Breakthrough in Autism Detection: A New System Patent by CSE Researchers
 In a significant advancement for neurodevelopmental research, Dr Nitul Dutta, Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD scholar Ms Surya Samantha Beri and BTech student Mr Nallamothu Sai Karthik, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “A System for Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection.” The application, numbered 202441053505, has been officially documented in the Patent Office Journal.
In a significant advancement for neurodevelopmental research, Dr Nitul Dutta, Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD scholar Ms Surya Samantha Beri and BTech student Mr Nallamothu Sai Karthik, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “A System for Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection.” The application, numbered 202441053505, has been officially documented in the Patent Office Journal.
The innovative system aims to enhance the early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), providing a more efficient and accessible method for diagnosis. By integrating advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, the system promises to analyse behavioural data effectively, allowing for timely interventions and support for individuals on the spectrum. Dr Dutta emphasised the importance of early detection, stating, “The earlier we can identify ASD, the better the outcomes for individuals and their families. Our system is designed to make this process more accurate and user-friendly.”
Ms Beri and Mr Karthik contributed significantly to the research, which reflects a collaborative effort between academia and technology. Their work not only demonstrates the potential for technological solutions in healthcare but also highlights the critical role of interdisciplinary approaches in addressing complex challenges.
This patent represents a crucial step forward in the field of autism research and is expected to pave the way for further innovations aimed at improving the lives of those affected by ASD.
Abstract of the Research
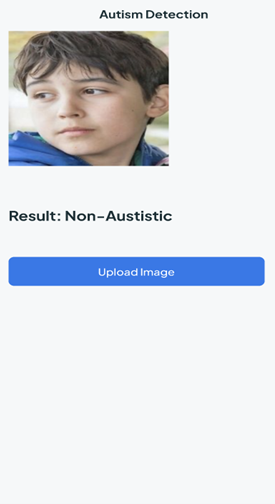
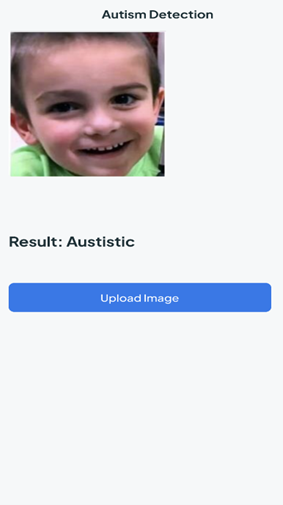
The system for autism spectrum disease detection incorporates a server with a hybrid application comprising several key modules: a capturing module receiving images from image-capturing devices , a data collection module gathering a dataset of images from multiple capturing devices, and a pre-processing module standardising and normalising images to generate a standardised dataset. Additionally, a feature extraction module collaborates with the pre-processing module to identify autism-indicative features in standardised images, preparing labelled standardised images stored in the data collection module.
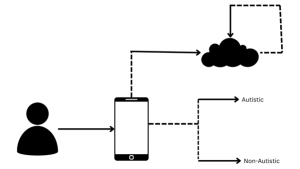
Furthermore, a data segmentation module segments standardised images into training and testing data, including a training module for real-time training of a convolutional neural network model and a testing module to evaluate the convolutional neural network model’s accuracy in detecting autism based on testing data.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
The background information herein below relates to the present disclosure but is not necessarily prior art. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurological or developmental disorder that profoundly impacts communication skills, social interaction, and cognitive abilities in individuals. Those with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often exhibit challenges in social interaction, limited eye contact, difficulty understanding social cues, and impaired language skills. Additionally, repetitive behaviours and sensory sensitivities are common characteristics.
The disorder arises from developmental changes in brain structure and can have various causes, including genetic factors, familial history of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), advanced parental age, or low birth weight. The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), stands at one in every 160 children. Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) effectively, as interventions such as medical and neurological examinations, cognitive and language assessments, and frequent observations, including blood and hearing tests, can significantly improve outcomes. Detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children below the age of 10 is comparatively easier than in adults, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis to facilitate timely interventions.
Current diagnostic processes for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often present significant challenges, particularly for young children, due to their limited ability to communicate and cooperate during assessments. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on structured interviews, behavioural observations, and standardised tests, which can be daunting and stressful for children, leading to inaccurate results. Moreover, these procedures are time-consuming and often require multiple visits to specialised clinics or healthcare facilities, causing inconvenience and financial strain for families. Also, the cost associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis can be prohibitive for many families.
Therefore, there is a pressing need for more accessible, less intrusive, and cost-effective methods for detecting autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in its early stages to ensure timely and effective intervention. Therefore, there is a need for a system for autism spectrum disorder detection that alleviates the drawbacks.
Practical and Social Implications Associated with the Research
Current diagnostic procedures for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face considerable technical challenges, particularly concerning young children’s limited ability to engage in conventional assessment methods. These methods typically rely on structured interviews, behavioural observations, and standardised tests, all of which can be arduous and distressing for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), potentially leading to unreliable outcomes. Furthermore, these procedures are resource-intensive, requiring multiple visits to specialised clinics or healthcare facilities, thereby causing logistical challenges and financial burdens for families. Current diagnostic processes for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often present significant challenges, particularly for young children, due to their limited ability to communicate and cooperate during assessments. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on structured interviews, behavioural observations, and standardised tests, which can be daunting and stressful for children, leading to inaccurate results. Moreover, these procedures are time-consuming and often require multiple visits to specialised clinics or healthcare facilities, causing inconvenience and financial strain for families. Also, the cost associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnosis can be prohibitive for many families. Therefore, there is a pressing need for more accessible, less intrusive, and cost-effective methods for detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in its early stages to ensure timely and effective intervention.
Collaborations
This research was done in collaboration with Professor George, Brunel University, London, United Kingdom
Future Research Plans
In the future, we will also try to diagnose the disorder by speech therapy using Natural Language Processing and integrate it with real-time industry in health care, which can be used by many doctors in their respective practices
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Patent Filed for Innovative Load Balancing System in Cloud Computing
 In a significant advancement for cloud computing technologies, Dr Kakumani K C Deepthi and Dr Prasanthi Boyapati, Assistant Professors in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, alongside B Tech student Ms Yarra Khyathisree, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATIC LOAD BALANCING FOR BANK OF CLOUD SERVERS.” The patent, registered with Application Number 202441057273, was officially published in the Patent Office Journal.
In a significant advancement for cloud computing technologies, Dr Kakumani K C Deepthi and Dr Prasanthi Boyapati, Assistant Professors in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, alongside B Tech student Ms Yarra Khyathisree, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATIC LOAD BALANCING FOR BANK OF CLOUD SERVERS.” The patent, registered with Application Number 202441057273, was officially published in the Patent Office Journal.
As cloud computing continues to expand, effective load balancing has become critical for optimizing distributed environments. Load balancing is essential for distributing data and services across a scalable network of nodes, ensuring that no single node becomes overwhelmed. This is particularly important as data storage needs in cloud environments grow exponentially.
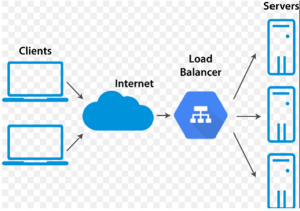
The newly patented system aims to enhance load balancing and job scheduling, addressing the increasing demand for efficient services. The article highlights various notification algorithms designed to improve these processes, comparing the latest methods to boost performance and user satisfaction.
This innovation marks a promising step forward in cloud computing technology, paving the way for more robust and efficient systems to meet the evolving needs of users and organizations alike.
Abstract of the Research
Load balancing is crucial for the efficient operation of distributed environments, especially with the rapid growth of cloud computing and increasing customer demands for more services and positive outcomes. Cloud load balancing involves transparently sharing data and delivering services through a scalable network of nodes. Due to the open and distributed nature of cloud computing, the amount of data storage grows rapidly, making load balancing a critical issue. Managing load information in such a vast system is costly. A major challenge in cloud computing is distributing dynamic workloads across multiple nodes to prevent any single node from becoming overwhelmed. Numerous algorithms have been proposed to effectively allocate customer requests to available cloud nodes. These methods aim to enhance the overall performance of the cloud and provide users with more satisfying and efficient services. This article reviews various notification algorithms to address cloud computing load balancing and job scheduling issues, comparing the latest methods in the field.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
In this patent, the common load-balancing algorithms in cloud computing include:
• Round Robin
• Least Connection
• Randomized
• Load Balancing Challenges in Cloud Computing
• Automated Service Provisioning
• Virtual Machine Migration
• Energy Management
• Stored Data Management
Future Research Plans
To implement automatic load balancing for not only banks but also some other applications where cloud servers can be designed by ensuring optimal resource utilization, performance, and reliability.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
B Tech Students Pave the Path for Future Entrepreneurs with Vascan Solutions
 SRM University-AP is honoured to recognise the impressive accomplishments of B Tech CSE third-year students Sai Tharun Nelluru and Mahendra Kumar Velicheti, co-founders of Vascan Solutions, a startup aiming to disrupt the retail space. This is especially so when one considers that the decision to venture into entrepreneurship entails taking risks that the norm would prescribe against – seeking employment graduates.
SRM University-AP is honoured to recognise the impressive accomplishments of B Tech CSE third-year students Sai Tharun Nelluru and Mahendra Kumar Velicheti, co-founders of Vascan Solutions, a startup aiming to disrupt the retail space. This is especially so when one considers that the decision to venture into entrepreneurship entails taking risks that the norm would prescribe against – seeking employment graduates.
Vascan Solutions, as a company, is a clear Shiff economics and architecture in Context business solving real problems in the business of retailing. Understanding the pain points that exist for both shoppers and retailers, Sai Tharun and Mahendra created a mobile app intending to improve retailing activity. Shoppers can search for items, navigate inside the store accurately and use their phones to pay for items. This improves the ease of shopping for customers. On the one hand, retailers get valuable information from consumers about what they choose and how often they come. With this information, it is easy for marketers to reorganise the store improve customer service and increase sales.
The creation of Vascan Solutions is a testament to the vision and commitment of SRM AP students. However, their success story also highlights the importance of mentorship, an integral aspect of SRM AP’s entrepreneurial ecosystem. Sai Tharun and Mahendra were guided by Dr Shobin CC and Dr Randhir Singh, who provided technical expertise that helped refine their product and strategy. Additionally, Mr Siddharth Shankar Tripathy, Director of Entrepreneurship & Innovation, SRM University-AP, played a pivotal role in mentoring the co-founders, offering them the support needed to navigate the complexities of launching a startup.
SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering entrepreneurship is evident in the success of Vascan Solutions. The university takes pride in cultivating an environment where students are encouraged to think creatively, innovate, and challenge the status quo. Sai Tharun and Mahendra’s decision to build their own business demonstrates the transformative potential of this environment. Their entrepreneurial journey serves as an inspiration not only to their peers but also to future generations of students who wish to explore non-traditional career paths and make a meaningful impact on society.
The establishment of Vascan Solutions aligns with SRM AP’s vision of empowering students to become leaders and innovators. The university strongly believes that entrepreneurship is not only a viable career option but also a path that can contribute to societal and economic development. Sai Tharun and Mahendra have proven that with determination, innovation, and the right mentorship, young entrepreneurs can turn challenges into opportunities.
Looking ahead, SRM University-AP is excited to see the continued growth of Vascan Solutions. With a solid foundation and a clear vision, the startup has the potential to scale and expand beyond the retail sector, further solidifying the impact of Sai Tharun and Mahendra’s contributions. As Vascan Solutions evolves, SRM AP remains committed to supporting entrepreneurial initiatives that empower students to become changemakers in their respective fields.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, IDEA NEWS, News
SMAFS Technology Gets Patented

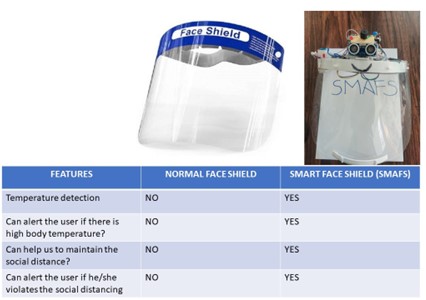
Dr Anirban Ghosh and his BTech students, Mr Taraka Sai Tanishq Chebrolu and Mr V.M.V.S. Aditya from his department, have come up with a pathbreaking innovation where a Smart Face Shield (SMAFS) helps detect a virus and reminds the wearer to maintain a safe distance. This innovation, patented under the Indian Patent Office Journal, with application number-202241000990 , marks a milestone step towards public health and safety.
Abstract:
The recent spurt of corona virus has wreaked havoc across the globe and led to huge loss of human lives. An intelligent system with innovative technologies can be implemented to address the rapid spread of the deadly virus. The wearable face shield that can not only help to maintain appropriate social distancing in a crowded place but also to identify a person with preliminary symptoms of corona virus. It is designed as a technically improved face shield to maintain social distancing by appropriate use of proximity sensor and to measure temperature of the wearer by using contact temperature sensor. LED’s and buzzer are placed strategically to alert people via visual and audio signals respectively. Such precautionary detection and proximity alert prototype can prove instrumental in early diagnosis and isolation aiding in crowd management and free movement in places of social gathering.
Practical Implementation of the Patent:
Such precautionary detection and proximity alert prototype can prove instrumental in early diagnosis and isolation aiding in crowd management and free movement in places of social gathering. Hence, wearable face shield ensures adequate separation between persons and facilitates temperature monitoring and early disease detection.
Future Research Plans:
Future research plans are to further improve the capability of the existing prototype for example integration of oxygen saturation measurement, Heartbeat, Blood pleasure, Temperature, Location, etc of the user. In the event of an emergency or critical drop in any of the vitals, the system can automatically alert the local hospital, ambulance service, and relatives.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Enhancing Visual Saliency in Group Photographs: A Novel Approach for Improved Security and Healthcare Applications

Dr Ravi Kant Kumar, an Assistant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and his research scholar, Ms Gayatri Dhara, have come up with a patent titled “A System and Method for Enhancement Of Visual Saliency Of Intended Face In Group Photography.” The patent, with Application Number 202441040020, employs pathbreaking technology to enhance security and healthcare applications, with real-time face recognition and remote diagnostics.
Abstract:
Visual saliency is a way of figuring out which parts of a scene draw our attention the most. When looking at a crowd or a group of faces, our eyes naturally focus more on certain faces than others. This happens because some faces have dominant features that stand out more. For faces that don’t naturally catch our attention, there is a need to make them more noticeable. This new method and system are designed to do just that. The system calculates scores based on various factors like skin tone, colour, contrast, position, and other visual details. These scores help identify which face needs enhancement, making it more prominent in a group of faces. The primary advantage of this invention is its potential to improve user experience in various applications, such as photo editing, social media, security systems, and more. By giving users, the control to select and enhance a specific face, it allows for a more personalised and targeted approach to face recognition and enhancement. This could be particularly beneficial in scenarios where the user wants to highlight a specific individual in a group photo or in a crowd. Overall, this invention represents a significant advancement in the field of face recognition and image enhancement, offering a novel and user-centric approach to visual saliency. It opens up new possibilities for user interaction and control in image editing and face recognition technology.
Practical and Social Implications
The practical implementation of this research lies in its ability to identify and enhance faces within a group or crowd that do not naturally draw attention. This innovative method and system address this issue by calculating saliency scores based on factors such as skin tone, colour, contrast, position, and other visual details. These scores are then used to identify faces that need enhancement to become more prominent in a group. The system’s ability to enhance specific faces has significant practical applications in several fields.
Photo Editing: Users can easily enhance specific individuals in group photos, ensuring that everyone stands out as desired. This is particularly useful for personal photos, event photography, and professional photo editing.
Social media: Enhanced face recognition and saliency can improve user experience by allowing users to highlight specific people in their posts, making photos more engaging and personalised.
Security Systems: In surveillance and security applications, the ability to enhance less prominent faces can improve the accuracy of face recognition systems, aiding in the identification of individuals in crowded or low-visibility conditions.
Collaborations:
SRM University-AP,
Dr Ravi Kant Kumar,
Mrs Gayathri Dhara.
Future Research Plans:
Future plans for this visual saliency-based face enhancement system include refining algorithms for greater accuracy and efficiency, and integrating with popular photo editing software and social media platforms for seamless user experience. The technology will be expanded into security and healthcare applications, enhancing real-time face recognition and remote diagnostics. Emphasis will be placed on reducing biases, ensuring privacy protection, and enabling user customisation. Collaborations with academic institutions will drive further research, while commercialisation efforts will focus on launching products globally.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research, Research News
Dr Mahesh Kumar Secures Patent for Advanced Data Generation Method
 In a significant achievement for the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dr Mahesh Kumar Morampudi, Assistant Professor, along with B.Tech. student Ms. Nunna Lakshmi Manasa, has been granted a patent for their groundbreaking invention titled “System and method for generating synthetic data based on variational autoencoder.” The patent, with Application Number: 202241049545, was officially recognised in the Indian Patent Office.
In a significant achievement for the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dr Mahesh Kumar Morampudi, Assistant Professor, along with B.Tech. student Ms. Nunna Lakshmi Manasa, has been granted a patent for their groundbreaking invention titled “System and method for generating synthetic data based on variational autoencoder.” The patent, with Application Number: 202241049545, was officially recognised in the Indian Patent Office.
This innovative system leverages the capabilities of variational autoencoders to generate synthetic data, which has vast applications in various fields, including machine learning, data privacy, and simulation. The ability to create high-quality synthetic datasets can significantly enhance research and development processes, providing researchers and practitioners with valuable tools for analysis and experimentation.
The recognition of this patent not only highlights the innovative spirit within the department but also underscores the collaborative efforts between faculty and students in advancing technology and contributing to the field of computer science.
Abstract of the Research
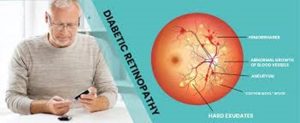
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a diabetes-related eye condition that occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, these damaged vessels can leak blood or other fluids, leading to vision impairment.
DR typically progresses through stages, starting with mild non-proliferative retinopathy, where small bulges form in the blood vessels, to proliferative retinopathy, the most severe stage, where new abnormal blood vessels grow on the retina and in the vitreous humor, potentially leading to blindness. Early detection and management are crucial to prevent significant vision loss, often involving regular eye exams, blood sugar control, and treatments like laser therapy or surgery.
Synthetic data generation for DR is an emerging approach to augment limited clinical datasets, enhancing the training of machine learning models for diagnosis and prognosis. The present disclosure envisages a system for generating synthetic data based on a variational autoencoder (VAE). This work explores the use of a VAE combined with deep learning for the detection and classification of DR. VAEs, known for their ability to learn compact and meaningful representations of complex data, are employed to generate latent features from retinal images, effectively capturing the subtle variations and anomalies indicative of DR. These latent features are then fed into a deep learning classifier, which is trained to categorise the severity of DR into various stages, ranging from no DR to proliferative DR.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
Imagine your eye is like a camera, and the retina at the back of your eye is the film that captures the pictures you see. DR is a condition that affects this “film” when someone has diabetes for a long time. High blood sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and, in severe cases, blindness.
Our research is about creating a computer program that can help doctors detect and classify this eye condition more accurately. We use a special kind of technology called a VAE, which is like a smart artist that learns to understand and recreate detailed images of the retina. This “artist” can pick up on the tiny changes and patterns in the retina that might be missed by the human eye. Once the VAE has learned these details, it passes them on to another program, which is really good at sorting things into categories. This second program, a deep learning classifier, uses the information from the VAE to decide how severe diabetic retinopathy is—whether it’s mild, moderate, or severe.
By combining these two technologies, our system can help doctors detect diabetic retinopathy earlier and more accurately, which is crucial for preventing vision loss in people with diabetes.
Title of the Patent in the Citation Format
Inventor Name(s):
Dr Mahesh Kumar Morampudi
Nunna Lakshmi Manasa
“System and method for generating synthetic data based on variational auto encoder” with Application Number: ” 202241049545.” Date of Patent Grant. 29/07/2024
Practical Implementation:
The practical implementation of our research involves integrating the VAE and deep learning classifier into a software tool that can be used by eye care professionals. Here’s how it might work in a real-world setting:
- Data Collection: Retinal images are collected from patients during routine eye exams. These images are fed into the system, which has been trained using a large dataset of retinal images, including those showing different stages of DR.
- Feature Extraction: The VAE processes these images, learning to capture and condense the important features that indicate the presence and severity of DR. This step is crucial because it allows the system to focus on the subtle details that might signify early stages of the disease.
- Classification: The deep learning classifier then takes these features and classifies the severity of DR. It provides a diagnosis, categorising the condition as no DR, mild, moderate, or severe. The system could also flag cases that need urgent attention, helping prioritise patient care.
- Clinical Decision Support: The results are presented to the healthcare provider through an intuitive interface. This tool could be used in clinics, especially in areas with limited access to specialised eye care, allowing general practitioners or technicians to screen for DR and refer patients for further treatment if needed.
Social Implications:
- Increased Access to Early Detection: By automating the detection of diabetic retinopathy, this technology can be deployed in remote or underserved areas where access to specialists is limited. Early detection is key to preventing vision loss, and this tool can make screening more accessible, especially in communities with high rates of diabetes.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can prevent the progression to more severe stages, reducing the need for expensive treatments like surgery or long-term care for blindness. This could lower healthcare costs for both patients and the healthcare system.
- Empowering Healthcare Providers: The tool can support general healthcare providers in making more accurate diagnoses, reducing the burden on specialists and allowing them to focus on more complex cases. This democratizes eye care, making it possible for more people to get the care they need without long delays.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: With more accurate and timely diagnosis, patients can receive treatment sooner, leading to better health outcomes and preserving vision. This can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals with diabetes, who might otherwise suffer from preventable blindness.
- Ethical Considerations: While technology offers many benefits, it also raises ethical questions about the use of AI in healthcare, such as ensuring that the system is fair, transparent, and does not introduce biases. Continuous monitoring and updates would be necessary to ensure the system remains accurate and equitable.
Future Research Plans
- Improving Model Robustness and Generalization: Enhance the VAE and deep learning classifier’s ability to generalize across diverse populations and imaging conditions.
- Incorporating Multimodal Data: Integrate additional data sources, such as patient medical history, blood sugar levels, and genetic information, to improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Real-Time Implementation and Mobile Integration: Adapt the system for real-time analysis and deploy it on mobile devices.
- Collaboration with Clinical Trials: Validate the AI system’s effectiveness through collaboration with clinical trials.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Naga Sravanthi Explores the Role of Blockchain in Food Marketing
 In a significant contribution to the field of food marketing and consumption, Ms P Naga Sravanthi, an Assistant Professor Ad hoc in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a book chapter titled “Blockchain-Based Food Influencer Verification.” The chapter is part of the book “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption,” shedding light on the emerging use of blockchain technology in authenticating food influencers.
In a significant contribution to the field of food marketing and consumption, Ms P Naga Sravanthi, an Assistant Professor Ad hoc in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a book chapter titled “Blockchain-Based Food Influencer Verification.” The chapter is part of the book “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption,” shedding light on the emerging use of blockchain technology in authenticating food influencers.
In the rapidly evolving world of food marketing, trust and authenticity have become more critical than ever. The book chapter delves into how blockchain technology can revolutionise the way food influencers are verified and trusted by their audiences. Blockchain technology, known for its transparency and security features, has been making waves across various industries, and its application in the food sector is no exception.
Ms Naga Sravanthi’s work focuses on utilising blockchain to verify the credibility and authenticity of food influencers, a vital aspect in today’s digital era, where influencer marketing plays a significant role in consumer decision-making. The book chapter explores how blockchain can address issues of trust and reliability in food marketing by providing a secure and immutable record of influencers’ endorsements and partnerships. This innovative approach not only benefits consumers by ensuring they receive genuine recommendations but also helps food brands collaborate with legitimate and reputable influencers.
The publication of this book chapter underscores SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering cutting-edge research and innovation in diverse fields, positioning its faculty members as thought leaders in their respective domains. Ms Naga Sravanthi’s work serves as a testament to the university’s dedication to academic excellence and pushing the boundaries of knowledge in emerging technologies.
Brief Description of the Book Chapter:
This chapter explores the integration of blockchain technology into the verification process of food influencers, providing a transparent and tamper-proof method to authenticate their influence and endorsements. By leveraging blockchain, the chapter outlines how the food industry can ensure that influencers are genuine, their endorsements are credible, and their impact is accurately measured. The chapter also delves into case studies and practical applications, demonstrating how this technology can reshape the landscape of influencer marketing in the food sector.
Significance of the Book Chapter
The significance of this chapter lies in its exploration of a cutting-edge application of blockchain technology in a field that deeply influences consumer behaviour in food marketing. As the digital space becomes more saturated with influencers, the need for a reliable verification system becomes paramount. This chapter is particularly meaningful because it addresses the growing concern of authenticity in influencer marketing, a crucial factor in maintaining consumer trust and brand integrity. For those passionate about the intersection of technology, marketing, and food, this chapter offers insights into how blockchain can be a game-changer in ensuring that the voices consumers trust is, indeed, trustworthy.
Target Audience
The book is primarily targeted at professionals in the food industry, including marketers, brand managers, and digital strategists, who are keen on understanding the latest trends shaping consumer behaviour and marketing practices. Additionally, this chapter will be valuable to academics and students in the fields of marketing, food science, and technology, as well as tech enthusiasts interested in the practical applications of blockchain.
Startups and entrepreneurs looking to innovate within the food sector will also find this book to be a vital resource, providing both theoretical insights and practical examples of how technology can redefine industry standards.In essence, “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption” and its chapter on blockchain-based influencer verification is an essential read for anyone looking to stay ahead of the curve in the dynamic world of food marketing.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Innovation Alert: Patent on Plant Disease Detection Published by CSE Team
 In an impressive achievement, Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Associate Professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD Scholar Ms Ghanta Swetha and BTech CSE students Mr Bandi Sai Harshith, Mr Estamsetty Srikanth, Mr Guduri Venkata Sai Kumar, and Mr Atmakuri Pavan Kumar, has successfully published a patent titled “A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATED PLANT DISEASE DETECTION.” The application has been officially recognised with Application Number: 202441052706, as recorded in the Patent Office Journal.
In an impressive achievement, Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Associate Professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD Scholar Ms Ghanta Swetha and BTech CSE students Mr Bandi Sai Harshith, Mr Estamsetty Srikanth, Mr Guduri Venkata Sai Kumar, and Mr Atmakuri Pavan Kumar, has successfully published a patent titled “A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATED PLANT DISEASE DETECTION.” The application has been officially recognised with Application Number: 202441052706, as recorded in the Patent Office Journal.
This innovative system aims to revolutionise the agricultural sector by providing an automated mechanism for detecting diseases in plants. Thus, it enhances crop management and ensures healthier yields. The team’s dedication to advancing technology and improving agricultural practices showcases the potential of computer science in solving real-world problems.
The patent not only reflects the hard work and collaboration among the faculty and students but also signifies a step forward in the integration of technology with agriculture. As the world faces challenges related to food security, such innovations play a critical role in safeguarding plant health and agricultural productivity.
Congratulations to Dr Pradhan, Ms Swetha, and the student inventors on this significant milestone in their academic and professional endeavours!
Abstract of the Research:
The innovation that is being presented in this project is a software-based system that is intended to help farmers by offering an automated way to identify plant diseases. This innovation combines a number of technological elements:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): These networks are used to recognise and categorise plant diseases from images of both healthy and sick plants with high accuracy. This is leveraging transfer learning with pre-trained CNN architectures to improve performance even with sparsely annotated data.
MobileNetV2 Architecture: Designed with the specific purpose of classifying agricultural diseases in mind, this model is effective and lightweight, making it ideal for use in resource- constrained settings such as farms.
Weather API Integration: This helps farmers make decisions about crop management and disease prevention by giving them access to real-time weather data.
AI-Powered Website: Acts as a user interface for farmers to communicate with the system, submit plant photos, post queries, and get weather and diagnostic updates.
Chatbot: Utilizes Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to respond to user inquiries and provide guidance on crop management and disease prevention.
All things considered, this innovation is a system that integrates various software components, artificial intelligence, and data integration to produce a complete tool for raising agricultural productivity and managing diseases.
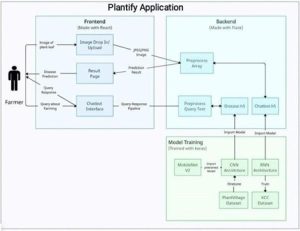
Research in Layperson’s Terms
1. Automated Plant Disease Prediction: Current approaches frequently use traditional diagnostic procedures and manual inspection, which can be laborious and prone to human mistakes. The suggested method uses CNNs to automatically and precisely recognise images, increasing the efficacy and precision of plant disease diagnosis.
2. This project assists farmers in making decisions on crop management and disease prevention by providing them with access to current weather information.
3. Farmers can query various farming issues and receive responses. This is done by leveraging RNNs and NLP.
4. Use of Transfer Learning: The system uses transfer learning to use pre-trained CNN architectures, which enables it to function well even with a small amount of annotated data. Compared to typical machine learning models, which frequently need big datasets and intensive training, this is a major improvement.
Integration with Smart Agriculture Systems: – This method combines disease prediction with smart agriculture systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and decision-making, in contrast to independent diagnostic instruments.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated
1. Field Diagnosis by Farmers: – Farmers can snap photos of their crops in the fields and instantly receive a disease diagnosis and treatment suggestions by using the platform.
2. Agricultural Extension Services: Using the system, agricultural extension agents may help farmers more effectively by offering guidance and support.
3. Agricultural Research: – Researchers can investigate plant diseases and create novel remedies and management techniques by utilizing the extensive annotated picture library and diagnostic tools.
4. Commercial Farming Operations: – By incorporating the system into their precision agriculture techniques, large-scale farming operations can maximize crop health management and operational effectiveness.
5. Policy Formation and Governance: – Governmental organizations can monitor plant disease outbreaks and create regional or national plans for disease control and prevention using aggregated data from the platform.
Future research plans
We may use privacy and security enhancement tools and techniques to make the data more secure
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Faculty and Students Leads to Patent Publication for Intelligent Shelf Management System
 In a groundbreaking collaboration, Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and Dr Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have joined forces with Btech-CSE students Mr Rohit Kumar Jupalle, Mr Dinesh Sai Sandeep Desu, and Mr Nikhil Kethavath to develop and patent an innovative invention.,” The team’s invention, titled “A SYSTEM FOR VISION-BASED INTELLIGENT SHELF MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND A METHOD THEREOF,” has been officially filed and published with Application Number 202441039394 in the Patent Office Journal. This invention showcases the academic excellence and collaborative spirit within the institution, as faculty members and students work together to push the boundaries of technology and create solutions with real-world impact.
In a groundbreaking collaboration, Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and Dr Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have joined forces with Btech-CSE students Mr Rohit Kumar Jupalle, Mr Dinesh Sai Sandeep Desu, and Mr Nikhil Kethavath to develop and patent an innovative invention.,” The team’s invention, titled “A SYSTEM FOR VISION-BASED INTELLIGENT SHELF MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND A METHOD THEREOF,” has been officially filed and published with Application Number 202441039394 in the Patent Office Journal. This invention showcases the academic excellence and collaborative spirit within the institution, as faculty members and students work together to push the boundaries of technology and create solutions with real-world impact.
This significant achievement not only highlights the creativity and dedication of the individuals involved but also underscores the institution’s commitment to fostering a culture of innovation and research. The publication of this invention paves the way for further exploration and development in the field of intelligent shelf management systems, demonstrating the potential for transformative contributions to the industry.
Abstract
This research offers the best solution to improve the business in the retail realm, maintaining On- Shelf Availability (OSA) is vital for customer satisfaction and profitability. Traditional OSA methods face accuracy challenges, prompting a shift to deep learning models like YOLO and CNN. However, data quality remains a hurdle. This research introduces OSA, a novel semi-supervised approach merging ’semi-supervised learning’ and ’on-shelf availability’ with YOLO. It reduces human effort and computation time, focusing on efficient empty-shelf detection. Implementing a Vision-Based Intelligent Shelf Management System empowers retailers with real-time insights, revolutionizing decision-making. The model is optimized for diverse devices and provides practical solutions for efficient retail operations. Balancing model complexity, size, latency, and accuracy, the research paves the way for an advanced, data-driven shelf management approach, contributing to improved shopping experiences and business profitability
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications Associated
1. The present invention is a time-saving method in maintaining the stocks.
2. The use Vision-Based Intelligent Shelf-Management System provide a well alternative in reducing the labor efforts.
3. The system will help in terms of self-management system using machine learning techniques to optimize restocking decisions.
The present invention can be used in shopping malls and business areas for enhancing customer experiences and business and few application areas are:
• Smart City and smart Village
This technique and system can reduce the human efforts in identifying vacant slots for items in business areas and provides necessary inputs to fill the same within a time frame.
• Automobile Industry
The system can be easily integrated with the showrooms to identify the empty spaces and inform to get it fill with products.
Collaborations
SRM AP Faculties and UROP Students
Future research plan
In the future, different deep learning and machine learning methods can be merged to explore better performance in identifying overlapping objects.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Dr Sanjay Kumar and Team Publish Digital Image Security Invention in the Patent Office Journal
 In a recent development, Dr Sanjay Kumar, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with a team comprising N Ujwala, J Yashwanth Sri Ram, J Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and K Heman Rai Choudhary, have successfully filed and published an innovative invention in the Patent Office Journal titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” with the application number “202441045387”.
In a recent development, Dr Sanjay Kumar, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with a team comprising N Ujwala, J Yashwanth Sri Ram, J Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and K Heman Rai Choudhary, have successfully filed and published an innovative invention in the Patent Office Journal titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” with the application number “202441045387”.
This invention holds great promise in the field of digital image security and watermarking. The patented system and method are based on the discrete wavelet transform (DWT), a widely used signal processing technique, to embed secure watermarks into digital images. The application of DWT ensures that the watermarking process is robust and secure, making it suitable for a wide range of applications where image integrity and authenticity need to be ensured.
Dr Sanjay Kumar’s expertise as an Assistant Professor, coupled with the team’s skills and dedication, has resulted in the successful development and patenting of this cutting-edge technology. The “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” promises to be a significant addition to the field of digital image security and watermarking, offering enhanced protection against unauthorised tampering and misuse of digital images. It is expected that this invention will garner attention from industry professionals, researchers, and policymakers, paving the way for its integration into diverse digital imaging systems.
Abstract
Our research introduces a robust image watermarking technique that combines Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and chaotic map-based encryption. The method analyzes high-frequency sub-bands derived from DWT applied to the blue channel of an RGB image, selecting the block with the highest energy for embedding a grayscale watermark encrypted with the Henon Map. The alpha blending technique is used to integrate the encrypted watermark, ensuring both imperceptibility and robustness. The method achieves an average PSNR of 43.7211 dB and SSIM of 0.9950. The watermark can be extracted by analyzing patterns in the high-frequency component, even after various attacks, using inverse DWT and Henon Map for decryption.
Explanation of the Patent in Layperson’s Terms
Our research focuses on protecting digital images by embedding a hidden watermark that is hard to remove. We use a mathematical method called the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to break down an image into different parts and find the best place to hide the watermark. The watermark is further secured by encrypting it with a technique called the Henon Map. Our method ensures that the watermark remains invisible to the naked eye while being resistant to tampering. This means the watermark can be detected and recovered even if the image is altered.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications
The primary application of our research is in protecting the ownership and integrity of digital images. This technique can be used by photographers, artists, and digital content creators to ensure their work is not copied or altered without permission. By embedding a secure, invisible watermark, they can prove ownership and detect unauthorised use. Additionally, this method can be applied in sensitive fields such as medical imaging and legal documents where tamper detection is crucial.
Collaborations
This research was conducted by the Visual Information Processing Lab at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University AP, Guntur, India. The team comprised Nadella Ujwala, Sanjay Kumar, Jayyavarapu Yaswanth Sri Ram, Jetti Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and Katragadda Heman Rai Choudhary.
Future Research Plans
Our future research will focus on enhancing the watermarking technique’s robustness against more sophisticated attacks, exploring real-time applications in video watermarking, and developing methods to embed multiple watermarks in a single image. We also aim to reduce the computational complexity to make the algorithm more efficient for practical applications.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News