WHO recognises research article on pandemic detection model
The healthcare system across the globe has been under colossal pressure since the emergence of novel coronavirus pandemic. The pandemic has also unveiled some of the greatest gaps in the existing healthcare systems. The research paper authored by Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan and his PhD student E Bhaskara Santhosh, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, proposing a blockchain-based pandemic detection model was recognised by WHO and the paper was listed in COVID-19 Global literature on coronavirus disease. The paper titled “iBlock: An Intelligent Decentralised Blockchain-based Pandemic Detection and Assisting System” was published in collaboration with Saraju Mohanty, University of North Texas and Dr Venkata Ramana Badarla, Associate Professor, IIT Tirupati. The authors have expressed their deepest gratitude to Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) for Grant number TAR/2019/000286 and SRM University-AP for supporting this work.
Abstract of the Research
The recent COVID-19 outbreak highlighted the requirement for a more sophisticated healthcare system and real-time data analytics in the pandemic mitigation process. Moreover, real-time data plays a crucial role in detection and alerting process. Combining smart healthcare systems with accurate real-time information about medical service availability, vaccination, and how the pandemic is spreading can directly affect the quality of life and economy. The existing architecture models become inadequate in handling the pandemic mitigation process in a real-time dataset. This is because, the present models are server-centric and controlled by a single party, hence to manage confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of dataset is a challenging task. Therefore, a decentralised user-centric model is essential, where the CIA of user data can be assured. In this paper, we have suggested a decentralized blockchain-based pandemic detection and assistance system named as (iBlock) that uses robust technologies like hybrid computing and IPFS to support system functionality. Moreover, a pseudo-anonymous personal identity is suggested using H-PCS and cryptography for anonymous data sharing. The distributed data management module guarantees data CIA, security, and privacy using cryptography mechanisms. Furthermore, it delivers useful intelligent information in the form of suggestions and alerts to assist the users. Finally, the iBlock reduces stress on healthcare infrastructure and workers by providing accurate predictions and early warnings using AI/ML technology.
Contributions of the Research
i) Proposes a novel architecture model for pandemic detection and alertness using a blockchain called as “iBlock”. It supports sharing of real-time data utilization.
ii) The proposed system introduces suitable privacy and security mechanisms to cover system-level data privacy and security.
iii) It also suggests a logical combination of blockchain and AI/ML on hybrid computing to support global level requirements during pandemic mitigation and alerting the systems.
Social Implications
The proposed system helps in the early detection of Covid-19 and encourages people to use their health data anonymously in pandemic detection and mitigation process. Moreover, iBlock maintains all crucial data on blockchain for future sustainable healthcare solutions. The majority of pandemic detection and alerting systems are limited to prediction, however iBlock further simplifies the area-labelling to cover area wise mitigation mechanisms. The classification of areas helps the government and healthcare organizations to plan sustainable preventive measures in a real-time scenario. It also helps in prediction of new cases and death rates with the aid of a dedicated AI/ML detection engine module. To motivate the people to share legitimate data, the proposed model even suggests a reward mechanism to influence the participants.
The research investigates the advanced possibilities in smart healthcare architecture to bring down the time and effort for pandemic mitigation activities. Read to know more.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
CSE students grab the coveted MITACS Globalink Research Internship
“When you want something, all the universe conspires in helping you to achieve it”– Paulo Coelho.
Be it a dream or a wish, when you are determined to pursue what the mind really wants, SRM University-AP helps you reach that goal. Ms Pragya Gupta and Ms Swikriti Khadke joined SRM AP with vibrant dreams, and in their third year, they have attained the prestigious Mitacs Globalink Research Internship. The students from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering will spend three months in Canadian universities as a part of this fully-funded research internship. Ms Swikriti will intern at Université du Québec en Outaouais – Gatineau on the research project titled “Systematic PV farm power losses calculation and modelling using computational intelligence techniques”. Ms Pragya will be going to Athabasca University – Edmonton as a research intern to work on the project titled “Blockchains for Data Storage and Mining in Learning Analytics”.
About Mitacs Globalink Research Internship
Mitacs Globalink Research Internship is a highly competitive programme that pairs top-ranked international students having specific research expertise from 15 countries worldwide with faculty at top Canadian academic institutions. This is a twelve (12) week research project of mutual interest between May and October 2022. The Canadian host faculty project leader makes selections by verifying the student’s background and skills in the research area and the unique contribution they will be made to the research during the stay. As a fully-funded programme, Mitacs and AICTE will administer the grant. Students can choose from about 14k+ projects in disciplines like Engineering, Life Sciences, Mathematics, Natural Sciences, Social Sciences, and the Humanities.
Mitacs will be responsible for providing the following to the students:
1. An airfare stipend of Can$1,500;
2. A stipend of Can$175 to contribute to the cost of transportation from the Canadian airport to accommodation unless otherwise arranged by your host institution
3. A stipend of Can$200 per week for living expenses
4. Ensure that students receive Canadian medical insurance.
5. A daily allowance of Can$45 for housing for the duration of the research internship.
6. A stipend of Can$300 for any student fees charged by the Canadian host institution
7. Reimbursement of immigration permit application fees (as required to participate in the research internship — up to a maximum of Can$240)
8. A stipend of Can$500 for any COVID-19-related expenses (e.g., COVID test, quarantine, expenses incurred during isolation, etc.)
The journey, in Pragya and Swikriti’s words:
The journey from applying for MITACS to getting selected as one of the GRI interns in one of the top-ranked universities in Canada was no less than a dream come true. The registration process included filling out an application form which was the most important step and a complicated one. This was also an elimination stage for many because writing down all our details in a limited number of words was quite difficult and challenging. After submitting the application form, the details about the Matching round were intimated in November. We received emails for the interview round from the professor himself. It was a technical interview that comprised of questions regarding our work experience, knowledge about the technology we will be contributing to the project during the internship, and personal details. The interview lasted for 30-45 mins, after which the professor assigned us some tasks to assess our knowledge regarding the topic. After completing and submitting the task, around Mid December, we received a congratulatory mail regarding our selection for MITACS GRI 2022, which will commence from May 2022 and continue for the next three months.
The Globalink Graduate Fellowship offers former Globalink research interns:
■ Direct financial support from Mitacs
■ Recognition as Globalink alumni
■ The opportunity to work with Canada’s research supervisors during your graduate studies
■ Additional exposure to the Canadian research and innovation landscape and increased Canadian experience.
A note of gratitude
“We would like to thank SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, for helping us build our skills and supporting us throughout the process. Our university management has always been kind and helpful to its students to explore new opportunities and create new relations. We would like to extend our gratitude to our mentors, Dr Goutam Kumar Dalapati and Dr Anil K Suresh, for their continuous support, guidance, and motivation. Last but not least, our parents have been our support system throughout our journey”.
- Published in Blog, CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research, Students Achievements
J Abbas Mohammed grabbed a staggering offer of CTC 44.91 LPA
J Abbas Mohammad was in a state of absolute euphoria as the news reached him. He has been placed with Predli, a top-performing AI company, with a staggering offer of CTC 44.91 LPA. With one more achievement to flaunt, SRM is surging ahead with an endless list of placement offers and achievement stories. Abbas is a final year student of the Department of Computer Science Engineering who has already demonstrated his calibre by grabbing a seat at UC Berkeley through the Semester Abroad Programme. His sheer will and dedication have always helped him break the records and fly to further heights.
SRM University-AP happened to be the perfect place that shaped him up to pursue the career of his dreams. Our collaboration with leading enterprises in the world turned out to be an excellent avenue for many to walk ahead to a horizon of opportunities. The Department of Corporate Relations & Careers Services is also doing an amazing job in training the students and encouraging them to apply for the best available prospects. Let us listen to Abbas as he pours out his excitement.
“I am truly delighted to have received this high-paying placement offer. And all of this became possible with the exposure I received from my university. I kept abreast of the latest technologies in the software industry and applied them through practical projects as part of our co-curricular activities in classrooms and university labs such as the Next Tech Lab. The experienced faculty and specially curated curriculum we follow here will always give an extra edge to the students. I am indeed thankful to Dr Sujith Kalluri and Dr Priyanka for assisting me on several occasions”, he said.
“It is the Semester Abroad Program at UC Berkeley, which allowed me to build a strong international networks, that eventually led to this offer. I’m immensely fortunate to land the job of my dream. In future, I hope to advance professionally and adapt to greater leadership roles with the goal of starting my own venture”, remarked Abbas.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements
C-SMILE: Pertinent feedbacks and effective learning

“The correct analogy for the mind is not a vessel that needs filling, but wood that needs igniting” – Plutarch
Where would you go to get the most appropriate feedback to improve your learning? Whom would you approach? An active learner requires continuous assessment. Exposure to relevant remarks can make a significant impact in the learning output. Choosing the right source of feedback is important to locate your position in the learning ecosystem. This is where C-SMILE enters the frame.
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to inform you that the patent application (202241010415) entitled ‘Classification of Student’s Misconceptions in Individualized Learning Environments (C-SMILE)’ got published. The patent application was submitted by Associate professor Dr Sobin C C and BTech final year student Meka Varsha as part of the Capstone Project.
C-SMILE is an innovative platform which allows students to take assessment and receive feedback based on their performance and misconceptions. This targets to refine their conceptual and individualised learning. The platform offers the benefits of automated identification of misconceptions and classification of their level of conceptual clarity. This eventually leads to pertinent feedbacks and ensures quality learning. It also helps engineering educators to classify their students into different categories based on their level of conceptual clarity. Short quizzes and multi-level assessments can utilise the objective of this platform.
Dr Sobin C C and Meka Varsha have collaborated with Mr Subheesh N P from IIT Madras and Mr Jahfar Ali from IIT Hyderabad as part of this work. The team has already published 2 conference papers. One of them is in the prestigious IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON 2022), which is the flagship conference of IEEE Education Society.
The researchers are now working on to extend this concept to incorporate Bloom’s taxonomy to formulate more specific questions based on their level in the cognitive domain.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Inventing an alternate universe of sign language
 Deaf and mute people have used sign language to communicate their thoughts and feelings for a long time. Since there is no universal sign language, the needy people use country-specific sign languages. An automated sign language recognition system is a universal solution to this impediment. Dr Manikandan V M, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science Engineering, and his student, Ms Bhavana Siddineni, have been working in this regard to ease the communication technology. They have published a chapter in the book, ‘Challenges and Applications for Hand Gesture Recognition’. The book is published by IGI Global Publishers, a leading international academic publisher. The chapter is titled “Recent Advancements in Design and Implementation of Automated Sign Language Recognition Systems”.
Deaf and mute people have used sign language to communicate their thoughts and feelings for a long time. Since there is no universal sign language, the needy people use country-specific sign languages. An automated sign language recognition system is a universal solution to this impediment. Dr Manikandan V M, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science Engineering, and his student, Ms Bhavana Siddineni, have been working in this regard to ease the communication technology. They have published a chapter in the book, ‘Challenges and Applications for Hand Gesture Recognition’. The book is published by IGI Global Publishers, a leading international academic publisher. The chapter is titled “Recent Advancements in Design and Implementation of Automated Sign Language Recognition Systems”.
Sign language systems in practice are invariably specific to a territory. For example, American Sign Language (ASL) is popularly used by Americans, and Indian Sign Language (ISL) is commonly practised in India. Communication between two people who know the specific sign language is relatively easy. But, if a mute person wants to communicate with another person who is not familiar with sign language, it is a difficult task, and a sign language interpreter is required to translate the signs. This issue motivated the computer scientist to work on automated sign language recognition systems capable of recognizing the signs from specific sign languages and converting them into text information or audio so that the common people can understand them easily.
Through the proposal put forward in the publication, our researchers are planning to design and implement a reliable Automated Sign Language Recognition system in the future. This book chapter will be a useful reference for students who wish to start their research work in the domain of Automated Sign Language Recognition.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Three patent publications from the Department of CSE
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is pleased to announce the publication of three different patent applications from the department. The patent applications were submitted by the BTech students; Mr Kandala Sree Rama Murthy, Ms Padmaja Buggaveeti, Ms Yadlapalli Sai Harshini, Mr Jagruth K, Ms Shikha Chauhan, and Ms Ravi Srihitha under the guidance of Assistant Professor Dr V M Manikandan. They are making the institution proud with their passion and enthusiasm for the research domain.
 The invention of a new scheme that will help to retrieve relevant videos from a large pool based on the given keyword is an impressive concept with societal relevance. Dr V M Manikandan and BTech students; Ms Yadlapalli Sai Harshini, Mr Jagruth K, Ms Shikha Chauhan, and Ms Ravi Srihitha got their patent application titled A novel video retrieval system and method based on textual information (application number: 202241002653) published.
The invention of a new scheme that will help to retrieve relevant videos from a large pool based on the given keyword is an impressive concept with societal relevance. Dr V M Manikandan and BTech students; Ms Yadlapalli Sai Harshini, Mr Jagruth K, Ms Shikha Chauhan, and Ms Ravi Srihitha got their patent application titled A novel video retrieval system and method based on textual information (application number: 202241002653) published.
The conventional video retrieval system uses the metadata to retrieve the appropriate videos. The new scheme processes the video and identifies the text information within the video, which will be compared with the given keyword. They introduced a scene change detection technique to select the frames for further processing in the new system to reduce the overall processing time.
The new scheme will help to retrieve appropriate educational videos from a large video pool based on the given keyword. The processing time is a significant concern in the scheme proposed. The researchers’ future work will be focused on improving the time complexity of the scheme.
 The other research team invented a prediction error histogram shifting-based approach to hide secret messages in a cover image. The patent application submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Third-year BTech-CSE Student, Ms Padmaja Buggaveeti, is titled A reversible data hiding system and method for image transmission (application number: 202241002654). The method ensures the lossless recovery of the original image during data extraction. The researchers considered the overflow issues in the histogram shifting approach and proposed an efficient method to handle this.
The other research team invented a prediction error histogram shifting-based approach to hide secret messages in a cover image. The patent application submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Third-year BTech-CSE Student, Ms Padmaja Buggaveeti, is titled A reversible data hiding system and method for image transmission (application number: 202241002654). The method ensures the lossless recovery of the original image during data extraction. The researchers considered the overflow issues in the histogram shifting approach and proposed an efficient method to handle this.
Reversible Data Hiding (RDH) provides a way to embed some data in a selected image so that in the future, the hidden data can be extracted along with the recovery of the original image. The new RDH scheme invented by the researchers can be used in the healthcare sector to embed patient reports in medical images, or cloud service providers can use it to embed metadata in the digital data. Their future work will focus on designing and implementing robust reversible data hiding schemes capable of resisting attacks.
 A system to facilitate secure transmission of an image along with embedded text (application number: 202241005221) is the third patent application that got published and was submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Final year B.Tech-CSE Student Mr Kandala Sree Rama Murthy. The researchers invented a method to embed a message into a selected image during the image encryption process, which provides secure transmission of messages. The receiver will be able to extract the hidden message during decryption. The presented method is useful in medical image transmission to store patient details in the medical image.
A system to facilitate secure transmission of an image along with embedded text (application number: 202241005221) is the third patent application that got published and was submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Final year B.Tech-CSE Student Mr Kandala Sree Rama Murthy. The researchers invented a method to embed a message into a selected image during the image encryption process, which provides secure transmission of messages. The receiver will be able to extract the hidden message during decryption. The presented method is useful in medical image transmission to store patient details in the medical image.
The transmission of medical images and health reports from one hospital to another is widespread in the healthcare sector. Hospitals may want to handle many medical images and health reports every day and ensuring the one-to-one correspondence between them is a tedious task. The invented method will help embed health reports in medical images during encryption. The encrypted medical images (embedded with health reports) can be transmitted securely. The receiver will be able to extract the hidden message after medical image decryption. The researchers’ future work will focus on improving the invented method’s embedding capacity so that lengthy reports can be embedded into the medical images.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Communication revolution and data security
The structure of human society is always profoundly affected by the developments happening in the domain of communication. Data security and privacy have always been a concern in the ongoing communication revolution. The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is glad to inform you that the paper, “An Efficient Spatial Transformation-based Entropy Retained Reversible Data Hiding Scheme in Encrypted Images,” has been published by Dr V M Manikandan, Assistant Professor, and his PhD student Mr Shaiju Panchikkil in “Optik Journal” with an impact factor of 2.443.
Abstract of the research
A critical issue with the current communication revolution is data security and privacy, which is an inevitable part of trustworthiness in the communication system. Hence, the applicability of the Reversible Data Hiding schemes (RDH) in this scenario is encouraging and critical, like medical image communication, satellite image transmission, etc. Earlier, we explored Arnold transform in one of our previous works to hide the secret data that uses the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model to design a complete RDH scheme. The proposed scheme follows a statistical approach to support recovering the cover image and the embedded information. This approach proves advantageous over the previous work following its computational capability. The scheme designed can retain the entropy of the encrypted images even after embedding the additional information, complementing the security of the encryption algorithm.
Explanation of the research
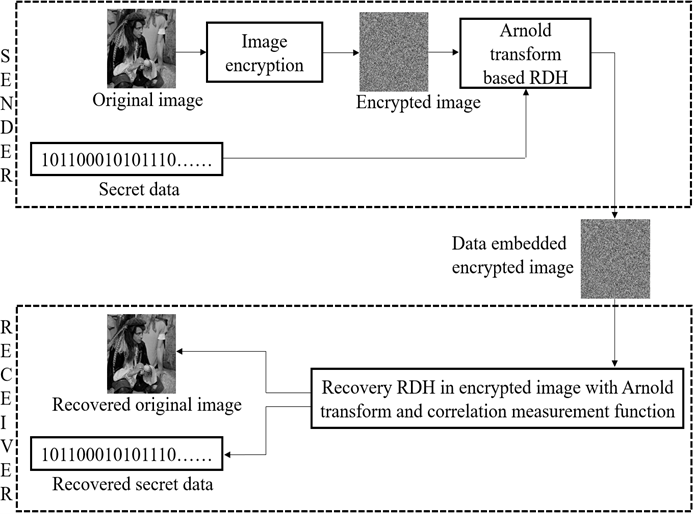 The research focuses on hiding information in an encrypted image and transmitting it to the receiver. Earlier, the researchers used the Arnold transform-based image scrambling algorithm to facilitate the data hiding. But at the receiver end, they have used a convolutional neural network model, which acts as a binary classifier to recover the image properly after extracting the hidden information. The researchers had a few overheads over there, like training the model and then sharing the same with the receiver to recover the original image efficiently. To overcome these overheads, they analysed the correlation of neighboring pixels and introduced a statistical measure at the receiver end to recover the exact image.
The research focuses on hiding information in an encrypted image and transmitting it to the receiver. Earlier, the researchers used the Arnold transform-based image scrambling algorithm to facilitate the data hiding. But at the receiver end, they have used a convolutional neural network model, which acts as a binary classifier to recover the image properly after extracting the hidden information. The researchers had a few overheads over there, like training the model and then sharing the same with the receiver to recover the original image efficiently. To overcome these overheads, they analysed the correlation of neighboring pixels and introduced a statistical measure at the receiver end to recover the exact image.
Social implications of the research
One of the various social implications of the research is an application concerning patient treatment. In a general scenario, during the covid 19 pandemic, people make an online consultation with the doctor by uploading their medical images. If the doctor wants to take a specialist’s opinion, he should send this image and the diagnosis report via a communication medium. The research team’s approach is meaningful in this aspect. The original image is initially encrypted, which makes it unreadable. The diagnosis report information is hidden over the encrypted image. Hence the doctor needs to send only a single file to the specialist. It is also difficult for an external agent or an unauthorized party to decode the report and the image as it is encrypted. Now it is essential to regain the original quality of the recovered image, as any degradation in the quality of the recovered image can lead to a wrong diagnosis. Hence, they have designed the recovery module carefully to extract all the hidden information and recover the original image without compromising its quality.
The researchers are in constant collaboration with Professor Yu-Dong Zhang from the University of Leicester, University Road, Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK, to introduce new strategies to elevate the embedding capacity from the current level without negotiating the quality of the recovered image.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
An IoT- based smart wallet prototype
 Dr Sonam Maurya, and her research team; Soha Muskaan Sayyad, Trisha Chilukuri, Samah Maaheen Sayyad, and Juhita Naga Priya Velagapudi from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering have innovated a smart wallet model based on IoT and got their patent “Smart Wallet with Enhanced Features for Preventing Misuse and Alarm System for the Same” published. This is a fitting solution to protect against the loss and theft of the wallet.
Dr Sonam Maurya, and her research team; Soha Muskaan Sayyad, Trisha Chilukuri, Samah Maaheen Sayyad, and Juhita Naga Priya Velagapudi from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering have innovated a smart wallet model based on IoT and got their patent “Smart Wallet with Enhanced Features for Preventing Misuse and Alarm System for the Same” published. This is a fitting solution to protect against the loss and theft of the wallet.
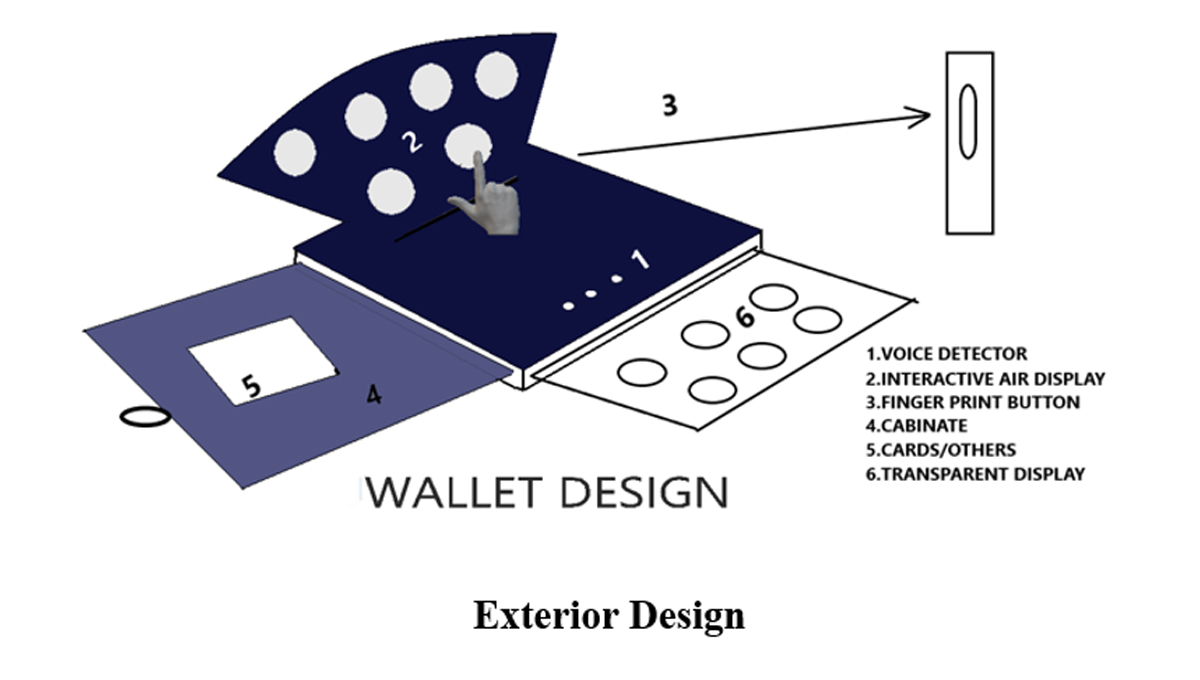
 A smart wallet is an excellent technology to safeguard your credit and debit cards. Wallets these days are getting smarter with the latest technologies induced to monitor its presence. The proposed IoT- based wallet model is more smart, intelligent, secure, and safe which encompasses the best use of the latest IoT technologies in our pocket. The prototype consists of fingerprinting access technology, Augmented Reality (AR) navigation, Interactive Air Display (IAD)/ Transparent Display (TD), Voice control mechanism, Emergency alerts, RFID features, and many more. The smart wallet is designed to overcome the shortcomings of the regular wallet types.
A smart wallet is an excellent technology to safeguard your credit and debit cards. Wallets these days are getting smarter with the latest technologies induced to monitor its presence. The proposed IoT- based wallet model is more smart, intelligent, secure, and safe which encompasses the best use of the latest IoT technologies in our pocket. The prototype consists of fingerprinting access technology, Augmented Reality (AR) navigation, Interactive Air Display (IAD)/ Transparent Display (TD), Voice control mechanism, Emergency alerts, RFID features, and many more. The smart wallet is designed to overcome the shortcomings of the regular wallet types.
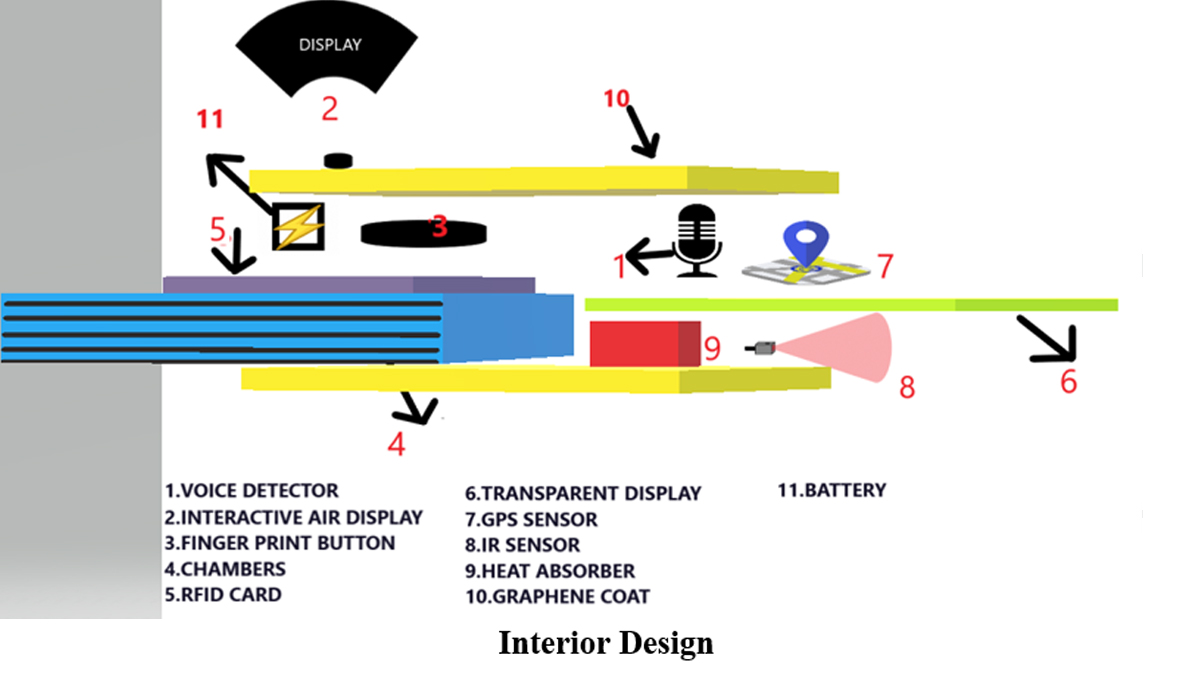
 The new technology of AR makes the tracking of the wallet easier with a graphical pathway. And the voice control functionalities help the user to make the process easier in comparison to manual opening. IAD/ TD is used to control the mechanisms like opening the card or money case. To keep the data more secure from hackers, an RFID technology-enabled card is also embedded in the wallet. The strong Graphene outer covering is used to make the materials inside more flexible and safer. Besides, there is an emergency voice control mechanism that takes the instruction from the user and makes the surroundings alert by sending an alert message to the emergency contacts. And the cash counting facility in the wallet to keep track of the cash makes it a wholesome package of digital innovation.
The new technology of AR makes the tracking of the wallet easier with a graphical pathway. And the voice control functionalities help the user to make the process easier in comparison to manual opening. IAD/ TD is used to control the mechanisms like opening the card or money case. To keep the data more secure from hackers, an RFID technology-enabled card is also embedded in the wallet. The strong Graphene outer covering is used to make the materials inside more flexible and safer. Besides, there is an emergency voice control mechanism that takes the instruction from the user and makes the surroundings alert by sending an alert message to the emergency contacts. And the cash counting facility in the wallet to keep track of the cash makes it a wholesome package of digital innovation.
The social implications of this smart wallet are:
• Enhanced features for preventing wallet misuse
• Alarm system to help in emergencies and threatening situations
• Best use of IoT technology in a user-friendly way
• Enabled with Wallet/ Card missing notifications
• Eco-friendly charging mechanism
With this innovation, the research team aims to bring technology to its fullest use to make significant transformations in the everyday life of society.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Research article accepted for IEEE conference IEMTRONICS 2022

SRM University-AP preserves a research-empowered ecosystem stimulating its faculty and students to roll out original and discerning studies capable of making instrumental contributions aiming the scientific and societal progress. Making strides with impactful research publications and groundbreaking achievements, the institution has carved a niche for itself in the academic milieu. We are glad to present yet another success story of our research community that keeps bringing laurels to the institutions from far and wide.
Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki and his PhD scholar Bevara Vasudeva, from the Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering, along with a group of Computer Science and Engineering students: Medarametla Depthi Supriya, Devireddy Vignesh, Peram Bhanu Sai Harshath, and Sravya Kuchina have got their paper titled ‘’VLSI Implementation of a Real-Time Modified Decision-Based Algorithm for Impulse Noise Removal’’ accepted in the IEEE conference IEMTRONICS 2022. This publication is a part of the Capstone project contributed by the students.
IEMTRONICS 2022 (International IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference) is an international conclave that aims to bring together scholars from different backgrounds to disseminate inventive ideas in the fields of IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics. The conference will also promote an intense dialogue between academia and industry to bridge the gap between academic research, industry initiatives, and governmental policies. This is fostered by panel discussions, invited talks, and industry exhibits where academia and industry will mutually benefit from each other.
Through the research paper, the team proposes a real-time impulse noise removal (RTINR) algorithm and its hardware architecture for denoising images corrupted with fixed valued impulse noise.
Abstract of the Research
A decision-based algorithm is modified in the proposed RTINR algorithm where the corrupted pixel is first detected and is restored with median or previous pixel value depending on the number of corrupted pixels in the image. The proposed RTINR architecture has been designed to reduce the hardware complexity as it requires 21 comparators, 4 adders, and 2 line buffers which in turn improve the execution time. The proposed architecture results better in qualitative and quantitative performance in comparison to different denoising schemes while evaluated based on the following parameters: PSNR, IEF, MSE, EKI, SSIM, FOM, and visual quality. The proposed architecture has been simulated using the XC7VX330T-FFG1761 VIRTEX7 FPGA device and the reported maximum post place and route frequency is 360.88 MHz. The proposed RTINR architecture is capable of denoising images of size 512 × 512 at 686 frames per second. The architecture has also been synthesized using UMC 90 nm technology where 103 mW power is consumed at a clock frequency of 100 MHz with a gate count of 2.3K (NAND2) including two memory buffers.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Computing Influential nodes in complex networks
With its vast applications in the industry, computing influential nodes is becoming a popular research field in recent days. The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to inform you that the paper, Computing Influential Nodes Using Nearest Neighborhood Trust Value and Pagerank in Complex Networks have been published by Dr Murali Krishna Enduri, Assistant Professor, Dr Satish Anamalamudi, Associate Professor, and the PhD students; Koduru Hazarathaiah, Ms Srilatha Tokala in the Entropy Journal (Q2 Journal), with an impact factor 2.587.
Abstract
 Computing influential nodes attract many researchers’ attention for spreading information in complex networks. It has vast applications such as viral marketing, social leaders, rumour control, and opinion monitoring. The information spreading ability of influential nodes is more compared with other nodes in the network. Several researchers proposed centrality measures to compute the influential nodes in the complex network, such as degree, betweenness, closeness, semi-local centralities, PageRank, etc. These centrality methods are defined based on the local and/or global information of nodes in the network. However, due to the high time complexity, centrality measures based on the global information of nodes have become unsuitable for large-scale networks. Very few centrality measures exist that are based on the attributes between nodes and the structure of the network. We propose the Nearest Neighbourhood Trust PageRank (NTPR) based on the structural attributes of neighbours and nearest neighbours of nodes. We define the measure based on the degree ratio, the similarity between nodes, the trust value of neighbours, and the nearest neighbours.
Computing influential nodes attract many researchers’ attention for spreading information in complex networks. It has vast applications such as viral marketing, social leaders, rumour control, and opinion monitoring. The information spreading ability of influential nodes is more compared with other nodes in the network. Several researchers proposed centrality measures to compute the influential nodes in the complex network, such as degree, betweenness, closeness, semi-local centralities, PageRank, etc. These centrality methods are defined based on the local and/or global information of nodes in the network. However, due to the high time complexity, centrality measures based on the global information of nodes have become unsuitable for large-scale networks. Very few centrality measures exist that are based on the attributes between nodes and the structure of the network. We propose the Nearest Neighbourhood Trust PageRank (NTPR) based on the structural attributes of neighbours and nearest neighbours of nodes. We define the measure based on the degree ratio, the similarity between nodes, the trust value of neighbours, and the nearest neighbours.
Explanation of the research
The research computes the influential nodes on the various real-world networks by using the proposed centrality method NTPR. The researchers find the maximum influence by using influential nodes with SIR and independent cascade methods. They also compare the maximum influence of our centrality measure with the existing basic centrality measures.
Social implications
Viral Marketing is a business strategy that uses existing social networks to promote products. The influential nodes in complex networks can be found using the centrality measure and can be used as the seed nodes for promoting products in the social networks. A rumour is a statement being said without knowing if it is true or not. The rumours can be easily controlled by discovering influential nodes. The researchers look forward to finding a centrality measure to detect the influential nodes efficiently.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News





