized that Reversible Data Hiding is an active research area in the realm of Information Security, which has extensive application in Medical Image Transmission, and Cloud Computing.
On approaching her professor, Dr Manikandan enthused Nikhila to embark on the research work and propose a new Reversible Data Hiding scheme in encrypted images by using a checkerboard pattern-based pixel inversion technique. Nikhila informs, “The proposed scheme ensures a better bit error rate without compromising on the embedding rate. The algorithms were implemented using Matlab-2019 and the experimental studies of the proposed scheme have been carried out using a standard image dataset (USC-SIPI) managed by the University of Southern California.”
This revolutionary approach is immensely beneficial when it comes to Data Security, and it is widely implemented in medical image transmission along with many other sectors. Fostering her interest in pursuing research and advanced studies, Nikhila plans to enhance her research work by focusing on designing and developing new Reversible Data Hiding schemes with better embedding rates without compromising other efficiency parameters such as computational complexity, robustness, and bit error rate.
- Published in CSE NEWS, News, Research News
Undergrad CSE student bags envious placement offer with a CTC of 20 Lakh LPA
 Another proud moment for SRM University-AP when Kattamuri Sai Krishna Rohith bagged an envious job offer from ODCEM Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (OneDirect) with a CTC of 20 Lakhs per annum. He is pursuing his B. Tech final year in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering.
Another proud moment for SRM University-AP when Kattamuri Sai Krishna Rohith bagged an envious job offer from ODCEM Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (OneDirect) with a CTC of 20 Lakhs per annum. He is pursuing his B. Tech final year in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering.
Mr Rohith will be joining the company as an intern for six months with monthly compensation of Rs. 20,000. After six months of internship, he will be offered the permanent employee as a Full Stack Developer with a CTC of Rs. 20,00,000 per annum.
Mr Rohith went through rigorous placement training programmes conducted by the Department of Corporate Relations and Career Services to secure the job offer. The job hiring process for this role was conducted in four stages. After preliminary selection, Mr Rohith had to prove his ability in coding, aptitude and other technical domains. The Director of Engineering himself took the final call before offering him a position in the company to see if Rohith is a proper fit for their company.
Rohith expressed his gratitude towards the CR & CS department of SRM University-AP, saying that the training sessions strengthened his core skills and abilities. He was also taught to face interviews and critical questions. Mr Rohith said, “Placement is an arduous process. I was offered another position in other company before, but I was not happy with that offer. I had faith in my abilities, so I continued searching for better opportunities and improve my skill set to secure the Super Dream offer. Keeping nerves in control, not panicking during interviews, excellent communication skills are some essential qualities that everyone should master to get good jobs. I am thankful to the CR & CS department for all their support and customised, personal, need-based assistance, which helped me a lot to prepare for the interviews,” said Mr Rohith.
After five months of determination, Mr Rohith finally secured the job that he was looking for. “The University has provided us with numerous opportunities with a flexible curriculum and Global standards. In addition to all the training, my mentors encouraged me to participate in Hackathons, apply for research internships, and attend conferences. Thanks to the extraordinary faculty that we have, the regular classes were of great help in enhancing my technical knowledge,” asserted Mr Rohith. Mr Rohith was a proud track-winner of Microsoft and EthDenver hackathons and a research Intern at Nanyang Technological University (NTU) Singapore.
He has shared his mantra to success with his fellows. Mr Rohith believes that instead of panicking or comparing with others, one should focus on becoming a better version of oneself, and the success will find him.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, CSE NEWS, News
Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash devices technique for easy detection of Interstitial Lung Diseases
 Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Associate Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a paper, “Content-based image retrieval system for HRCT lung images: Assisting radiologists in self-learning and diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases” in the reputed Springer Journal- Multimedia Tools and Applications. The research has been carried out in collaboration with Prof. Sudipta Mukhopadhyay, IIT Kharagpur and Professor & Head, Department of RADIO DIAGNOSIS & IMAGING, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh.
Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Associate Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a paper, “Content-based image retrieval system for HRCT lung images: Assisting radiologists in self-learning and diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases” in the reputed Springer Journal- Multimedia Tools and Applications. The research has been carried out in collaboration with Prof. Sudipta Mukhopadhyay, IIT Kharagpur and Professor & Head, Department of RADIO DIAGNOSIS & IMAGING, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh.
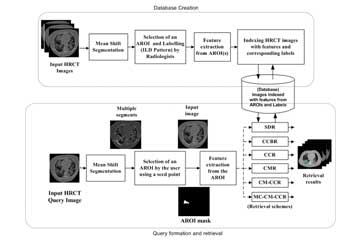 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) is a technique that can exploit the wealth of the data stored in the repository and help radiologists in decision making by providing references to the image in hand. A CBIR system for High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) lung images depicting the sign of Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs) is built, and the system can be used as a self-learning tool by budding radiologists. The system is built by addressing several challenges using advanced machine learning techniques. The objective of this work is to develop a CBIR system for ILDs that is reliable and needs minimal human intervention for ling disease diagnosis.
Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) is a technique that can exploit the wealth of the data stored in the repository and help radiologists in decision making by providing references to the image in hand. A CBIR system for High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) lung images depicting the sign of Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs) is built, and the system can be used as a self-learning tool by budding radiologists. The system is built by addressing several challenges using advanced machine learning techniques. The objective of this work is to develop a CBIR system for ILDs that is reliable and needs minimal human intervention for ling disease diagnosis.
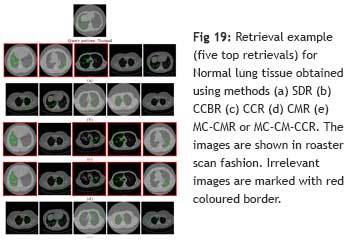 The system developed will act as a helping tool for radiologist by providing a second opinion for the diagnosis of a diverse group of lung diseases called Interstitial Lung Disease. It will help the budding radiologist for self-learning. When used in daily medical practice, the system may reduce the workload of radiologists in countries, having a low number of physicians per inhabitants.
The system developed will act as a helping tool for radiologist by providing a second opinion for the diagnosis of a diverse group of lung diseases called Interstitial Lung Disease. It will help the budding radiologist for self-learning. When used in daily medical practice, the system may reduce the workload of radiologists in countries, having a low number of physicians per inhabitants.
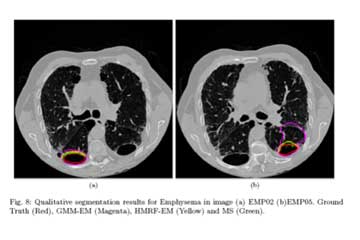 Dr Dash is associated with SRM University-AP for almost three years. His research interests include Content-Based Image Retrieval, Medical Image Analysis and Texture Analysis. He has currently employed his time into the design and development of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Lung Cancer Screening.
Dr Dash is associated with SRM University-AP for almost three years. His research interests include Content-Based Image Retrieval, Medical Image Analysis and Texture Analysis. He has currently employed his time into the design and development of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Lung Cancer Screening.
Read More: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11042-020-10173-4
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News


